Rv2241 (aceE)
Current annotations:
TBCAP: (community-based annotations - see table at bottom of page )
TBDB: pyruvate dehydrogenase E1 component
REFSEQ: pyruvate dehydrogenase subunit E1
PATRIC: Pyruvate dehydrogenase E1 component (EC 1.2.4.1)
TUBERCULIST: Pyruvate dehydrogenase E1 component AceE (pyruvate decarboxylase) (pyruvate dehydrogenase) (pyruvic dehydrogenase)
NCBI: Pyruvate dehydrogenase E1 component AceE (pyruvate decarboxylase) (pyruvate dehydrogenase) (pyruvic dehydrogenase)
updated information (H37Rv4):
gene name: aceE
function:
reference:
Coordinates in H37Rv: 2512539 - 2515244
Gene length: 2706 bp (with stop codon), 901 aa (without stop codon)
Operon:
Trans-membrane region:
Role: I.B.2 - Pyruvate dehydrogenase
GO terms:
Reaction(s) (based on iSM810 metabolic model):
Gene Expression Profile Gene Modules Orthologs among selected mycobacteria Protein structure:
Search for Homologs in PDB Top 10 Homologs in PDB (as of Nov 2020): PDB aa ident species PDB title 4QOY 52% Escherichia coli Novel binding motif and new flexibility revealed by structural analysis of a pyruvate dehydrogenase-dihydrolipoyl acetyltransferase sub-complex from the escherichia coli pyruvate dehydrogenase multi-enzyme complex 2IEA 52% Escherichia coli E. coli pyruvate dehydrogenase 2G67 52% Escherichia coli E. Coli Pyruvate Dehydrogenase E1 Component (Apoenzyme) 2G28 52% Escherichia coli E. Coli Pyruvate Dehydrogenase H407A variant Phosphonolactylthiamin Diphosphate Complex 2G25 52% Escherichia coli E. Coli Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Phosphonolactylthiamin Diphosphate Complex 1RP7 52% Escherichia coli E. COLI PYRUVATE DEHYDROGENASE INHIBITOR COMPLEX 1L8A 52% Escherichia coli E. COLI PYRUVATE DEHYDROGENASE 3LQ4 52% Escherichia coli E. coli pyruvate dehydrogenase complex E1 E235A mutant with high TDP concentration 3LQ2 52% Escherichia coli E. coli pyruvate dehydrogenase complex E1 E235A mutant with low TDP concentration 3LPL 52% Escherichia coli E. coli pyruvate dehydrogenase complex E1 component E571A mutant
Links to additional information on aceE:
Amino Acid Sequence
VASYLPDIDPEETSEWLESFDTLLQRCGPSRARYLMLRLLERAGEQRVAIPALTSTDYVNTIPTELEPWFPGDEDVERRYRAWIRWNAAIMVHRAQRPGV
GVGGHISTYASSAALYEVGFNHFFRGKSHPGGGDQVFIQGHASPGIYARAFLEGRLTAEQLDGFRQEHSHVGGGLPSYPHPRLMPDFWEFPTVSMGLGPL
NAIYQARFNHYLHDRGIKDTSDQHVWCFLGDGEMDEPESRGLAHVGALEGLDNLTFVINCNLQRLDGPVRGNGKIIQELESFFRGAGWNVIKVVWGREWD
ALLHADRDGALVNLMNTTPDGDYQTYKANDGGYVRDHFFGRDPRTKALVENMSDQDIWNLKRGGHDYRKVYAAYRAAVDHKGQPTVILAKTIKGYALGKH
FEGRNATHQMKKLTLEDLKEFRDTQRIPVSDAQLEENPYLPPYYHPGLNAPEIRYMLDRRRALGGFVPERRTKSKALTLPGRDIYAPLKKGSGHQEVATT
MATVRTFKEVLRDKQIGPRIVPIIPDEARTFGMDSWFPSLKIYNRNGQLYTAVDADLMLAYKESEVGQILHEGINEAGSVGSFIAAGTSYATHNEPMIPI
YIFYSMFGFQRTGDSFWAAADQMARGFVLGATAGRTTLTGEGLQHADGHSLLLAATNPAVVAYDPAFAYEIAYIVESGLARMCGENPENIFFYITVYNEP
