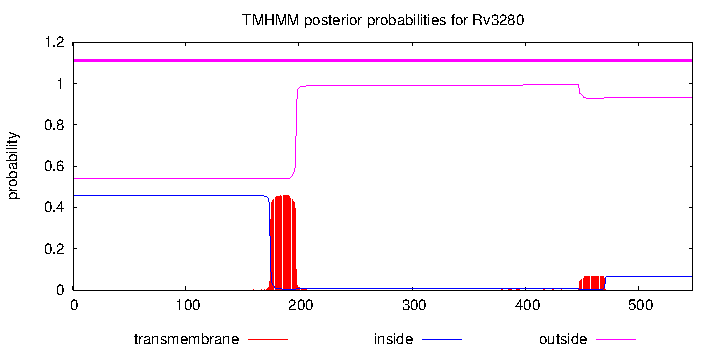
| Property | Value | Creator | Evidence | PMID | Comment |
| Citation | Biochemical and structural characterization of an essential acyl coenzyme A carboxylase from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. G. Gago, D. Kurth et al. J. Bacteriol. 2006 | njamshidi | IDA | 16385038 | PMID: 16385038 AccE5 neede for max catalytic activity |
| Term | EC:6.4.1.2 Acetyl-CoA carboxylase. - IDA | njamshidi | IDA | 16385038 | PMID: 16385038 AccE5 neede for max catalytic activity
G. Gago, D. Kurth et al. Biochemical and structural characterization of an essential acyl coenzyme A carboxylase from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J. Bacteriol. 2006 |
| Term | TBRXN:ACCOACr acetyl-CoA carboxylase, reversible reaction - IDA | njamshidi | IDA | 16385038 | PMID: 16385038 AccE5 neede for max catalytic activity
G. Gago, D. Kurth et al. Biochemical and structural characterization of an essential acyl coenzyme A carboxylase from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J. Bacteriol. 2006 |
| Citation | Biochemical and structural characterization of an essential acyl coenzyme A carboxylase from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. G. Gago, D. Kurth et al. J. Bacteriol. 2006 | njamshidi | ISS | 16385038 | PMID: 16385038 AccE5 neede for max catalytic activity |
| Term | EC:6.4.1.2 Acetyl-CoA carboxylase. - ISS | njamshidi | ISS | 16385038 | PMID: 16385038 AccE5 neede for max catalytic activity
G. Gago, D. Kurth et al. Biochemical and structural characterization of an essential acyl coenzyme A carboxylase from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J. Bacteriol. 2006 |
| Term | TBRXN:ACCOACr acetyl-CoA carboxylase, reversible reaction - ISS | njamshidi | ISS | 16385038 | PMID: 16385038 AccE5 neede for max catalytic activity
G. Gago, D. Kurth et al. Biochemical and structural characterization of an essential acyl coenzyme A carboxylase from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J. Bacteriol. 2006 |
| Citation | Biochemical and structural characterization of an essential acyl coenzyme A carboxylase from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. G. Gago, D. Kurth et al. J. Bacteriol. 2006 | njamshidi | IDA | 16385038 | PMID: 16385038 AccE5 neede for max catalytic activity |
| Term | EC:6.4.1.2 Acetyl-CoA carboxylase. - IDA | njamshidi | IDA | 16385038 | PMID: 16385038 AccE5 neede for max catalytic activity
G. Gago, D. Kurth et al. Biochemical and structural characterization of an essential acyl coenzyme A carboxylase from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J. Bacteriol. 2006 |
| Term | TBRXN:ACCOACr acetyl-CoA carboxylase, reversible reaction - IDA | njamshidi | IDA | 16385038 | PMID: 16385038 AccE5 neede for max catalytic activity
G. Gago, D. Kurth et al. Biochemical and structural characterization of an essential acyl coenzyme A carboxylase from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J. Bacteriol. 2006 |
| Citation | Biochemical and structural characterization of an essential acyl coenzyme A carboxylase from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. G. Gago, D. Kurth et al. J. Bacteriol. 2006 | njamshidi | ISS | 16385038 | PMID: 16385038 AccE5 neede for max catalytic activity |
| Term | EC:6.4.1.2 Acetyl-CoA carboxylase. - ISS | njamshidi | ISS | 16385038 | PMID: 16385038 AccE5 neede for max catalytic activity
G. Gago, D. Kurth et al. Biochemical and structural characterization of an essential acyl coenzyme A carboxylase from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J. Bacteriol. 2006 |
| Term | TBRXN:ACCOACr acetyl-CoA carboxylase, reversible reaction - ISS | njamshidi | ISS | 16385038 | PMID: 16385038 AccE5 neede for max catalytic activity
G. Gago, D. Kurth et al. Biochemical and structural characterization of an essential acyl coenzyme A carboxylase from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J. Bacteriol. 2006 |
