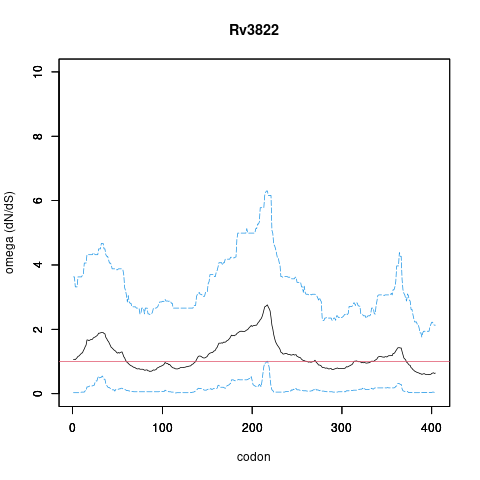
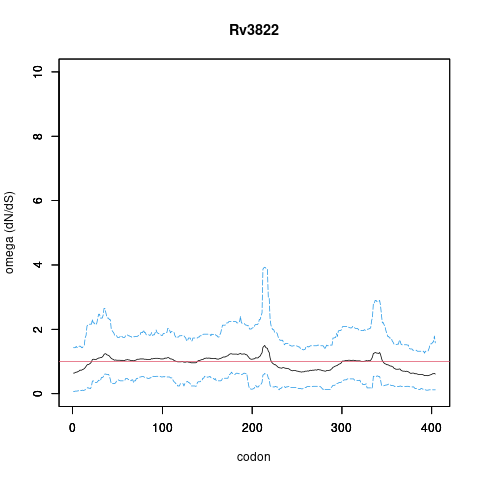
| Property | Value | Creator | Evidence | PMID | Comment |
| Interaction | Transcription Rv0757 | sourish10 | IEP | | Co-expression (Functional linkage)
SB. Walters, E. Dubnau et al. The Mycobacterium tuberculosis PhoPR two-component system regulates genes essential for virulence and complex lipid biosynthesis. Mol. Microbiol. 2006 |
| Citation | Sequence analysis corresponding to the PPE and PE proteins in Mycobacterium tuberculosis and other genomes. authors,S. Adindla,L. Guruprasad J. Biosci. 2003 | sourish10 | IEP | 12711809 | Co-expression (Functional linkage) |
| Interaction | Transcription Rv0757 | sourish10 | IEP | | Co-expression (Functional linkage)
authors,S. Adindla,L. Guruprasad Sequence analysis corresponding to the PPE and PE proteins in Mycobacterium tuberculosis and other genomes. J. Biosci. 2003 |
| Citation | The Mycobacterium tuberculosis PhoPR two-component system regulates genes essential for virulence and complex lipid biosynthesis. SB. Walters, E. Dubnau et al. Mol. Microbiol. 2006 | sourish10 | IEP | 16573683 | Co-expression (Functional linkage) |
| Interaction | Regulatory Rv0757 | singhpankaj2116 | IEP | | Co-expression (Functional linkage)
ML. Chesne-Seck, N. Barilone et al. A point mutation in the two-component regulator PhoP-PhoR accounts for the absence of polyketide-derived acyltrehaloses but not that of phthiocerol dimycocerosates in Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Ra. J. Bacteriol. 2008 |
| Interaction | Regulatory Rv0757 | singhpankaj2116 | IEP | | Co-expression (Functional linkage)
authors,A. Sola-Landa,RS. Moura,JF. Martn The two-component PhoR-PhoP system controls both primary metabolism and secondary metabolite biosynthesis in Streptomyces lividans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2003 |
| Interaction | Regulatory Rv0757 | singhpankaj2116 | IEP | | Co-expression (Functional linkage)
J. Gonzalo Asensio, C. Maia et al. The virulence-associated two-component PhoP-PhoR system controls the biosynthesis of polyketide-derived lipids in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2006 |
| Interaction | Regulatory Rv0757 | singhpankaj2116 | IEP | | Co-expression (Functional linkage)
J. Gonzalo-Asensio, CY. Soto et al. The Mycobacterium tuberculosis phoPR operon is positively autoregulated in the virulent strain H37Rv. J. Bacteriol. 2008 |
| Interaction | Regulatory Rv0757 | singhpankaj2116 | IEP | | Co-expression (Functional linkage)
A. Sinha, S. Gupta et al. PhoP-PhoP interaction at adjacent PhoP binding sites is influenced by protein phosphorylation. J. Bacteriol. 2008 |
| Interaction | Regulatory Rv0757 | singhpankaj2116 | IEP | | Co-expression (Functional linkage)
J. Gonzalo Asensio, C. Maia et al. The virulence-associated two-component PhoP-PhoR system controls the biosynthesis of polyketide-derived lipids in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2006 |
| Interaction | Regulatory Rv0757 | singhpankaj2116 | IEP | | Co-expression (Functional linkage)
M. Ryndak, S. Wang et al. PhoP, a key player in Mycobacterium tuberculosis virulence. Trends Microbiol. 2008 |
| Interaction | Regulatory Rv0757 | singhpankaj2116 | IEP | | Co-expression (Functional linkage)
JA. Asensio, A. Arbus et al. Live tuberculosis vaccines based on phoP mutants: a step towards clinical trials. Expert opinion on biological therapy 2008 |
| Interaction | Regulatory Rv0757 | singhpankaj2116 | IEP | | Co-expression (Functional linkage)
SB. Walters, E. Dubnau et al. The Mycobacterium tuberculosis PhoPR two-component system regulates genes essential for virulence and complex lipid biosynthesis. Mol. Microbiol. 2006 |
| Interaction | Regulatory Rv0757 | singhpankaj2116 | IEP | | Co-expression (Functional linkage)
J. Gonzalo-Asensio, S. Mostowy et al. PhoP: a missing piece in the intricate puzzle of Mycobacterium tuberculosis virulence. PLoS ONE 2008 |
| Interaction | RegulatedBy Rv0348 | yamir.moreno | IEP | | Microarrays. mRNA levels of regulated element measured and compared between wild-type and trans-element mutation (knockout, over expression etc.) performed by using microarray (or macroarray) experiments..