YVQPPEPENFDPEGVLRGIYRYHAATEQRTNKAQILASGVAMPAALRAAQMLAAEWDVAADVWSVTSWGELNRDGVAIETEKLRHPDRPAGVPYVTRALE
NARGPVIAVSDWMRAVPEQIRPWVPGTYLTLGTDGFGFSDTRPAARRYFNTDAESQVVAVLEALAGDGEIDPSVPVAAARQYRIDDVAAAPEQTTDPGPG
A
(
Nucleotide sequence available on
KEGG )
Additional Information
MtbTnDB - interactive tool for exploring a database of published TnSeq datasets for Mtb
TnSeqCorr
Rv2241/aceE,
gene len: 2705 bp, num TA sites: 58
condition dataset call medium method notes
in-vitro DeJesus 2017 mBio non-essential 7H9 HMM fully saturated, 14 TnSeq libraries combined
in-vitro Sassetti 2003 Mol Micro growth-defect 7H9 TRASH essential if hybridization ratio<0.2
in-vivo (mice) Sassetti 2003 PNAS essential BL6 mice TRASH essential if hybridization ratio<0.4, min over 4 timepoints (1-8 weeks)
in-vitro (glycerol) Griffin 2011 PPath essential M9 minimal+glycerol Gumbel 2 replicates; Padj<0.05
in-vitro (cholesterol) Griffin 2011 PPath essential M9 minimal+cholesterol Gumbel 3 replicates; Padj<0.05
differentially essential in cholesterol Griffin 2011 PPath NO (LFC=0.0) cholesterol vs glycerol resampling-SR YES if Padj<0.05, else not significant; LFC<0 means less insertions/more essential in cholesterol
in-vitro Smith 2022 eLife growth defect 7H9 HMM 6 replicates (raw data in Subramaniam 2017, PMID 31752678)
in-vivo (mice) Smith 2022 eLife growth defect BL6 mice HMM 6 replicates (raw data in Subramaniam 2017, PMID 31752678)
differentially essential in mice Smith 2022 eLife YES (LFC=-0.674) in-vivo vs in-vitro ZINB YES if Padj<0.05, else not significant; LFC<0 means less insertions/more essential in mice
in-vitro (minimal) Minato 2019 mSys growth defect minimal medium HMM
in-vitro (YM rich medium) Minato 2019 mSys non-essential YM rich medium HMM 7H9 supplemented with ~20 metabolites (amino acids, cofactors)
differentially essential in YM rich medium Minato 2019 mSys YES (LFC=3.29) YM rich vs minimal medium resampling
Analysis of Positive Selection in Clinical Isolates
*new*
data from Culviner et al (2025) (55,259 Mtb clinical isolates)
overall pN/pS for Rv2241: 0.401620684
lineage-specific pN/pS in L1: 0.476805257
lineage-specific pN/pS in L2: 0.319334492
lineage-specific pN/pS in L3: 0.302824681
lineage-specific pN/pS in L4: 0.429191015
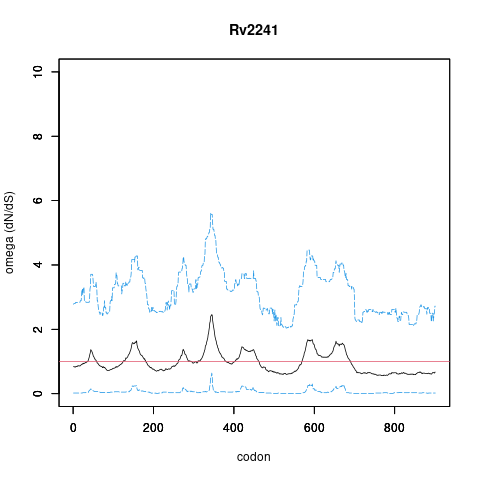
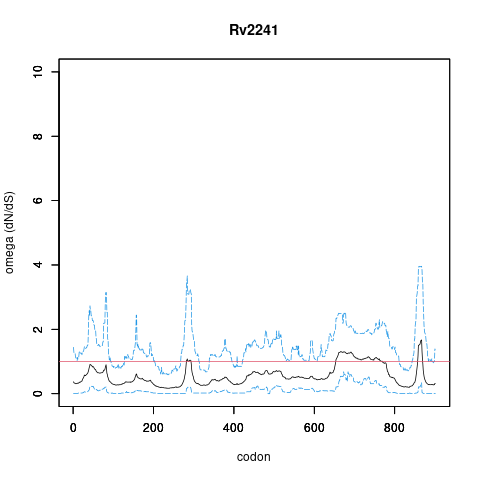
Analysis of dN/dS (omega) in two collections of Mtb clinical isolates using GenomegaMap (Window model) (see description of methods )
Moldova: 2,057 clinical isolates
global set: 5,195 clinical isolates from 15 other countries
In the omega plots, the black line shows the mean estimate of omega (dN/dS) at each codon, and the blue lines are the bounds for the 95% credible interval (95%CI, from MCMC sampling).
