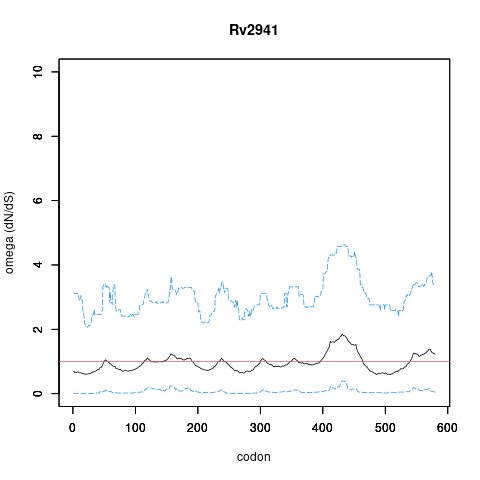
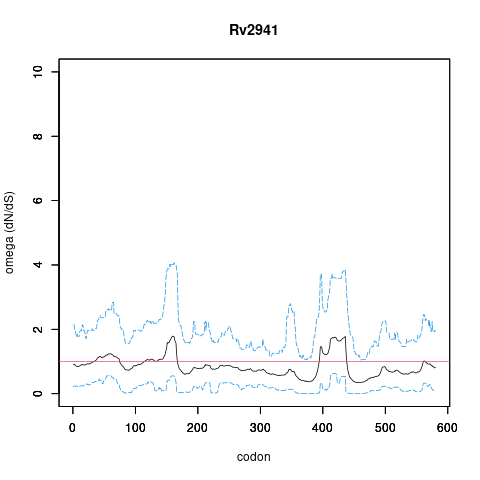
| Property | Value | Creator | Evidence | PMID | Comment |
| Term | TBRXN:PPDIMAS PPDIM synthesis (Mycobacterium Tuberculosis) - IPI | njamshidi | IPI | 12031661 | Actually a fatty acyl co-ligase, however condensation reaction is using free forms of fatty-acids or phthiocerol. see PMID: 12031661 and Cole et al Tuberculosis and the Tubercle Bacillus text, also PMID 15292272. PMID: 12730158 starts to elucidate which genes may be involved, but not yet definitively associated genes with the pathways leading up to pdima synthesis.
E. Prez, P. Constant et al. Characterization of three glycosyltransferases involved in the biosynthesis of the phenolic glycolipid antigens from the Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex. J. Biol. Chem. 2004 |
| Citation | Attenuation of Mycobacterium tuberculosis by disruption of a mas-like gene or a chalcone synthase-like gene, which causes deficiency in dimycocerosyl phthiocerol synthesis. TD. Sirakova, VS. Dubey et al. J. Bacteriol. 2003 | njamshidi | IPI | 12031661|12730158 | Actually a fatty acyl co-ligase, however condensation reaction is using free forms of fatty-acids or phthiocerol. see PMID: 12031661 and Cole et al Tuberculosis and the Tubercle Bacillus text, also PMID 15292272. PMID: 12730158 starts to elucidate which genes may be involved, but not yet definitively associated genes with the pathways leading up to pdima synthesis. |
| Term | TBRXN:PPDIMAS PPDIM synthesis (Mycobacterium Tuberculosis) - IPI | njamshidi | IPI | 12031661 | Actually a fatty acyl co-ligase, however condensation reaction is using free forms of fatty-acids or phthiocerol. see PMID: 12031661 and Cole et al Tuberculosis and the Tubercle Bacillus text, also PMID 15292272. PMID: 12730158 starts to elucidate which genes may be involved, but not yet definitively associated genes with the pathways leading up to pdima synthesis.
TD. Sirakova, VS. Dubey et al. Attenuation of Mycobacterium tuberculosis by disruption of a mas-like gene or a chalcone synthase-like gene, which causes deficiency in dimycocerosyl phthiocerol synthesis. J. Bacteriol. 2003 |
| Term | TBRXN:PPDIMAS PPDIM synthesis (Mycobacterium Tuberculosis) - ISS | njamshidi | ISS | 12031661 | Actually a fatty acyl co-ligase, however condensation reaction is using free forms of fatty-acids or phthiocerol. see PMID: 12031661 and Cole et al Tuberculosis and the Tubercle Bacillus text, also PMID 15292272. PMID: 12730158 starts to elucidate which genes may be involved, but not yet definitively associated genes with the pathways leading up to pdima synthesis.
