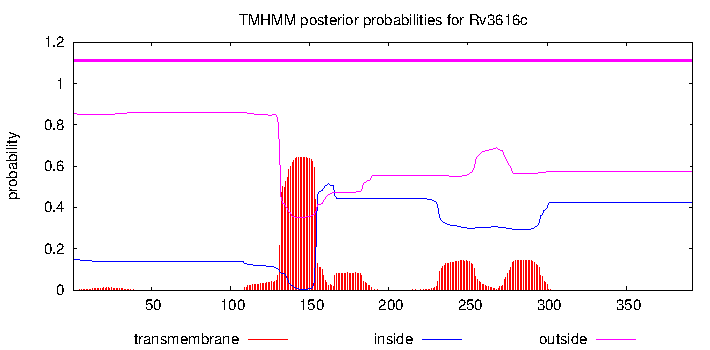
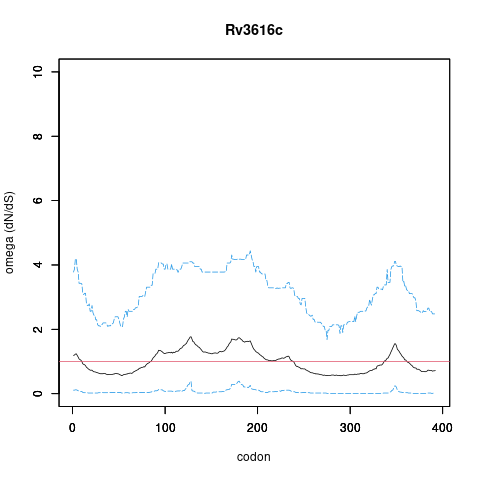
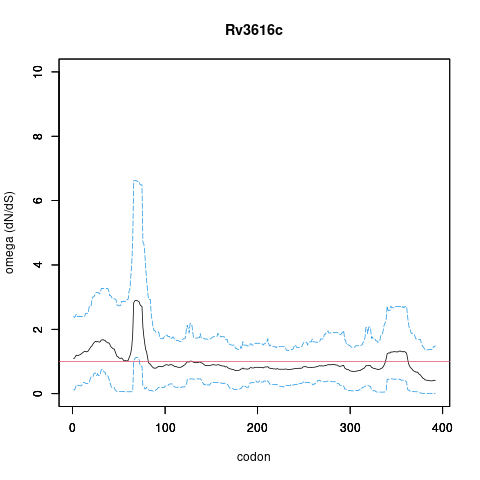
| Property | Value | Creator | Evidence | PMID | Comment |
| Interaction | Transcription Rv3849 | shahanup86 | IEP | | Co-expression (Functional linkage)
S. Raghavan, P. Manzanillo et al. Secreted transcription factor controls Mycobacterium tuberculosis virulence. Nature 2008 |
| Interaction | Transcription Rv3849 | shahanup86 | IEP | | Co-expression (Functional linkage)
authors,R. Simeone,D. Bottai,R. Brosch ESX/type VII secretion systems and their role in host-pathogen interaction. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2009 |
| Interaction | PhysicalInteraction Rv3614c | darhngu | IMP | | Co-expression (Functional Linkage)
authors,SM. Fortune,A. Jaeger,DA. Sarracino,MR. Chase,CM. Sassetti,DR. Sherman,BR. Bloom,EJ. Rubin Mutually dependent secretion of proteins required for mycobacterial virulence. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2005 |
| Interaction | PhysicalInteraction Rv3849 | darhngu | IMP | | Co-expression (Functional Linkage)
authors,SM. Fortune,A. Jaeger,DA. Sarracino,MR. Chase,CM. Sassetti,DR. Sherman,BR. Bloom,EJ. Rubin Mutually dependent secretion of proteins required for mycobacterial virulence. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2005 |
| Citation | Secreted transcription factor controls Mycobacterium tuberculosis virulence. S. Raghavan, P. Manzanillo et al. Nature 2008 | darhngu | IMP | 18685700 | Co-expression (Functional Linkage) |
| Interaction | PhysicalInteraction Rv3615c | darhngu | IMP | | Co-expression (Functional Linkage)
S. Raghavan, P. Manzanillo et al. Secreted transcription factor controls Mycobacterium tuberculosis virulence. Nature 2008 |
| Interaction | PhysicalInteraction Rv3614c | darhngu | IMP | | Co-expression (Functional Linkage)
S. Raghavan, P. Manzanillo et al. Secreted transcription factor controls Mycobacterium tuberculosis virulence. Nature 2008 |
| Interaction | PhysicalInteraction Rv3849 | darhngu | IMP | | Co-expression (Functional Linkage)
S. Raghavan, P. Manzanillo et al. Secreted transcription factor controls Mycobacterium tuberculosis virulence. Nature 2008 |
| Interaction | PhysicalInteraction Rv3615c | darhngu | IMP | | Co-expression (Functional Linkage)
B. Sidders, C. Pirson et al. Screening of highly expressed mycobacterial genes identifies Rv3615c as a useful differential diagnostic antigen for the Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex. Infect. Immun. 2008 |
| Interaction | PhysicalInteraction Rv3615c | darhngu | IMP | | Co-expression (Functional Linkage)
authors,SM. Fortune,A. Jaeger,DA. Sarracino,MR. Chase,CM. Sassetti,DR. Sherman,BR. Bloom,EJ. Rubin Mutually dependent secretion of proteins required for mycobacterial virulence. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2005 |
| Citation | Mutually dependent secretion of proteins required for mycobacterial virulence. authors,SM. Fortune,A. Jaeger,DA. Sarracino,MR. Chase,CM. Sassetti,DR. Sherman,BR. Bloom,EJ. Rubin Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2005 | darhngu | IMP | 16030141 | Co-expression (Functional Linkage) |
| Interaction | PhysicalInteraction Rv3615c | darhngu | IMP | | Co-expression (Functional Linkage)
authors,SM. Fortune,A. Jaeger,DA. Sarracino,MR. Chase,CM. Sassetti,DR. Sherman,BR. Bloom,EJ. Rubin Mutually dependent secretion of proteins required for mycobacterial virulence. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2005 |
| Interaction | PhysicalInteraction Rv3614c | darhngu | IMP | | Co-expression (Functional Linkage)
authors,SM. Fortune,A. Jaeger,DA. Sarracino,MR. Chase,CM. Sassetti,DR. Sherman,BR. Bloom,EJ. Rubin Mutually dependent secretion of proteins required for mycobacterial virulence. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2005 |