B. Abomoelak, EA. Hoye et al. mosR, a novel transcriptional regulator of hypoxia and virulence in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J. Bacteriol. 2009 |
| Interaction | RegulatedBy Rv0757 | yamir.moreno | IEP | | Microarrays. mRNA levels of regulated element measured and compared between wild-type and trans-element mutation (knockout, over expression etc.) performed by using microarray (or macroarray) experiments..
J. Gonzalo Asensio, C. Maia et al. The virulence-associated two-component PhoP-PhoR system controls the biosynthesis of polyketide-derived lipids in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2006 |
| Interaction | RegulatedBy Rv0757 | yamir.moreno | IEP | | Microarrays. mRNA levels of regulated element measured and compared between wild-type and trans-element mutation (knockout, over expression etc.) performed by using microarray (or macroarray) experiments..
SB. Walters, E. Dubnau et al. The Mycobacterium tuberculosis PhoPR two-component system regulates genes essential for virulence and complex lipid biosynthesis. Mol. Microbiol. 2006 |
| Interaction | RegulatedBy Rv1221 | yamir.moreno | IEP | | Microarrays. mRNA levels of regulated element measured and compared between wild-type and trans-element mutation (knockout, over expression etc.) performed by using microarray (or macroarray) experiments..
R. Manganelli, MI. Voskuil et al. The Mycobacterium tuberculosis ECF sigma factor sigmaE: role in global gene expression and survival in macrophages. Mol. Microbiol. 2001 |
| Symbol | chp1 | mjackson | IMP | | Polymethyl-branched acyltrehaloses |
| Name | Membrane-associated acyltransferase responsible for the synthesis of the tri- and tetra-acylated forms of sulfolipids | mjackson | IMP | | Polymethyl-branched acyltrehaloses |
| Symbol | chp1 | mjackson | IDA | | Polymethyl-branched acyltrehaloses |
| Name | Membrane-associated acyltransferase responsible for the synthesis of the tri- and tetra-acylated forms of sulfolipids | mjackson | IDA | | Polymethyl-branched acyltrehaloses |
| Other | TBPWY:Polymethyl-branched acyltrehaloses | mjackson | | | Membrane-associated acyltransferase responsible for the synthesis of the tri- and tetra-acylated forms of sulfolipids (phenotypic [mycobacterial recombinant strains]; enzymatic)
authors,JC. Seeliger,CM. Holsclaw,MW. Schelle,Z. Botyanszki,SA. Gilmore,SE. Tully,M. Niederweis,BF. Cravatt,JA. Leary,CR. Bertozzi Elucidation and Chemical Modulation of Sulfolipid-1 Biosynthesis in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. The Journal of biological chemistry 2011 |
| Symbol | chp1 | mjackson | | | Membrane-associated acyltransferase responsible for the synthesis of the tri- and tetra-acylated forms of sulfolipids (phenotypic [mycobacterial recombinant strains]; enzymatic)
authors,JC. Seeliger,CM. Holsclaw,MW. Schelle,Z. Botyanszki,SA. Gilmore,SE. Tully,M. Niederweis,BF. Cravatt,JA. Leary,CR. Bertozzi Elucidation and Chemical Modulation of Sulfolipid-1 Biosynthesis in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. The Journal of biological chemistry 2011 |
| Citation | Elucidation and Chemical Modulation of Sulfolipid-1 Biosynthesis in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. authors,JC. Seeliger,CM. Holsclaw,MW. Schelle,Z. Botyanszki,SA. Gilmore,SE. Tully,M. Niederweis,BF. Cravatt,JA. Leary,CR. Bertozzi The Journal of biological chemistry 2011 | mjackson | | 22194604 | Membrane-associated acyltransferase responsible for the synthesis of the tri- and tetra-acylated forms of sulfolipids (phenotypic [mycobacterial recombinant strains]; enzymatic) |