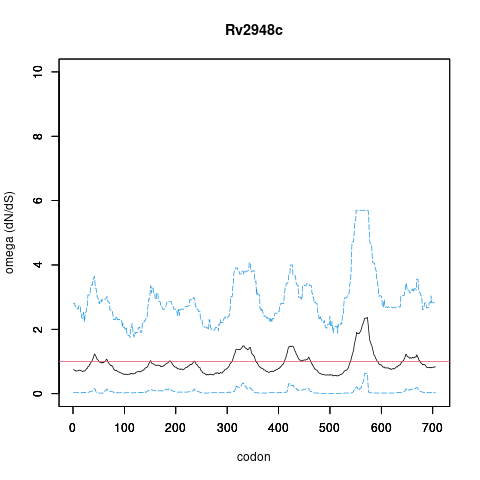
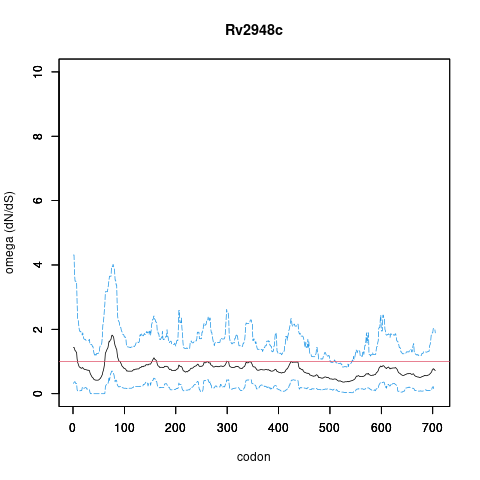
| Property | Value | Creator | Evidence | PMID | Comment |
| Interaction | Operon Rv2950c | ashwinigbhat | IEP | | Co-expression (Functional linkage)
B. Abomoelak, EA. Hoye et al. mosR, a novel transcriptional regulator of hypoxia and virulence in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J. Bacteriol. 2009 |
| Citation | mosR, a novel transcriptional regulator of hypoxia and virulence in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. B. Abomoelak, EA. Hoye et al. J. Bacteriol. 2009 | ashwinigbhat | NAS | 19648248 | Co-expression (Functional linkage) |
| Interaction | Operon Rv2949c | ashwinigbhat | NAS | | Co-expression (Functional linkage)
B. Abomoelak, EA. Hoye et al. mosR, a novel transcriptional regulator of hypoxia and virulence in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J. Bacteriol. 2009 |
| Interaction | Operon Rv2450c | ashwinigbhat | NAS | | Co-expression (Functional linkage)
B. Abomoelak, EA. Hoye et al. mosR, a novel transcriptional regulator of hypoxia and virulence in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J. Bacteriol. 2009 |
| Citation | mosR, a novel transcriptional regulator of hypoxia and virulence in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. B. Abomoelak, EA. Hoye et al. J. Bacteriol. 2009 | ashwinigbhat | IEP | 19648248 | Co-expression (Functional linkage) |
| Interaction | Regulatory Rv0348 | ashwinigbhat | IEP | | Co-expression (Functional linkage)
B. Abomoelak, EA. Hoye et al. mosR, a novel transcriptional regulator of hypoxia and virulence in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J. Bacteriol. 2009 |
| Interaction | RegulatedBy Rv0348 | yamir.moreno | IEP | | Microarrays. mRNA levels of regulated element measured and compared between wild-type and trans-element mutation (knockout, over expression etc.) performed by using microarray (or macroarray) experiments..