A gene is under significant positive selection if the lower-bound of the 95%CI of omega (lower blue line) exceeds 1.0 at any codon.
Moldova (2,057) global set (5,195)
under significant positive selection? NO NO
omega peak height (95%CI lower bound) 2.46 (0.64) 1.26 (0.68)
codons under selection
omega plots
genetic variants* link link
statistics at each codon link link
* example format for variants: "D27 (GAC): D27H (CAC,11)" means "Asp27 (native codon GAC) mutated to His (codon CAC) in 11 isolates"
TnSeq Data No data currently available.
No TnSeq data currently available for this Target.
RNASeq Data No data currently available.
No RNA-Seq data currently available for this Target.
Metabolomic Profiles No data currently available.
No Metabolomic data currently available for this Target.
Proteomic Data No data currently available.
No Proteomic data currently available for this Target.
Regulatory Relationships from Systems Biology
BioCyc
Gene interactions based on ChIPSeq and Transcription Factor Over-Expression (TFOE) (Systems Biology )
NOTE:
Green edges represent the connected genes being classified as differentially essential as a result of the middle gene being knocked out. These interactions are inferred based on RNASeq.
Interactions based on ChIPSeq data
RNA processing and modification
Energy production and conversion
Chromatin structure and dynamics
Amino acid transport and metabolism
Cell cycle control, cell division, chromosome partitioning
Carbohydrate transport and metabolism
Nucleotide transport and metabolism
Lipid transport and metabolism
Coenzyme transport and metabolism
Translation, ribosomal structure and biogenesis
Cell wall/membrane/envelope biogenesis
Replication, recombination and repair
Posttranslational modification, protein turnover, chaperones
Secondary metabolites biosynthesis, transport and catabolism
Inorganic ion transport and metabolism
General function prediction only
Intracellular trafficking, secretion, and vesicular transport
Signal transduction mechanisms
Differentially expressed as result of RNASeq in glycerol environment (Only top 20 genes shown sorted by log fold change with p_adj 0.05).
Conditionally essential as result of TNSeq (Only top 20 genes shown sorted by log fold change with p_adj 0.05).
Binds To:
No bindings to other targets were found.
Bound By:
No bindings from other targets were found.
Binds To:
No bindings to other targets were found.
Bound By:
No bindings to other targets were found.
Upregulates:
Does not upregulate other genes.
Upregulated by:
Not upregulated by other genes.
Downregulates:
Does not downregulate other genes.
Downregulated by:
Not downregulated by other genes.
Property Value Creator Evidence PMID Comment
Citation Mycobacterium tuberculosis appears to lack alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase and encodes pyruvate dehydrogenase in widely separated genes. J. Tian, R. Bryk et al. Mol. Microbiol. 2005 njamshidi IDA 16045627 previous annotations with sequence based annotations of pdhA, pdhB, pdhC (Rv2497c, Rv2496c,Rv2495c) were found to be incorrect and removed - this is the appropriate annotation for PDH according to PMID: 16045627.
