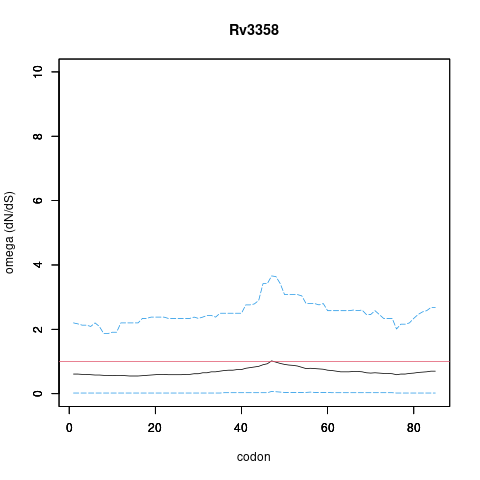
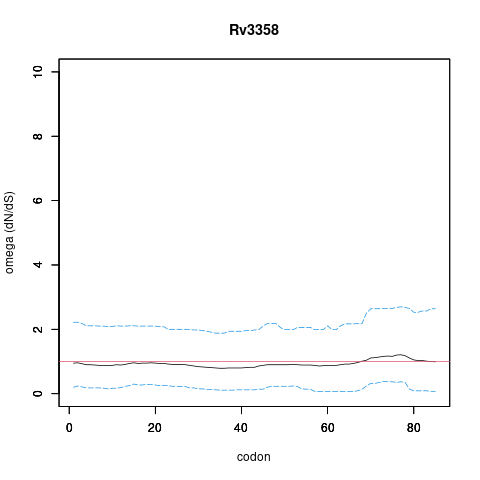
| Property | Value | Creator | Evidence | PMID | Comment |
| Citation | The three RelE homologs of Mycobacterium tuberculosis have individual, drug-specific effects on bacterial antibiotic tolerance. authors,R. Singh,CE. Barry,HI. Boshoff J. Bacteriol. 2010 | shahanup86 | IPI | 20061486 | Affinity purification (Physical interaction) |
| Interaction | PhysicalInteraction Rv3357 | shahanup86 | IPI | | Affinity purification (Physical interaction)
authors,R. Singh,CE. Barry,HI. Boshoff The three RelE homologs of Mycobacterium tuberculosis have individual, drug-specific effects on bacterial antibiotic tolerance. J. Bacteriol. 2010 |
| Citation | Crystal structure of Mycobacterium tuberculosis YefM antitoxin reveals that it is not an intrinsically unstructured protein. authors,P. Kumar,B. Issac,EJ. Dodson,JP. Turkenburg,SC. Mande J. Mol. Biol. 2008 | vashishtrv | IPI | 18793646 | Affinity purification (Physical interaction) |
| Interaction | PhysicalInteraction Rv3357 | vashishtrv | IPI | | Affinity purification (Physical interaction)
authors,P. Kumar,B. Issac,EJ. Dodson,JP. Turkenburg,SC. Mande Crystal structure of Mycobacterium tuberculosis YefM antitoxin reveals that it is not an intrinsically unstructured protein. J. Mol. Biol. 2008 |
| Citation | Three Mycobacterium tuberculosis Rel toxin:antitoxin modules inhibit mycobacterial growth and are expressed in human-infected macrophages. SB. Korch, H. Contreras et al. J. Bacteriol. 2008 | vashishtrv | IPI | 19114484 | Affinity purification (Physical interaction) |
| Interaction | PhysicalInteraction Rv3357 | vashishtrv | IPI | | Affinity purification (Physical interaction)
SB. Korch, H. Contreras et al. Three Mycobacterium tuberculosis Rel toxin:antitoxin modules inhibit mycobacterial growth and are expressed in human-infected macrophages. J. Bacteriol. 2008 |
| Citation | The three RelE homologs of Mycobacterium tuberculosis have individual, drug-specific effects on bacterial antibiotic tolerance. authors,R. Singh,CE. Barry,HI. Boshoff J. Bacteriol. 2010 | vashishtrv | IPI | 20061486 | Affinity purification (Physical interaction) |
| Interaction | PhysicalInteraction Rv3357 | vashishtrv | IPI | | Affinity purification (Physical interaction)
authors,R. Singh,CE. Barry,HI. Boshoff The three RelE homologs of Mycobacterium tuberculosis have individual, drug-specific effects on bacterial antibiotic tolerance. J. Bacteriol. 2010 |
| Interaction | PhysicalInteraction Rv3357 | vashishtrv | IPI | | Affinity purification (Physical interaction)
authors,P. Kumar,B. Issac,EJ. Dodson,JP. Turkenburg,SC. Mande Crystal structure of Mycobacterium tuberculosis YefM antitoxin reveals that it is not an intrinsically unstructured protein. J. Mol. Biol. 2008 |
| Interaction | PhysicalInteraction Rv3357 | vashishtrv | IPI | | Affinity purification (Physical interaction)
SB. Korch, H. Contreras et al. Three Mycobacterium tuberculosis Rel toxin:antitoxin modules inhibit mycobacterial growth and are expressed in human-infected macrophages. J. Bacteriol. 2008 |
| Interaction | PhysicalInteraction Rv3357 | vashishtrv | IPI | | Affinity purification (Physical interaction)
authors,R. Singh,CE. Barry,HI. Boshoff The three RelE homologs of Mycobacterium tuberculosis have individual, drug-specific effects on bacterial antibiotic tolerance. J. Bacteriol. 2010 |