| Interaction | PhysicalInteraction Rv3801c | sourish10 | TAS | | Affinity purification (Physical interaction)
SK. Parker, RM. Barkley et al. Mycobacterium tuberculosis Rv3802c encodes a phospholipase/thioesterase and is inhibited by the antimycobacterial agent tetrahydrolipstatin. PLoS ONE 2009 |
| Interaction | PhysicalInteraction Rv3281 | priti.priety | IDA | | Spectrophotometric
G. Gago, D. Kurth et al. Biochemical and structural characterization of an essential acyl coenzyme A carboxylase from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J. Bacteriol. 2006 |
| Interaction | PhysicalInteraction Rv3281 | priti.priety | IDA | | Spectrophotometric
TW. Lin, MM. Melgar et al. Structure-based inhibitor design of AccD5, an essential acyl-CoA carboxylase carboxyltransferase domain of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2006 |
| Interaction | PhysicalInteraction Rv3281 | priti.priety | IDA | | Structural Analysis
G. Gago, D. Kurth et al. Biochemical and structural characterization of an essential acyl coenzyme A carboxylase from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J. Bacteriol. 2006 |
| Interaction | PhysicalInteraction Rv3281 | priti.priety | IDA | | Structural Analysis
TW. Lin, MM. Melgar et al. Structure-based inhibitor design of AccD5, an essential acyl-CoA carboxylase carboxyltransferase domain of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2006 |
| Interaction | RegulatedBy Rv1221 | yamir.moreno | IEP | | Microarrays. mRNA levels of regulated element measured and compared between wild-type and trans-element mutation (knockout, over expression etc.) performed by using microarray (or macroarray) experiments..
R. Manganelli, MI. Voskuil et al. The Mycobacterium tuberculosis ECF sigma factor sigmaE: role in global gene expression and survival in macrophages. Mol. Microbiol. 2001 |
| Name | Biotin-dependent propionyl-CoA carboxylase beta-5 subunit involved in the synthesis of methyl-malonyl-CoA required for the biosynthesis of multiple methyl-branched fatty acids; the enzyme complex made of AccA3-AccD5-AccE5 shows a clear substrate preference for propionyl-CoA compared with acetyl-CoA (used in the generation of malonyl-CoA) | mjackson | IDA | | Claisen-type condensation |
| Citation | Identification and characterization of Rv3281 as a novel subunit of a biotin-dependent acyl-CoA Carboxylase in Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv. TJ. Oh, J. Daniel et al. J. Biol. Chem. 2006 | mjackson | | 16354663 | Biotin-dependent propionyl-CoA carboxylase beta-5 subunit involved in the synthesis of methyl-malonyl-CoA required for the biosynthesis of multiple methyl-branched fatty acids (enzymatic); the enzyme complex made of AccA3-AccD5-AccE5 shows a clear substrate preference for propionyl-CoA compared with acetyl-CoA (used in the generation of malonyl-CoA) |
| Other | TBPWY:Methyl-malonyl-CoA synthesis | mjackson | | | Biotin-dependent propionyl-CoA carboxylase beta-5 subunit involved in the synthesis of methyl-malonyl-CoA required for the biosynthesis of multiple methyl-branched fatty acids (enzymatic); the enzyme complex made of AccA3-AccD5-AccE5 shows a clear substrate preference for propionyl-CoA compared with acetyl-CoA (used in the generation of malonyl-CoA)
TJ. Oh, J. Daniel et al. Identification and characterization of Rv3281 as a novel subunit of a biotin-dependent acyl-CoA Carboxylase in Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv. J. Biol. Chem. 2006 |
| Citation | Biochemical and structural characterization of an essential acyl coenzyme A carboxylase from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. G. Gago, D. Kurth et al. J. Bacteriol. 2006 | mjackson | | 16385038 | Biotin-dependent propionyl-CoA carboxylase beta-5 subunit involved in the synthesis of methyl-malonyl-CoA required for the biosynthesis of multiple methyl-branched fatty acids (enzymatic); the enzyme complex made of AccA3-AccD5-AccE5 shows a clear substrate preference for propionyl-CoA compared with acetyl-CoA (used in the generation of malonyl-CoA) |