Term TBRXN:PDH pyruvate dehydrogenase - IDA njamshidi IDA 16045627 previous annotations with sequence based annotations of pdhA, pdhB, pdhC (Rv2497c, Rv2496c,Rv2495c) were found to be incorrect and removed - this is the appropriate annotation for PDH according to PMID: 16045627.J. Tian, R. Bryk et al. Mycobacterium tuberculosis appears to lack alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase and encodes pyruvate dehydrogenase in widely separated genes. Mol. Microbiol. 2005
Citation Mycobacterium tuberculosis appears to lack alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase and encodes pyruvate dehydrogenase in widely separated genes. J. Tian, R. Bryk et al. Mol. Microbiol. 2005 njamshidi ISS 16045627 previous annotations with sequence based annotations of pdhA, pdhB, pdhC (Rv2497c, Rv2496c,Rv2495c) were found to be incorrect and removed - this is the appropriate annotation for PDH according to PMID: 16045627.
Term TBRXN:PDH pyruvate dehydrogenase - ISS njamshidi ISS 16045627 previous annotations with sequence based annotations of pdhA, pdhB, pdhC (Rv2497c, Rv2496c,Rv2495c) were found to be incorrect and removed - this is the appropriate annotation for PDH according to PMID: 16045627.J. Tian, R. Bryk et al. Mycobacterium tuberculosis appears to lack alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase and encodes pyruvate dehydrogenase in widely separated genes. Mol. Microbiol. 2005
Interaction Signaling Rv1571 razeeth.new IEP Co-expressionAH. Li, WL. Lam et al. Bacterial artificial chromosome fingerprint arrays for the differentiation of transcriptomic differences in mycobacteria. J. Microbiol. Methods 2008
Interaction Signaling Rv1571 razeeth.new IEP Co-expressionAH. Li, WL. Lam et al. Characterization of genes differentially expressed within macrophages by virulent and attenuated Mycobacterium tuberculosis identifies candidate genes involved in intracellular growth. Microbiology (Reading, Engl.) 2008
Interaction RegulatedBy Rv1221 yamir.moreno IEP Microarrays. mRNA levels of regulated element measured and compared between wild-type and trans-element mutation (knockout, over expression etc.) performed by using microarray (or macroarray) experiments..R. Manganelli, MI. Voskuil et al. The Mycobacterium tuberculosis ECF sigma factor sigmaE: role in global gene expression and survival in macrophages. Mol. Microbiol. 2001
Citation Variant tricarboxylic acid cycle in Mycobacterium tuberculosis: identification of alpha-ketoglutarate decarboxylase. J. Tian, R. Bryk et al. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2005 jjmcfadden 16027371 Inferred from direct assay
Term EC:1.2.4.1 Pyruvate dehydrogenase (acetyl-transferring). - NR jjmcfadden NR Inferred from direct assayJ. Tian, R. Bryk et al. Variant tricarboxylic acid cycle in Mycobacterium tuberculosis: identification of alpha-ketoglutarate decarboxylase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2005
Citation Central carbon metabolism in Mycobacterium tuberculosis: an unexpected frontier. authors,KY. Rhee,LP. de Carvalho,R. Bryk,S. Ehrt,J. Marrero,SW. Park,D. Schnappinger,A. Venugopal,C. Nathan Trends Microbiol. 2011 extern:JZUCKER 21561773 Traceable author statement to experimental support
Term EC:1.2.4.1 Pyruvate dehydrogenase (acetyl-transferring). - NR extern:JZUCKER NR Traceable author statement to experimental supportauthors,KY. Rhee,LP. de Carvalho,R. Bryk,S. Ehrt,J. Marrero,SW. Park,D. Schnappinger,A. Venugopal,C. Nathan Central carbon metabolism in Mycobacterium tuberculosis: an unexpected frontier. Trends Microbiol. 2011
Citation Mycobacterium tuberculosis appears to lack alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase and encodes pyruvate dehydrogenase in widely separated genes. J. Tian, R. Bryk et al. Mol. Microbiol. 2005 extern:JZUCKER 16045627 Inferred from mutant phenotype
Term EC:1.2.4.1 Pyruvate dehydrogenase (acetyl-transferring). - NR extern:JZUCKER NR Inferred from mutant phenotypeJ. Tian, R. Bryk et al. Mycobacterium tuberculosis appears to lack alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase and encodes pyruvate dehydrogenase in widely separated genes. Mol. Microbiol. 2005