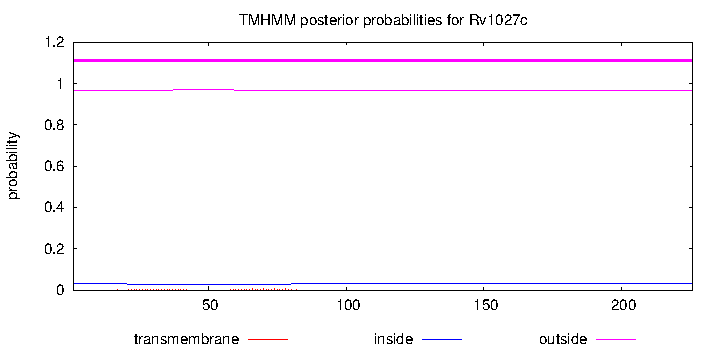
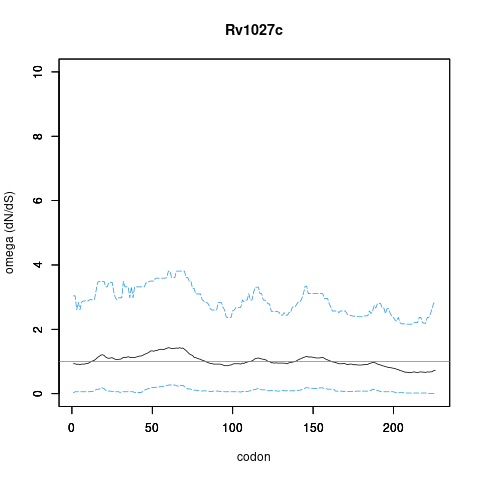
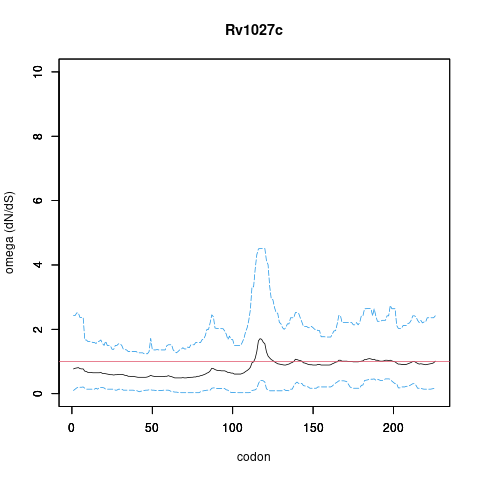
| Property | Value | Creator | Evidence | PMID | Comment |
| Interaction | Regulatory Rv1028c | akankshajain.21 | IPI | | Protein fragment complementation
T. Parish, DA. Smith et al. Deletion of two-component regulatory systems increases the virulence of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Infect. Immun. 2003 |
| Interaction | Regulatory Rv1028c | akankshajain.21 | IPI | | Protein fragment complementation
A. Singh, D. Mai et al. Dissecting virulence pathways of Mycobacterium tuberculosis through protein-protein association. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2006 |
| Citation | Dissecting virulence pathways of Mycobacterium tuberculosis through protein-protein association. A. Singh, D. Mai et al. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2006 | darhngu | IPI | 16844784 | Protein fragment complementation |
| Interaction | Regulatory Rv1028c | darhngu | IPI | | Protein fragment complementation
A. Singh, D. Mai et al. Dissecting virulence pathways of Mycobacterium tuberculosis through protein-protein association. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2006 |
| Interaction | Signaling Rv1029 | ahal4789 | ISO | |
authors,A. Ballal,B. Basu,SK. Apte The Kdp-ATPase system and its regulation. J. Biosci. 2007 |
| Interaction | Signaling Rv1030 | ahal4789 | ISO | |
authors,A. Ballal,B. Basu,SK. Apte The Kdp-ATPase system and its regulation. J. Biosci. 2007 |
| Interaction | Signaling Rv1031 | ahal4789 | ISO | |
authors,A. Ballal,B. Basu,SK. Apte The Kdp-ATPase system and its regulation. J. Biosci. 2007 |
| Citation | The Kdp-ATPase system and its regulation. authors,A. Ballal,B. Basu,SK. Apte J. Biosci. 2007 | sourish10 | ISO | 17536175 | None |
| Interaction | Signaling Rv1028A | sourish10 | ISO | |
authors,A. Ballal,B. Basu,SK. Apte The Kdp-ATPase system and its regulation. J. Biosci. 2007 |
| Interaction | Signaling Rv1029 | sourish10 | ISO | |
authors,A. Ballal,B. Basu,SK. Apte The Kdp-ATPase system and its regulation. J. Biosci. 2007 |
| Interaction | Signaling Rv1030 | sourish10 | ISO | |
authors,A. Ballal,B. Basu,SK. Apte The Kdp-ATPase system and its regulation. J. Biosci. 2007 |
| Interaction | Signaling Rv1031 | sourish10 | ISO | |
authors,A. Ballal,B. Basu,SK. Apte The Kdp-ATPase system and its regulation. J. Biosci. 2007 |
| Citation | Deletion of two-component regulatory systems increases the virulence of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. T. Parish, DA. Smith et al. Infect. Immun. 2003 | darhngu | IPI | 12595424 | Protein fragment complementation |
| Interaction | Regulatory Rv1028c | darhngu | IPI | | Protein fragment complementation
T. Parish, DA. Smith et al. Deletion of two-component regulatory systems increases the virulence of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Infect. Immun. 2003 |
| Citation | The Kdp-ATPase system and its regulation. authors,A. Ballal,B. Basu,SK. Apte J. Biosci. 2007 | ahal4789 | ISO | 17536175 | None |
| Interaction | Signaling Rv1028A | ahal4789 | ISO | |
authors,A. Ballal,B. Basu,SK. Apte The Kdp-ATPase system and its regulation. J. Biosci. 2007 |
| Citation | The temporal response of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis gene regulatory network during growth arrest. G. Balzsi, AP. Heath et al. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2008 | yamir.moreno | ISO | 18985025 | E.coli orthology based inference. Orthologous pair regulator-target found in E.coli. |