B. Abomoelak, EA. Hoye et al. mosR, a novel transcriptional regulator of hypoxia and virulence in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J. Bacteriol. 2009 |
| Name | p-hydroxybenzoyl-AMP ligase involved in the biosynthesis of phenolic glycolipids; catalyzes the activation of p-hydroxybenzoic acid and its subsequent transfer onto Pks15/1 for the production of p-hydroxyphenylalkanoates | mjackson | IMP | | Phthiocerol dimycocerosates (PDIM), phenolic glycolipids (PGL) and para-hydroxybenzoic acid derivatives |
| Name | p-hydroxybenzoyl-AMP ligase involved in the biosynthesis of phenolic glycolipids; catalyzes the activation of p-hydroxybenzoic acid and its subsequent transfer onto Pks15/1 for the production of p-hydroxyphenylalkanoates | mjackson | IDA | | Phthiocerol dimycocerosates (PDIM), phenolic glycolipids (PGL) and para-hydroxybenzoic acid derivatives |
| Citation | Mycobacterial phenolic glycolipid virulence factor biosynthesis: mechanism and small-molecule inhibition of polyketide chain initiation. JA. Ferreras, KL. Stirrett et al. Chem. Biol. 2008 | mjackson | | 18158259 | p-hydroxybenzoyl-AMP ligase involved in the biosynthesis of phenolic glycolipids; catalyzes the activation of p-hydroxybenzoic acid and its subsequent transfer onto Pks15/1 for the production of p-hydroxyphenylalkanoates (phenotypic [mycobacterial recombinant strains]; enzymatic) |
| Other | TBPWY:Phthiocerol dimycocerosates, PGL & pHBAD | mjackson | | | p-hydroxybenzoyl-AMP ligase involved in the biosynthesis of phenolic glycolipids; catalyzes the activation of p-hydroxybenzoic acid and its subsequent transfer onto Pks15/1 for the production of p-hydroxyphenylalkanoates (phenotypic [mycobacterial recombinant strains]; enzymatic)
JA. Ferreras, KL. Stirrett et al. Mycobacterial phenolic glycolipid virulence factor biosynthesis: mechanism and small-molecule inhibition of polyketide chain initiation. Chem. Biol. 2008 |
| Citation | Cooperation between a coenzyme A-independent stand-alone initiation module and an iterative type I polyketide synthase during synthesis of mycobacterial phenolic glycolipids. W. He,CE. Soll,SS. Chavadi,G. Zhang,JD. Warren,LE. Quadri J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009 | mjackson | | 19799378 | p-hydroxybenzoyl-AMP ligase involved in the biosynthesis of phenolic glycolipids; catalyzes the activation of p-hydroxybenzoic acid and its subsequent transfer onto Pks15/1 for the production of p-hydroxyphenylalkanoates (phenotypic [mycobacterial recombinant strains]; enzymatic) |
| Other | TBPWY:Phthiocerol dimycocerosates, PGL & pHBAD | mjackson | | | p-hydroxybenzoyl-AMP ligase involved in the biosynthesis of phenolic glycolipids; catalyzes the activation of p-hydroxybenzoic acid and its subsequent transfer onto Pks15/1 for the production of p-hydroxyphenylalkanoates (phenotypic [mycobacterial recombinant strains]; enzymatic)
W. He,CE. Soll,SS. Chavadi,G. Zhang,JD. Warren,LE. Quadri Cooperation between a coenzyme A-independent stand-alone initiation module and an iterative type I polyketide synthase during synthesis of mycobacterial phenolic glycolipids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009 |
| Citation | Delineation of the roles of FadD22, FadD26 and FadD29 in the biosynthesis of phthiocerol dimycocerosates and related compounds in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. authors,R. Simone,M. Lger,P. Constant,W. Malaga,H. Marrakchi,M. Daff,C. Guilhot,C. Chalut FEBS J. 2010 | mjackson | | 20553505 | p-hydroxybenzoyl-AMP ligase involved in the biosynthesis of phenolic glycolipids; catalyzes the activation of p-hydroxybenzoic acid and its subsequent transfer onto Pks15/1 for the production of p-hydroxyphenylalkanoates (phenotypic [mycobacterial recombinant strains]; enzymatic) |
| Other | TBPWY:Phthiocerol dimycocerosates, PGL & pHBAD | mjackson | | | p-hydroxybenzoyl-AMP ligase involved in the biosynthesis of phenolic glycolipids; catalyzes the activation of p-hydroxybenzoic acid and its subsequent transfer onto Pks15/1 for the production of p-hydroxyphenylalkanoates (phenotypic [mycobacterial recombinant strains]; enzymatic)
authors,R. Simone,M. Lger,P. Constant,W. Malaga,H. Marrakchi,M. Daff,C. Guilhot,C. Chalut Delineation of the roles of FadD22, FadD26 and FadD29 in the biosynthesis of phthiocerol dimycocerosates and related compounds in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. FEBS J. 2010 |