authors,DE. Minnikin,L. Kremer,LG. Dover,GS. Besra The methyl-branched fortifications of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Chem. Biol. 2002 |
| Citation | Characterization of three glycosyltransferases involved in the biosynthesis of the phenolic glycolipid antigens from the Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex. E. Prez, P. Constant et al. J. Biol. Chem. 2004 | njamshidi | ISS | 12031661|15292272 | Actually a fatty acyl co-ligase, however condensation reaction is using free forms of fatty-acids or phthiocerol. see PMID: 12031661 and Cole et al Tuberculosis and the Tubercle Bacillus text, also PMID 15292272. PMID: 12730158 starts to elucidate which genes may be involved, but not yet definitively associated genes with the pathways leading up to pdima synthesis. |
| Term | TBRXN:PPDIMAS PPDIM synthesis (Mycobacterium Tuberculosis) - ISS | njamshidi | ISS | 12031661 | Actually a fatty acyl co-ligase, however condensation reaction is using free forms of fatty-acids or phthiocerol. see PMID: 12031661 and Cole et al Tuberculosis and the Tubercle Bacillus text, also PMID 15292272. PMID: 12730158 starts to elucidate which genes may be involved, but not yet definitively associated genes with the pathways leading up to pdima synthesis.
E. Prez, P. Constant et al. Characterization of three glycosyltransferases involved in the biosynthesis of the phenolic glycolipid antigens from the Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex. J. Biol. Chem. 2004 |
| Citation | Attenuation of Mycobacterium tuberculosis by disruption of a mas-like gene or a chalcone synthase-like gene, which causes deficiency in dimycocerosyl phthiocerol synthesis. TD. Sirakova, VS. Dubey et al. J. Bacteriol. 2003 | njamshidi | ISS | 12031661|12730158 | Actually a fatty acyl co-ligase, however condensation reaction is using free forms of fatty-acids or phthiocerol. see PMID: 12031661 and Cole et al Tuberculosis and the Tubercle Bacillus text, also PMID 15292272. PMID: 12730158 starts to elucidate which genes may be involved, but not yet definitively associated genes with the pathways leading up to pdima synthesis. |
| Term | TBRXN:PPDIMAS PPDIM synthesis (Mycobacterium Tuberculosis) - ISS | njamshidi | ISS | 12031661 | Actually a fatty acyl co-ligase, however condensation reaction is using free forms of fatty-acids or phthiocerol. see PMID: 12031661 and Cole et al Tuberculosis and the Tubercle Bacillus text, also PMID 15292272. PMID: 12730158 starts to elucidate which genes may be involved, but not yet definitively associated genes with the pathways leading up to pdima synthesis.
TD. Sirakova, VS. Dubey et al. Attenuation of Mycobacterium tuberculosis by disruption of a mas-like gene or a chalcone synthase-like gene, which causes deficiency in dimycocerosyl phthiocerol synthesis. J. Bacteriol. 2003 |
| Citation | The methyl-branched fortifications of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. authors,DE. Minnikin,L. Kremer,LG. Dover,GS. Besra Chem. Biol. 2002 | njamshidi | IPI | 12031661 | Actually a fatty acyl co-ligase, however condensation reaction is using free forms of fatty-acids or phthiocerol. see PMID: 12031661 and Cole et al Tuberculosis and the Tubercle Bacillus text, also PMID 15292272. PMID: 12730158 starts to elucidate which genes may be involved, but not yet definitively associated genes with the pathways leading up to pdima synthesis. |
| Term | TBRXN:PPDIMAS PPDIM synthesis (Mycobacterium Tuberculosis) - IPI | njamshidi | IPI | 12031661 | Actually a fatty acyl co-ligase, however condensation reaction is using free forms of fatty-acids or phthiocerol. see PMID: 12031661 and Cole et al Tuberculosis and the Tubercle Bacillus text, also PMID 15292272. PMID: 12730158 starts to elucidate which genes may be involved, but not yet definitively associated genes with the pathways leading up to pdima synthesis.
