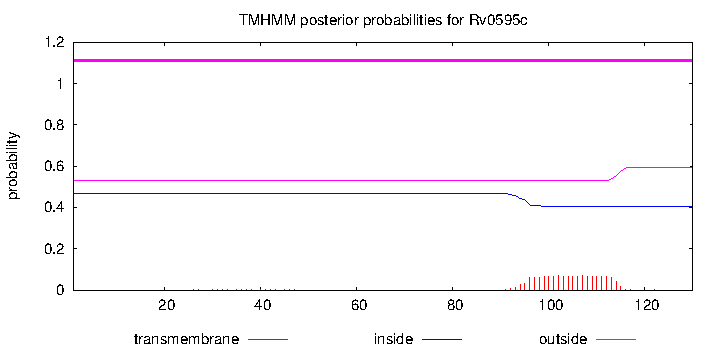
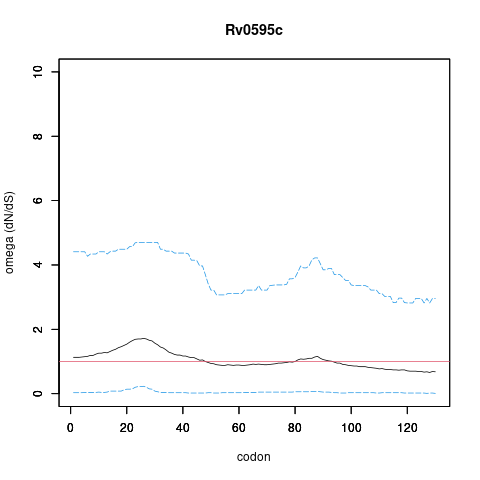
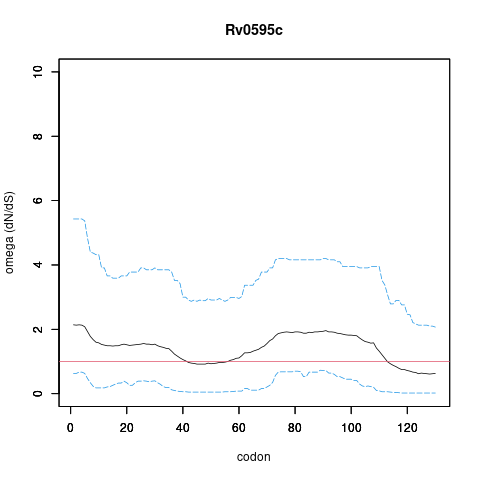
| Property | Value | Creator | Evidence | PMID | Comment |
| Citation | Comprehensive functional analysis of Mycobacterium tuberculosis toxin-antitoxin systems: implications for pathogenesis, stress responses, and evolution. authors,HR. Ramage,LE. Connolly,JS. Cox PLoS Genet. 2009 | shahanup86 | IEP | 20011113 | Co-expression (Functional linkage) |
| Interaction | Inhibition Rv0596c | shahanup86 | IEP | | Co-expression (Functional linkage)
authors,HR. Ramage,LE. Connolly,JS. Cox Comprehensive functional analysis of Mycobacterium tuberculosis toxin-antitoxin systems: implications for pathogenesis, stress responses, and evolution. PLoS Genet. 2009 |
| Interaction | Inhibition Rv0596c | shahanup86 | IEP | | Co-expression (Functional linkage)
authors,DJ. Beste,M. Espasa,B. Bonde,AM. Kierzek,GR. Stewart,J. McFadden The genetic requirements for fast and slow growth in mycobacteria. PLoS ONE 2009 |
| Interaction | Inhibition Rv0596c | shahanup86 | IEP | | Co-expression (Functional linkage)
authors,VL. Arcus,PB. Rainey,SJ. Turner The PIN-domain toxin-antitoxin array in mycobacteria. Trends Microbiol. 2005 |
| Interaction | Inhibition Rv0596c | shahanup86 | IEP | | Co-expression (Functional linkage)
authors,HR. Ramage,LE. Connolly,JS. Cox Comprehensive functional analysis of Mycobacterium tuberculosis toxin-antitoxin systems: implications for pathogenesis, stress responses, and evolution. PLoS Genet. 2009 |
| Citation | The genetic requirements for fast and slow growth in mycobacteria. authors,DJ. Beste,M. Espasa,B. Bonde,AM. Kierzek,GR. Stewart,J. McFadden PLoS ONE 2009 | shahanup86 | IEP | 19479006 | Co-expression (Functional linkage) |
| Interaction | Inhibition Rv0596c | shahanup86 | IEP | | Co-expression (Functional linkage)
authors,DJ. Beste,M. Espasa,B. Bonde,AM. Kierzek,GR. Stewart,J. McFadden The genetic requirements for fast and slow growth in mycobacteria. PLoS ONE 2009 |
| Citation | The PIN-domain toxin-antitoxin array in mycobacteria. authors,VL. Arcus,PB. Rainey,SJ. Turner Trends Microbiol. 2005 | shahanup86 | IEP | 15993073 | Co-expression (Functional linkage) |
| Interaction | Inhibition Rv0596c | shahanup86 | IEP | | Co-expression (Functional linkage)
authors,VL. Arcus,PB. Rainey,SJ. Turner The PIN-domain toxin-antitoxin array in mycobacteria. Trends Microbiol. 2005 |
| Citation | Comprehensive functional analysis of Mycobacterium tuberculosis toxin-antitoxin systems: implications for pathogenesis, stress responses, and evolution. authors,HR. Ramage,LE. Connolly,JS. Cox PLoS Genet. 2009 | jlew | | 20011113 | VapC homolog, PIN domain, Not toxic when expressed in Msmeg |
| Symbol | vapC-mt4 | jlew | | | VapC-mt4 expression resulted in growth arrest in E coli, M. smeg and Mtb. Its expression led to translation inhibition accompanied by a gradual decrease in the steady-state levels of several mRNAs. VapC-mt4 exhibited sequence-specific endoribonuclease activity on mRNA templates at ACGC and AC(A/U)GC sequences. VapC-mt4 is mechanistically distinct from other TA toxins since it appears to primarily inhibit translation through selective, stable binding to RNA.. Expressed 23 VapC toxins in EC lacking TA modules. 4 inhibited growth.