| Citation | Crystal structure of Mycobacterium tuberculosis YefM antitoxin reveals that it is not an intrinsically unstructured protein. authors,P. Kumar,B. Issac,EJ. Dodson,JP. Turkenburg,SC. Mande J. Mol. Biol. 2008 | shahanup86 | IPI | 18793646 | Affinity purification (Physical interaction) |
| Interaction | PhysicalInteraction Rv3357 | shahanup86 | IPI | | Affinity purification (Physical interaction)
authors,P. Kumar,B. Issac,EJ. Dodson,JP. Turkenburg,SC. Mande Crystal structure of Mycobacterium tuberculosis YefM antitoxin reveals that it is not an intrinsically unstructured protein. J. Mol. Biol. 2008 |
| Citation | Three Mycobacterium tuberculosis Rel toxin:antitoxin modules inhibit mycobacterial growth and are expressed in human-infected macrophages. SB. Korch, H. Contreras et al. J. Bacteriol. 2008 | shahanup86 | IPI | 19114484 | Affinity purification (Physical interaction) |
| Interaction | PhysicalInteraction Rv3357 | shahanup86 | IPI | | Affinity purification (Physical interaction)
SB. Korch, H. Contreras et al. Three Mycobacterium tuberculosis Rel toxin:antitoxin modules inhibit mycobacterial growth and are expressed in human-infected macrophages. J. Bacteriol. 2008 |
| Interaction | PhysicalInteraction Rv3357 | shahanup86 | IPI | | Affinity purification (Physical interaction)
authors,P. Kumar,B. Issac,EJ. Dodson,JP. Turkenburg,SC. Mande Crystal structure of Mycobacterium tuberculosis YefM antitoxin reveals that it is not an intrinsically unstructured protein. J. Mol. Biol. 2008 |
| Interaction | PhysicalInteraction Rv3357 | shahanup86 | IPI | | Affinity purification (Physical interaction)
SB. Korch, H. Contreras et al. Three Mycobacterium tuberculosis Rel toxin:antitoxin modules inhibit mycobacterial growth and are expressed in human-infected macrophages. J. Bacteriol. 2008 |
| Interaction | PhysicalInteraction Rv3357 | shahanup86 | IPI | | Affinity purification (Physical interaction)
authors,R. Singh,CE. Barry,HI. Boshoff The three RelE homologs of Mycobacterium tuberculosis have individual, drug-specific effects on bacterial antibiotic tolerance. J. Bacteriol. 2010 |
| Citation | Comprehensive functional analysis of Mycobacterium tuberculosis toxin-antitoxin systems: implications for pathogenesis, stress responses, and evolution. authors,HR. Ramage,LE. Connolly,JS. Cox PLoS Genet. 2009 | jlew | | 20011113 | RelE homolog, Toxic when expressed in Msmeg, not rescued by antitoxin (Rv3358) |
| Symbol | relK | jlew | | | Each pair shows interaction by two-hybrid and GST pulldown. F and B each interact with E, G, K, and itself.
authors,M. Yang,C. Gao,Y. Wang,H. Zhang,ZG. He Characterization of the interaction and cross-regulation of three Mycobacterium tuberculosis RelBE modules. PLoS ONE 2010 |
| Citation | Characterization of the interaction and cross-regulation of three Mycobacterium tuberculosis RelBE modules. authors,M. Yang,C. Gao,Y. Wang,H. Zhang,ZG. He PLoS ONE 2010 | jlew | | 20498855 | Each pair shows interaction by two-hybrid and GST pulldown. F and B each interact with E, G, K, and itself. |
| Symbol | relE3 | jlew | | | Each toxin individually arrests growth of both M. tuberculosis and E. coli, an effect that is neutralized by coexpression of the cognate antitoxin.