authors,DE. Minnikin,L. Kremer,LG. Dover,GS. Besra The methyl-branched fortifications of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Chem. Biol. 2002 |
| Citation | Characterization of three glycosyltransferases involved in the biosynthesis of the phenolic glycolipid antigens from the Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex. E. Prez, P. Constant et al. J. Biol. Chem. 2004 | njamshidi | IPI | 12031661|15292272 | Actually a fatty acyl co-ligase, however condensation reaction is using free forms of fatty-acids or phthiocerol. see PMID: 12031661 and Cole et al Tuberculosis and the Tubercle Bacillus text, also PMID 15292272. PMID: 12730158 starts to elucidate which genes may be involved, but not yet definitively associated genes with the pathways leading up to pdima synthesis. |
| Citation | The methyl-branched fortifications of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. authors,DE. Minnikin,L. Kremer,LG. Dover,GS. Besra Chem. Biol. 2002 | njamshidi | ISS | 12031661 | Actually a fatty acyl co-ligase, however condensation reaction is using free forms of fatty-acids or phthiocerol. see PMID: 12031661 and Cole et al Tuberculosis and the Tubercle Bacillus text, also PMID 15292272. PMID: 12730158 starts to elucidate which genes may be involved, but not yet definitively associated genes with the pathways leading up to pdima synthesis. |
| Citation | The methyl-branched fortifications of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. authors,DE. Minnikin,L. Kremer,LG. Dover,GS. Besra Chem. Biol. 2002 | njamshidi | ISS | 12031661 | Actually a fatty acyl co-ligase, however condensation reaction is using free forms of fatty-acids or phthiocerol. see PMID: 12031661 and Cole et al Tuberculosis and the Tubercle Bacillus text. PMID: 12730158 starts to elucidate which genes may be involved, but not yet definitively associated genes with the pathways leading up to pdima synthesis. |
| Term | TBRXN:PDIMAS PDIM A synthesis (Mycobacterium Tuberculosis) - ISS | njamshidi | ISS | 12031661 | Actually a fatty acyl co-ligase, however condensation reaction is using free forms of fatty-acids or phthiocerol. see PMID: 12031661 and Cole et al Tuberculosis and the Tubercle Bacillus text. PMID: 12730158 starts to elucidate which genes may be involved, but not yet definitively associated genes with the pathways leading up to pdima synthesis.
authors,DE. Minnikin,L. Kremer,LG. Dover,GS. Besra The methyl-branched fortifications of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Chem. Biol. 2002 |
| Citation | Attenuation of Mycobacterium tuberculosis by disruption of a mas-like gene or a chalcone synthase-like gene, which causes deficiency in dimycocerosyl phthiocerol synthesis. TD. Sirakova, VS. Dubey et al. J. Bacteriol. 2003 | njamshidi | ISS | 12031661|12730158 | Actually a fatty acyl co-ligase, however condensation reaction is using free forms of fatty-acids or phthiocerol. see PMID: 12031661 and Cole et al Tuberculosis and the Tubercle Bacillus text. PMID: 12730158 starts to elucidate which genes may be involved, but not yet definitively associated genes with the pathways leading up to pdima synthesis. |
| Term | TBRXN:PDIMAS PDIM A synthesis (Mycobacterium Tuberculosis) - ISS | njamshidi | ISS | 12031661 | Actually a fatty acyl co-ligase, however condensation reaction is using free forms of fatty-acids or phthiocerol. see PMID: 12031661 and Cole et al Tuberculosis and the Tubercle Bacillus text. PMID: 12730158 starts to elucidate which genes may be involved, but not yet definitively associated genes with the pathways leading up to pdima synthesis.
TD. Sirakova, VS. Dubey et al. Attenuation of Mycobacterium tuberculosis by disruption of a mas-like gene or a chalcone synthase-like gene, which causes deficiency in dimycocerosyl phthiocerol synthesis. J. Bacteriol. 2003 |
| Citation | The methyl-branched fortifications of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. authors,DE. Minnikin,L. Kremer,LG. Dover,GS. Besra Chem. Biol. 2002 | njamshidi | IPI | 12031661 | Actually a fatty acyl co-ligase, however condensation reaction is using free forms of fatty-acids or phthiocerol. see PMID: 12031661 and Cole et al Tuberculosis and the Tubercle Bacillus text. PMID: 12730158 starts to elucidate which genes may be involved, but not yet definitively associated genes with the pathways leading up to pdima synthesis. |
| Term | TBRXN:PDIMAS PDIM A synthesis (Mycobacterium Tuberculosis) - IPI | njamshidi | IPI | 12031661 | Actually a fatty acyl co-ligase, however condensation reaction is using free forms of fatty-acids or phthiocerol. see PMID: 12031661 and Cole et al Tuberculosis and the Tubercle Bacillus text. PMID: 12730158 starts to elucidate which genes may be involved, but not yet definitively associated genes with the pathways leading up to pdima synthesis.
