| Property | Value | Creator | Evidence | PMID | Comment |
| Citation | The Mycobacterium tuberculosis PhoPR two-component system regulates genes essential for virulence and complex lipid biosynthesis. SB. Walters, E. Dubnau et al. Mol. Microbiol. 2006 | sourish10 | IEP | 16573683 | Co-expression (Functional linkage) |
| Interaction | Transcription Rv0757 | sourish10 | IEP | | Co-expression (Functional linkage)
SB. Walters, E. Dubnau et al. The Mycobacterium tuberculosis PhoPR two-component system regulates genes essential for virulence and complex lipid biosynthesis. Mol. Microbiol. 2006 |
| Interaction | RegulatedBy Rv0348 | yamir.moreno | IEP | | Microarrays. mRNA levels of regulated element measured and compared between wild-type and trans-element mutation (knockout, over expression etc.) performed by using microarray (or macroarray) experiments..
B. Abomoelak, EA. Hoye et al. mosR, a novel transcriptional regulator of hypoxia and virulence in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J. Bacteriol. 2009 |
| Interaction | RegulatedBy Rv0757 | yamir.moreno | IEP | | Microarrays. mRNA levels of regulated element measured and compared between wild-type and trans-element mutation (knockout, over expression etc.) performed by using microarray (or macroarray) experiments.. qRT-PCR. mRNA expression levels of regulated element measured and compared between wild-type and trans-element mutation (knockout, over expression etc.) performed by using qRT-PCR technique.
SB. Walters, E. Dubnau et al. The Mycobacterium tuberculosis PhoPR two-component system regulates genes essential for virulence and complex lipid biosynthesis. Mol. Microbiol. 2006 |
| Interaction | RegulatedBy Rv0757 | yamir.moreno | IEP | | Microarrays. mRNA levels of regulated element measured and compared between wild-type and trans-element mutation (knockout, over expression etc.) performed by using microarray (or macroarray) experiments.. qRT-PCR. mRNA expression levels of regulated element measured and compared between wild-type and trans-element mutation (knockout, over expression etc.) performed by using qRT-PCR technique.
SB. Walters, E. Dubnau et al. The Mycobacterium tuberculosis PhoPR two-component system regulates genes essential for virulence and complex lipid biosynthesis. Mol. Microbiol. 2006 |
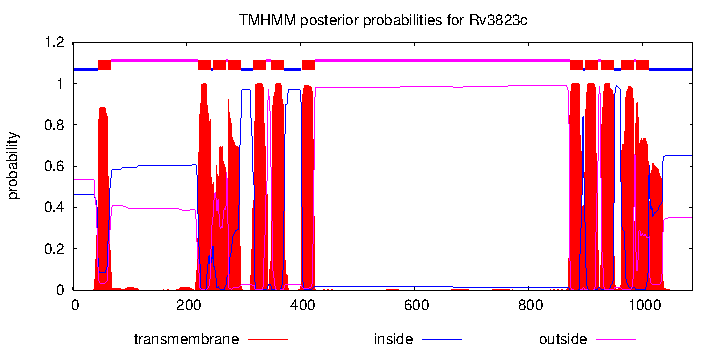
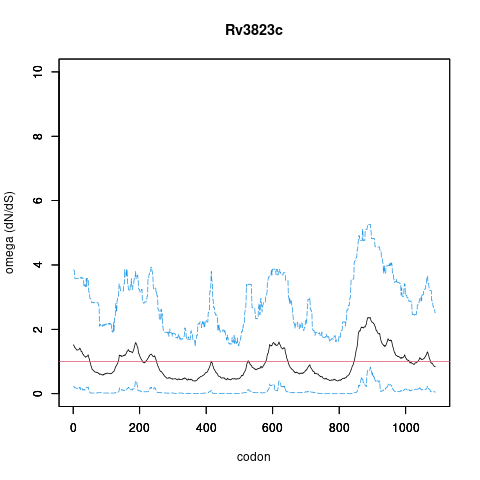
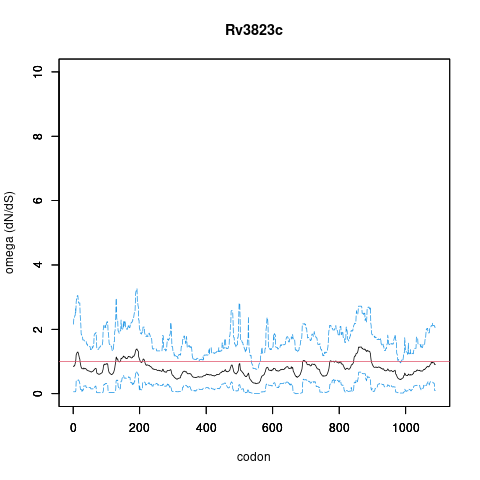
| Name | RND superfamily inner membrane transporter thought to be involved in the translocation of a diacylated precursor of sulfolipid I across the plasma membrane | mjackson | IMP | | Polymethyl-branched acyltrehaloses |
| Citation | The role of MmpL8 in sulfatide biogenesis and virulence of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. P. Domenech, MB. Reed et al. J. Biol. Chem. 2004 | mjackson | | 15001577 | RND superfamily inner membrane transporter thought to be involved in the translocation of a diacylated precursor of sulfolipid I across the plasma membrane (phenotypic [mycobacterial recombinant strains]) |
| Other | TBPWY:Polymethyl-branched acyltrehaloses | mjackson | | | RND superfamily inner membrane transporter thought to be involved in the translocation of a diacylated precursor of sulfolipid I across the plasma membrane (phenotypic [mycobacterial recombinant strains])
P. Domenech, MB. Reed et al. The role of MmpL8 in sulfatide biogenesis and virulence of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2004 |
| Citation | MmpL8 is required for sulfolipid-1 biosynthesis and Mycobacterium tuberculosis virulence. SE. Converse, JD. Mougous et al. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2003 | mjackson | | 12724526 | RND superfamily inner membrane transporter thought to be involved in the translocation of a diacylated precursor of sulfolipid I across the plasma membrane (phenotypic [mycobacterial recombinant strains]) |
| Other | TBPWY:Polymethyl-branched acyltrehaloses | mjackson | | | RND superfamily inner membrane transporter thought to be involved in the translocation of a diacylated precursor of sulfolipid I across the plasma membrane (phenotypic [mycobacterial recombinant strains])
SE. Converse, JD. Mougous et al. MmpL8 is required for sulfolipid-1 biosynthesis and Mycobacterium tuberculosis virulence. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2003 |
| Citation | MmpL8 is required for sulfolipid-1 biosynthesis and Mycobacterium tuberculosis virulence. SE. Converse, JD. Mougous et al. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2003 | jjmcfadden | | 12724526 | Inferred from direct assay |
| Other | EC: | jjmcfadden | | | Inferred from direct assay
SE. Converse, JD. Mougous et al. MmpL8 is required for sulfolipid-1 biosynthesis and Mycobacterium tuberculosis virulence. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2003 |