| Other | TBPWY:Methyl-malonyl-CoA synthesis | mjackson | | | Biotin-dependent propionyl-CoA carboxylase beta-5 subunit involved in the synthesis of methyl-malonyl-CoA required for the biosynthesis of multiple methyl-branched fatty acids (enzymatic); the enzyme complex made of AccA3-AccD5-AccE5 shows a clear substrate preference for propionyl-CoA compared with acetyl-CoA (used in the generation of malonyl-CoA)
G. Gago, D. Kurth et al. Biochemical and structural characterization of an essential acyl coenzyme A carboxylase from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J. Bacteriol. 2006 |
| Citation | Structure-based inhibitor design of AccD5, an essential acyl-CoA carboxylase carboxyltransferase domain of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. TW. Lin, MM. Melgar et al. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2006 | mjackson | | 16492739 | Biotin-dependent propionyl-CoA carboxylase beta-5 subunit involved in the synthesis of methyl-malonyl-CoA required for the biosynthesis of multiple methyl-branched fatty acids (enzymatic); the enzyme complex made of AccA3-AccD5-AccE5 shows a clear substrate preference for propionyl-CoA compared with acetyl-CoA (used in the generation of malonyl-CoA) |
| Other | TBPWY:Methyl-malonyl-CoA synthesis | mjackson | | | Biotin-dependent propionyl-CoA carboxylase beta-5 subunit involved in the synthesis of methyl-malonyl-CoA required for the biosynthesis of multiple methyl-branched fatty acids (enzymatic); the enzyme complex made of AccA3-AccD5-AccE5 shows a clear substrate preference for propionyl-CoA compared with acetyl-CoA (used in the generation of malonyl-CoA)
TW. Lin, MM. Melgar et al. Structure-based inhibitor design of AccD5, an essential acyl-CoA carboxylase carboxyltransferase domain of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2006 |
| Term | EC:6.4.1.3 Propionyl-CoA carboxylase. - NR | jjmcfadden | NR | | Inferred from direct assay
D. Portevin, C. de Sousa-D'Auria et al. The acyl-AMP ligase FadD32 and AccD4-containing acyl-CoA carboxylase are required for the synthesis of mycolic acids and essential for mycobacterial growth: identification of the carboxylation product and determination of the acyl-CoA carboxylase components. J. Biol. Chem. 2005 |
| Citation | The acyl-AMP ligase FadD32 and AccD4-containing acyl-CoA carboxylase are required for the synthesis of mycolic acids and essential for mycobacterial growth: identification of the carboxylation product and determination of the acyl-CoA carboxylase components. D. Portevin, C. de Sousa-D'Auria et al. J. Biol. Chem. 2005 | jjmcfadden | | 15632194 | Inferred from direct assay |
| Term | EC:4.1.1.41 Methylmalonyl-CoA decarboxylase. - NR | jjmcfadden | NR | | Inferred from direct assay
D. Portevin, C. de Sousa-D'Auria et al. The acyl-AMP ligase FadD32 and AccD4-containing acyl-CoA carboxylase are required for the synthesis of mycolic acids and essential for mycobacterial growth: identification of the carboxylation product and determination of the acyl-CoA carboxylase components. J. Biol. Chem. 2005 |
| Term | EC:6.4.1.4 Methylcrotonoyl-CoA carboxylase. - NR | jjmcfadden | NR | | Inferred from direct assay
D. Portevin, C. de Sousa-D'Auria et al. The acyl-AMP ligase FadD32 and AccD4-containing acyl-CoA carboxylase are required for the synthesis of mycolic acids and essential for mycobacterial growth: identification of the carboxylation product and determination of the acyl-CoA carboxylase components. J. Biol. Chem. 2005 |
| Term | EC:6.4.1.2 Acetyl-CoA carboxylase. - NR | jjmcfadden | NR | | Inferred from direct assay
D. Portevin, C. de Sousa-D'Auria et al. The acyl-AMP ligase FadD32 and AccD4-containing acyl-CoA carboxylase are required for the synthesis of mycolic acids and essential for mycobacterial growth: identification of the carboxylation product and determination of the acyl-CoA carboxylase components. J. Biol. Chem. 2005 |