authors,JD. Sharp,JW. Cruz,S. Raman,M. Inouye,RN. Husson,NA. Woychik Growth and translation inhibition through sequence specific RNA binding by a mycobacterium tuberculosis VAPC toxin. The Journal of biological chemistry 2012 |
| Citation | Growth and translation inhibition through sequence specific RNA binding by a mycobacterium tuberculosis VAPC toxin. authors,JD. Sharp,JW. Cruz,S. Raman,M. Inouye,RN. Husson,NA. Woychik The Journal of biological chemistry 2012 | jlew | | 22354968 | VapC-mt4 expression resulted in growth arrest in E coli, M. smeg and Mtb. Its expression led to translation inhibition accompanied by a gradual decrease in the steady-state levels of several mRNAs. VapC-mt4 exhibited sequence-specific endoribonuclease activity on mRNA templates at ACGC and AC(A/U)GC sequences. VapC-mt4 is mechanistically distinct from other TA toxins since it appears to primarily inhibit translation through selective, stable binding to RNA.. Expressed 23 VapC toxins in EC lacking TA modules. 4 inhibited growth. |
| Symbol | VapC | jlew | | | Growth inhibitory in Mt and MS. In MS, not rescued by Rv2550c or Rv2830c. Rv0595c interacts with Rv0596c but not the other 3 VapBs, by Y2H.
authors,BA. Ahidjo,D. Kuhnert,JL. McKenzie,EE. Machowski,BG. Gordhan,V. Arcus,GL. Abrahams,V. Mizrahi VapC toxins from Mycobacterium tuberculosis are ribonucleases that differentially inhibit growth and are neutralized by cognate VapB antitoxins. PLoS ONE 2011 |
| Citation | VapC toxins from Mycobacterium tuberculosis are ribonucleases that differentially inhibit growth and are neutralized by cognate VapB antitoxins. authors,BA. Ahidjo,D. Kuhnert,JL. McKenzie,EE. Machowski,BG. Gordhan,V. Arcus,GL. Abrahams,V. Mizrahi PLoS ONE 2011 | jlew | | 21738782 | Growth inhibitory in Mt and MS. In MS, not rescued by Rv2550c or Rv2830c. Rv0595c interacts with Rv0596c but not the other 3 VapBs, by Y2H. |
| Symbol | VapC4 | jlew | | | Toxic to Ecoli growth. We report the heterologous toxicity of these TA loci in Escherichia coli and show that only a few of the M. tuberculosis-encoded toxins can inhibit E. coli growth and have a killing effect. This killing effect can be suppressed by coexpression of the cognate antitoxin.
authors,A. Gupta Killing activity and rescue function of genome-wide toxin-antitoxin loci of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2009 |
| Citation | Killing activity and rescue function of genome-wide toxin-antitoxin loci of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. authors,A. Gupta FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2009 | jlew | | 19016878 | Toxic to Ecoli growth. We report the heterologous toxicity of these TA loci in Escherichia coli and show that only a few of the M. tuberculosis-encoded toxins can inhibit E. coli growth and have a killing effect. This killing effect can be suppressed by coexpression of the cognate antitoxin. |
| Other | start:694839 | rslayden | | | Conserved hypothetical protein, similar to other conserved hypothetical proteins e.g. Rv0627 (135 aa) and Rv0665 (112 aa) from Mycobacterium tuberculosis; and STBB_PSESM |
| Other | stop:695231 | rslayden | | | Conserved hypothetical protein, similar to other conserved hypothetical proteins e.g. Rv0627 (135 aa) and Rv0665 (112 aa) from Mycobacterium tuberculosis; and STBB_PSESM |
| Other | strand:+ | rslayden | | | Conserved hypothetical protein, similar to other conserved hypothetical proteins e.g. Rv0627 (135 aa) and Rv0665 (112 aa) from Mycobacterium tuberculosis; and STBB_PSESM |
| Other | start:694839 | rslayden | | | Q52562 plasmid stability protein from Pseudomonas syringae (139 aa), FASTA scores: opt: 131, E(): 0.0035, (35.2% identity in 88 aa overlap). |
| Other | stop:695231 | rslayden | | | Q52562 plasmid stability protein from Pseudomonas syringae (139 aa), FASTA scores: opt: 131, E(): 0.0035, (35.2% identity in 88 aa overlap). |
| Other | strand:+ | rslayden | | | Q52562 plasmid stability protein from Pseudomonas syringae (139 aa), FASTA scores: opt: 131, E(): 0.0035, (35.2% identity in 88 aa overlap). |