| Interaction | PhysicalInteraction Rv3614c | darhngu | IMP | | Co-expression (Functional Linkage)
S. Raghavan, P. Manzanillo et al. Secreted transcription factor controls Mycobacterium tuberculosis virulence. Nature 2008 |
| Interaction | RegulatedBy Rv3911 | yamir.moreno | IEP | | Microarrays. mRNA levels of regulated element measured and compared between wild-type and trans-element mutation (knockout, over expression etc.) performed by using microarray (or macroarray) experiments..
S. Raman, X. Puyang et al. Mycobacterium tuberculosis SigM positively regulates Esx secreted protein and nonribosomal peptide synthetase genes and down regulates virulence-associated surface lipid synthesis. J. Bacteriol. 2006 |
| Interaction | RegulatedBy Rv0757 | yamir.moreno | IEP | | Microarrays. mRNA levels of regulated element measured and compared between wild-type and trans-element mutation (knockout, over expression etc.) performed by using microarray (or macroarray) experiments..
SB. Walters, E. Dubnau et al. The Mycobacterium tuberculosis PhoPR two-component system regulates genes essential for virulence and complex lipid biosynthesis. Mol. Microbiol. 2006 |
| Interaction | RegulatedBy Rv1221 | yamir.moreno | IEP | | Microarrays. mRNA levels of regulated element measured and compared between wild-type and trans-element mutation (knockout, over expression etc.) performed by using microarray (or macroarray) experiments..
R. Manganelli, MI. Voskuil et al. The Mycobacterium tuberculosis ECF sigma factor sigmaE: role in global gene expression and survival in macrophages. Mol. Microbiol. 2001 |
| Interaction | RegulatedBy Rv3849 | yamir.moreno | IDA | | Microarrays. mRNA levels of regulated element measured and compared between wild-type and trans-element mutation (knockout, over expression etc.) performed by using microarray (or macroarray) experiments.. qRT-PCR. mRNA expression levels of regulated element measured and compared between wild-type and trans-element mutation (knockout, over expression etc.) performed by using qRT-PCR technique. Electrophoretic mobility shift assays EMSA. Physical binding of the regulator to the regulated promoter proved by using electrophoretic mobility shift assay. .
S. Raghavan, P. Manzanillo et al. Secreted transcription factor controls Mycobacterium tuberculosis virulence. Nature 2008 |
| Interaction | RegulatedBy Rv3849 | yamir.moreno | IEP | | Microarrays. mRNA levels of regulated element measured and compared between wild-type and trans-element mutation (knockout, over expression etc.) performed by using microarray (or macroarray) experiments.. qRT-PCR. mRNA expression levels of regulated element measured and compared between wild-type and trans-element mutation (knockout, over expression etc.) performed by using qRT-PCR technique. Electrophoretic mobility shift assays EMSA. Physical binding of the regulator to the regulated promoter proved by using electrophoretic mobility shift assay. .
S. Raghavan, P. Manzanillo et al. Secreted transcription factor controls Mycobacterium tuberculosis virulence. Nature 2008 |
| Interaction | RegulatedBy Rv3849 | yamir.moreno | IEP | | Microarrays. mRNA levels of regulated element measured and compared between wild-type and trans-element mutation (knockout, over expression etc.) performed by using microarray (or macroarray) experiments.. qRT-PCR. mRNA expression levels of regulated element measured and compared between wild-type and trans-element mutation (knockout, over expression etc.) performed by using qRT-PCR technique. Electrophoretic mobility shift assays EMSA. Physical binding of the regulator to the regulated promoter proved by using electrophoretic mobility shift assay. .
S. Raghavan, P. Manzanillo et al. Secreted transcription factor controls Mycobacterium tuberculosis virulence. Nature 2008 |