| Interaction | Regulates Rv1029 | yamir.moreno | ISO | | E.coli orthology based inference. Orthologous pair regulator-target found in E.coli.
G. Balzsi, AP. Heath et al. The temporal response of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis gene regulatory network during growth arrest. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2008 |
| Citation | The temporal response of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis gene regulatory network during growth arrest. G. Balzsi, AP. Heath et al. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2008 | yamir.moreno | ISO | 18985025 | E.coli orthology based inference. Orthologous pair regulator-target found in E.coli. |
| Interaction | Regulates Rv1030 | yamir.moreno | ISO | | E.coli orthology based inference. Orthologous pair regulator-target found in E.coli.
G. Balzsi, AP. Heath et al. The temporal response of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis gene regulatory network during growth arrest. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2008 |
| Citation | The temporal response of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis gene regulatory network during growth arrest. G. Balzsi, AP. Heath et al. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2008 | yamir.moreno | ISO | 18985025 | E.coli orthology based inference. Orthologous pair regulator-target found in E.coli. |
| Interaction | Regulates Rv1031 | yamir.moreno | ISO | | E.coli orthology based inference. Orthologous pair regulator-target found in E.coli.
G. Balzsi, AP. Heath et al. The temporal response of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis gene regulatory network during growth arrest. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2008 |
| Interaction | Regulates Rv1029 | yamir.moreno | ISO | | E.coli orthology based inference. Orthologous pair regulator-target found in E.coli.
authors,M. Madan Babu,SA. Teichmann,L. Aravind Evolutionary dynamics of prokaryotic transcriptional regulatory networks. J. Mol. Biol. 2006 |
| Citation | Evolutionary dynamics of prokaryotic transcriptional regulatory networks. authors,M. Madan Babu,SA. Teichmann,L. Aravind J. Mol. Biol. 2006 | yamir.moreno | ISO | 16530225 | E.coli orthology based inference. Orthologous pair regulator-target found in E.coli. |
| Interaction | Regulates Rv1030 | yamir.moreno | ISO | | E.coli orthology based inference. Orthologous pair regulator-target found in E.coli.
authors,M. Madan Babu,SA. Teichmann,L. Aravind Evolutionary dynamics of prokaryotic transcriptional regulatory networks. J. Mol. Biol. 2006 |
| Citation | Evolutionary dynamics of prokaryotic transcriptional regulatory networks. authors,M. Madan Babu,SA. Teichmann,L. Aravind J. Mol. Biol. 2006 | yamir.moreno | ISO | 16530225 | E.coli orthology based inference. Orthologous pair regulator-target found in E.coli. |
| Interaction | Regulates Rv1031 | yamir.moreno | ISO | | E.coli orthology based inference. Orthologous pair regulator-target found in E.coli.
authors,M. Madan Babu,SA. Teichmann,L. Aravind Evolutionary dynamics of prokaryotic transcriptional regulatory networks. J. Mol. Biol. 2006 |
| Citation | Evolutionary dynamics of prokaryotic transcriptional regulatory networks. authors,M. Madan Babu,SA. Teichmann,L. Aravind J. Mol. Biol. 2006 | yamir.moreno | ISO | 16530225 | E.coli orthology based inference. Orthologous pair regulator-target found in E.coli. |