authors,DE. Minnikin,L. Kremer,LG. Dover,GS. Besra The methyl-branched fortifications of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Chem. Biol. 2002 |
| Citation | Attenuation of Mycobacterium tuberculosis by disruption of a mas-like gene or a chalcone synthase-like gene, which causes deficiency in dimycocerosyl phthiocerol synthesis. TD. Sirakova, VS. Dubey et al. J. Bacteriol. 2003 | njamshidi | IPI | 12031661|12730158 | Actually a fatty acyl co-ligase, however condensation reaction is using free forms of fatty-acids or phthiocerol. see PMID: 12031661 and Cole et al Tuberculosis and the Tubercle Bacillus text. PMID: 12730158 starts to elucidate which genes may be involved, but not yet definitively associated genes with the pathways leading up to pdima synthesis. |
| Term | TBRXN:PDIMAS PDIM A synthesis (Mycobacterium Tuberculosis) - IPI | njamshidi | IPI | 12031661 | Actually a fatty acyl co-ligase, however condensation reaction is using free forms of fatty-acids or phthiocerol. see PMID: 12031661 and Cole et al Tuberculosis and the Tubercle Bacillus text. PMID: 12730158 starts to elucidate which genes may be involved, but not yet definitively associated genes with the pathways leading up to pdima synthesis.
TD. Sirakova, VS. Dubey et al. Attenuation of Mycobacterium tuberculosis by disruption of a mas-like gene or a chalcone synthase-like gene, which causes deficiency in dimycocerosyl phthiocerol synthesis. J. Bacteriol. 2003 |
| Interaction | PhysicalInteraction Rv2940c | shahanup86 | IMP | | Affinity purification (Physical interaction)
AM. Fitzmaurice & PE. Kolattukudy An acyl-CoA synthase (acoas) gene adjacent to the mycocerosic acid synthase (mas) locus is necessary for mycocerosyl lipid synthesis in Mycobacterium tuberculosis var. bovis BCG. J. Biol. Chem. 1998 |
| Interaction | RegulatedBy Rv1221 | yamir.moreno | IEP | | Microarrays. mRNA levels of regulated element measured and compared between wild-type and trans-element mutation (knockout, over expression etc.) performed by using microarray (or macroarray) experiments..
R. Manganelli, MI. Voskuil et al. The Mycobacterium tuberculosis ECF sigma factor sigmaE: role in global gene expression and survival in macrophages. Mol. Microbiol. 2001 |
| Name | Long chain fatty acyl-AMP ligase responsible for providing the long-chain fatty acid starter unit to Mas for the generation of mycocerosic acids | mjackson | IMP | | Phthiocerol dimycocerosates (PDIM), phenolic glycolipids (PGL) and para-hydroxybenzoic acid derivatives |
| Name | Long chain fatty acyl-AMP ligase responsible for providing the long-chain fatty acid starter unit to Mas for the generation of mycocerosic acids | mjackson | IDA | | Phthiocerol dimycocerosates (PDIM), phenolic glycolipids (PGL) and para-hydroxybenzoic acid derivatives |
| Citation | Open reading frame 3, which is adjacent to the mycocerosic acid synthase gene, is expressed as an acyl coenzyme A synthase in Mycobacterium bovis BCG. authors,AM. Fitzmaurice,PE. Kolattukudy J. Bacteriol. 1997 | mjackson | | 9098059 | Long chain fatty acyl-AMP ligase responsible for providing the long-chain fatty acid starter unit to Mas for the generation of mycocerosic acids (phenotypic [mycobacterial recombinant strains]; enzymatic) |
| Other | TBPWY:Phthiocerol dimycocerosates, PGL & pHBAD | mjackson | | | Long chain fatty acyl-AMP ligase responsible for providing the long-chain fatty acid starter unit to Mas for the generation of mycocerosic acids (phenotypic [mycobacterial recombinant strains]; enzymatic)
authors,AM. Fitzmaurice,PE. Kolattukudy Open reading frame 3, which is adjacent to the mycocerosic acid synthase gene, is expressed as an acyl coenzyme A synthase in Mycobacterium bovis BCG. J. Bacteriol. 1997 |
| Citation | An acyl-CoA synthase (acoas) gene adjacent to the mycocerosic acid synthase (mas) locus is necessary for mycocerosyl lipid synthesis in Mycobacterium tuberculosis var. bovis BCG. AM. Fitzmaurice & PE. Kolattukudy J. Biol. Chem. 1998 | mjackson | | 9525903 | Long chain fatty acyl-AMP ligase responsible for providing the long-chain fatty acid starter unit to Mas for the generation of mycocerosic acids (phenotypic [mycobacterial recombinant strains]; enzymatic) |
| Other | TBPWY:Phthiocerol dimycocerosates, PGL & pHBAD | mjackson | | | Long chain fatty acyl-AMP ligase responsible for providing the long-chain fatty acid starter unit to Mas for the generation of mycocerosic acids (phenotypic [mycobacterial recombinant strains]; enzymatic)