| Citation | Deciphering the biology of Mycobacterium tuberculosis from the complete genome sequence. authors,ST. Cole,R. Brosch,J. Parkhill,T. Garnier,C. Churcher,D. Harris,SV. Gordon,K. Eiglmeier,S. Gas,CE. Barry,F. Tekaia,K. Badcock,D. Basham,D. Brown,T. Chillingworth,R. Connor,R. Davies,K. Devlin,T. Feltwell,S. Gentles,N. Hamlin,S. Holroyd,T. Hornsby,K. Jagels,A. Krogh,J. McLean,S. Moule,L. Murphy,K. Oliver,J. Osborne,MA. Quail,MA. Rajandream,J. Rogers,S. Rutter,K. Seeger,J. Skelton,R. Squares,S. Squares,JE. Sulston,K. Taylor,S. Whitehead,BG. Barrell Nature 1998 | extern:JZUCKER | | 9634230 | Human inference of function from sequence |
| Term | EC:6.4.1.2 Acetyl-CoA carboxylase. - NR | extern:JZUCKER | NR | | Human inference of function from sequence
authors,ST. Cole,R. Brosch,J. Parkhill,T. Garnier,C. Churcher,D. Harris,SV. Gordon,K. Eiglmeier,S. Gas,CE. Barry,F. Tekaia,K. Badcock,D. Basham,D. Brown,T. Chillingworth,R. Connor,R. Davies,K. Devlin,T. Feltwell,S. Gentles,N. Hamlin,S. Holroyd,T. Hornsby,K. Jagels,A. Krogh,J. McLean,S. Moule,L. Murphy,K. Oliver,J. Osborne,MA. Quail,MA. Rajandream,J. Rogers,S. Rutter,K. Seeger,J. Skelton,R. Squares,S. Squares,JE. Sulston,K. Taylor,S. Whitehead,BG. Barrell Deciphering the biology of Mycobacterium tuberculosis from the complete genome sequence. Nature 1998 |
| Term | EC:6.4.1.3 Propionyl-CoA carboxylase. - NR | extern:JZUCKER | NR | | Human inference of function from sequence
authors,ST. Cole,R. Brosch,J. Parkhill,T. Garnier,C. Churcher,D. Harris,SV. Gordon,K. Eiglmeier,S. Gas,CE. Barry,F. Tekaia,K. Badcock,D. Basham,D. Brown,T. Chillingworth,R. Connor,R. Davies,K. Devlin,T. Feltwell,S. Gentles,N. Hamlin,S. Holroyd,T. Hornsby,K. Jagels,A. Krogh,J. McLean,S. Moule,L. Murphy,K. Oliver,J. Osborne,MA. Quail,MA. Rajandream,J. Rogers,S. Rutter,K. Seeger,J. Skelton,R. Squares,S. Squares,JE. Sulston,K. Taylor,S. Whitehead,BG. Barrell Deciphering the biology of Mycobacterium tuberculosis from the complete genome sequence. Nature 1998 |
| Citation | Central carbon metabolism in Mycobacterium tuberculosis: an unexpected frontier. authors,KY. Rhee,LP. de Carvalho,R. Bryk,S. Ehrt,J. Marrero,SW. Park,D. Schnappinger,A. Venugopal,C. Nathan Trends Microbiol. 2011 | extern:JZUCKER | | 21561773 | Traceable author statement to experimental support |
| Term | EC:6.4.1.2 Acetyl-CoA carboxylase. - NR | extern:JZUCKER | NR | | Traceable author statement to experimental support
authors,KY. Rhee,LP. de Carvalho,R. Bryk,S. Ehrt,J. Marrero,SW. Park,D. Schnappinger,A. Venugopal,C. Nathan Central carbon metabolism in Mycobacterium tuberculosis: an unexpected frontier. Trends Microbiol. 2011 |
| Term | EC:6.4.1.3 Propionyl-CoA carboxylase. - NR | extern:JZUCKER | NR | | Traceable author statement to experimental support
authors,KY. Rhee,LP. de Carvalho,R. Bryk,S. Ehrt,J. Marrero,SW. Park,D. Schnappinger,A. Venugopal,C. Nathan Central carbon metabolism in Mycobacterium tuberculosis: an unexpected frontier. Trends Microbiol. 2011 |
| Citation | Biochemical and structural characterization of an essential acyl coenzyme A carboxylase from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. G. Gago, D. Kurth et al. J. Bacteriol. 2006 | extern:JZUCKER | | 16385038 | Inferred from mutant phenotype |
| Term | EC:6.4.1.2 Acetyl-CoA carboxylase. - NR | extern:JZUCKER | NR | | Inferred from mutant phenotype
G. Gago, D. Kurth et al. Biochemical and structural characterization of an essential acyl coenzyme A carboxylase from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J. Bacteriol. 2006 |
| Term | EC:6.4.1.3 Propionyl-CoA carboxylase. - NR | extern:JZUCKER | NR | | Inferred from mutant phenotype
G. Gago, D. Kurth et al. Biochemical and structural characterization of an essential acyl coenzyme A carboxylase from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J. Bacteriol. 2006 |