authors,R. Singh,CE. Barry,HI. Boshoff The three RelE homologs of Mycobacterium tuberculosis have individual, drug-specific effects on bacterial antibiotic tolerance. J. Bacteriol. 2010 |
| Citation | The three RelE homologs of Mycobacterium tuberculosis have individual, drug-specific effects on bacterial antibiotic tolerance. authors,R. Singh,CE. Barry,HI. Boshoff J. Bacteriol. 2010 | jlew | | 20061486 | Each toxin individually arrests growth of both M. tuberculosis and E. coli, an effect that is neutralized by coexpression of the cognate antitoxin. |
| Symbol | relK | jlew | | | Overexpression of Mtb relE, relG and relK induces growth arrest in Msmeg; reversed by expression of relB, relF and relJ
SB. Korch, H. Contreras et al. Three Mycobacterium tuberculosis Rel toxin:antitoxin modules inhibit mycobacterial growth and are expressed in human-infected macrophages. J. Bacteriol. 2008 |
| Citation | Three Mycobacterium tuberculosis Rel toxin:antitoxin modules inhibit mycobacterial growth and are expressed in human-infected macrophages. SB. Korch, H. Contreras et al. J. Bacteriol. 2008 | jlew | | 19114484 | Overexpression of Mtb relE, relG and relK induces growth arrest in Msmeg; reversed by expression of relB, relF and relJ |
| Symbol | RelE3 | jlew | | | We report the heterologous toxicity of these TA loci in Escherichia coli and show that only a few of the M. tuberculosis-encoded toxins can inhibit E. coli growth and have a killing effect. This killing effect can be suppressed by coexpression of the cognate antitoxin.
authors,A. Gupta Killing activity and rescue function of genome-wide toxin-antitoxin loci of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2009 |
| Citation | Killing activity and rescue function of genome-wide toxin-antitoxin loci of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. authors,A. Gupta FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2009 | jlew | | 19016878 | We report the heterologous toxicity of these TA loci in Escherichia coli and show that only a few of the M. tuberculosis-encoded toxins can inhibit E. coli growth and have a killing effect. This killing effect can be suppressed by coexpression of the cognate antitoxin. |
| Other | start:3771045 | rslayden | | | SAV2407 from Staphylococcus aureus subsp. aureus Mu50 (88 aa), FASTA scores: opt: 250, E(): 2e-11, (40.5% identity in 84 aa overlap); etc. |
| Other | stop:3771302 | rslayden | | | SAV2407 from Staphylococcus aureus subsp. aureus Mu50 (88 aa), FASTA scores: opt: 250, E(): 2e-11, (40.5% identity in 84 aa overlap); etc. |
| Other | strand:+ | rslayden | | | SAV2407 from Staphylococcus aureus subsp. aureus Mu50 (88 aa), FASTA scores: opt: 250, E(): 2e-11, (40.5% identity in 84 aa overlap); etc. |
| Other | start:3771045 | rslayden | | | Conserved hypohetical protein, highly similar to other hypohetical proteins e.g. Q9Z4V8 |
| Other | stop:3771302 | rslayden | | | Conserved hypohetical protein, highly similar to other hypohetical proteins e.g. Q9Z4V8 |
| Other | strand:+ | rslayden | | | Conserved hypohetical protein, highly similar to other hypohetical proteins e.g. Q9Z4V8 |
| Other | start:3771045 | rslayden | | | SCBAC17D6.03 from Streptomyces coelicolor (84 aa), FASTA scores: opt: 393, E(): 1.1e-21, (59.75% identity in 82 aa overlap); P56605 |
| Other | stop:3771302 | rslayden | | | SCBAC17D6.03 from Streptomyces coelicolor (84 aa), FASTA scores: opt: 393, E(): 1.1e-21, (59.75% identity in 82 aa overlap); P56605 |
| Other | strand:+ | rslayden | | | SCBAC17D6.03 from Streptomyces coelicolor (84 aa), FASTA scores: opt: 393, E(): 1.1e-21, (59.75% identity in 82 aa overlap); P56605 |
| Other | start:3771045 | rslayden | | | YOEB_ECOLI from Escherichia coli (84 aa), FASTA scores: opt: 305, E(): 2.2e-15, (49.35% identity in 77 aa overlap); Q9Z5W7 PUTATIVE DOC PROTEIN from Francisella novicida (68 aa), FASTA scores: opt: 253, E(): 9.6e-12, (51.6% identity in 62 aa overlap); BAB58569 |
| Other | stop:3771302 | rslayden | | | YOEB_ECOLI from Escherichia coli (84 aa), FASTA scores: opt: 305, E(): 2.2e-15, (49.35% identity in 77 aa overlap); Q9Z5W7 PUTATIVE DOC PROTEIN from Francisella novicida (68 aa), FASTA scores: opt: 253, E(): 9.6e-12, (51.6% identity in 62 aa overlap); BAB58569 |
| Other | strand:+ | rslayden | | | YOEB_ECOLI from Escherichia coli (84 aa), FASTA scores: opt: 305, E(): 2.2e-15, (49.35% identity in 77 aa overlap); Q9Z5W7 PUTATIVE DOC PROTEIN from Francisella novicida (68 aa), FASTA scores: opt: 253, E(): 9.6e-12, (51.6% identity in 62 aa overlap); BAB58569 |