AM. Fitzmaurice & PE. Kolattukudy An acyl-CoA synthase (acoas) gene adjacent to the mycocerosic acid synthase (mas) locus is necessary for mycocerosyl lipid synthesis in Mycobacterium tuberculosis var. bovis BCG. J. Biol. Chem. 1998 |
| Citation | Complex lipid determines tissue-specific replication of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in mice. authors,JS. Cox,B. Chen,M. McNeil,WR. Jacobs Nature 1999 | mjackson | | 10573420 | Long chain fatty acyl-AMP ligase responsible for providing the long-chain fatty acid starter unit to Mas for the generation of mycocerosic acids (phenotypic [mycobacterial recombinant strains]; enzymatic) |
| Other | TBPWY:Phthiocerol dimycocerosates, PGL & pHBAD | mjackson | | | Long chain fatty acyl-AMP ligase responsible for providing the long-chain fatty acid starter unit to Mas for the generation of mycocerosic acids (phenotypic [mycobacterial recombinant strains]; enzymatic)
authors,JS. Cox,B. Chen,M. McNeil,WR. Jacobs Complex lipid determines tissue-specific replication of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in mice. Nature 1999 |
| Citation | Analysis of the phthiocerol dimycocerosate locus of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Evidence that this lipid is involved in the cell wall permeability barrier. LR. Camacho, P. Constant et al. J. Biol. Chem. 2001 | mjackson | | 11279114 | Long chain fatty acyl-AMP ligase responsible for providing the long-chain fatty acid starter unit to Mas for the generation of mycocerosic acids (phenotypic [mycobacterial recombinant strains]; enzymatic) |
| Other | TBPWY:Phthiocerol dimycocerosates, PGL & pHBAD | mjackson | | | Long chain fatty acyl-AMP ligase responsible for providing the long-chain fatty acid starter unit to Mas for the generation of mycocerosic acids (phenotypic [mycobacterial recombinant strains]; enzymatic)
LR. Camacho, P. Constant et al. Analysis of the phthiocerol dimycocerosate locus of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Evidence that this lipid is involved in the cell wall permeability barrier. J. Biol. Chem. 2001 |
| Citation | Enzymic activation and transfer of fatty acids as acyl-adenylates in mycobacteria. OA. Trivedi,P. Arora,V. Sridharan,R. Tickoo,D. Mohanty,RS. Gokhale Nature 2004 | mjackson | | 15042094 | Long chain fatty acyl-AMP ligase responsible for providing the long-chain fatty acid starter unit to Mas for the generation of mycocerosic acids (phenotypic [mycobacterial recombinant strains]; enzymatic) |
| Other | TBPWY:Phthiocerol dimycocerosates, PGL & pHBAD | mjackson | | | Long chain fatty acyl-AMP ligase responsible for providing the long-chain fatty acid starter unit to Mas for the generation of mycocerosic acids (phenotypic [mycobacterial recombinant strains]; enzymatic)
OA. Trivedi,P. Arora,V. Sridharan,R. Tickoo,D. Mohanty,RS. Gokhale Enzymic activation and transfer of fatty acids as acyl-adenylates in mycobacteria. Nature 2004 |
| Citation | Role of the pks15/1 gene in the biosynthesis of phenolglycolipids in the Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex. Evidence that all strains synthesize glycosylated p-hydroxybenzoic methyl esters and that strains devoid of phenolglycolipids harbor a frameshift mutation in the pks15/1 gene. P. Constant, E. Perez et al. J. Biol. Chem. 2002 | jjmcfadden | | 12138124 | Inferred from direct assay |
| Term | EC:6.2.1.- Ligases. Forming carbon-sulfur bonds. Acid--thiol ligases. - NR | jjmcfadden | NR | | Inferred from direct assay
P. Constant, E. Perez et al. Role of the pks15/1 gene in the biosynthesis of phenolglycolipids in the Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex. Evidence that all strains synthesize glycosylated p-hydroxybenzoic methyl esters and that strains devoid of phenolglycolipids harbor a frameshift mutation in the pks15/1 gene. J. Biol. Chem. 2002 |
| Term | EC:6.2.1.3 Long-chain-fatty-acid--CoA ligase. - NR | jjmcfadden | NR | | Inferred from direct assay
P. Constant, E. Perez et al. Role of the pks15/1 gene in the biosynthesis of phenolglycolipids in the Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex. Evidence that all strains synthesize glycosylated p-hydroxybenzoic methyl esters and that strains devoid of phenolglycolipids harbor a frameshift mutation in the pks15/1 gene. J. Biol. Chem. 2002 |