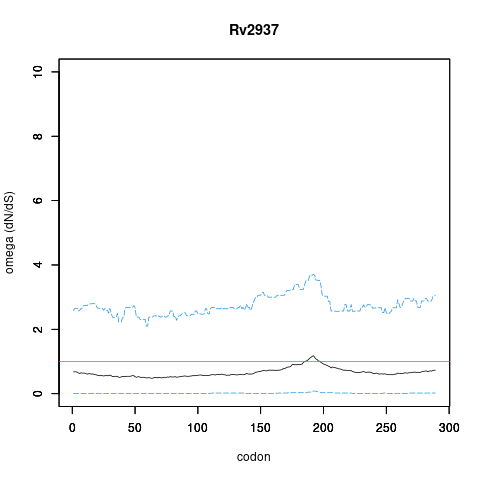
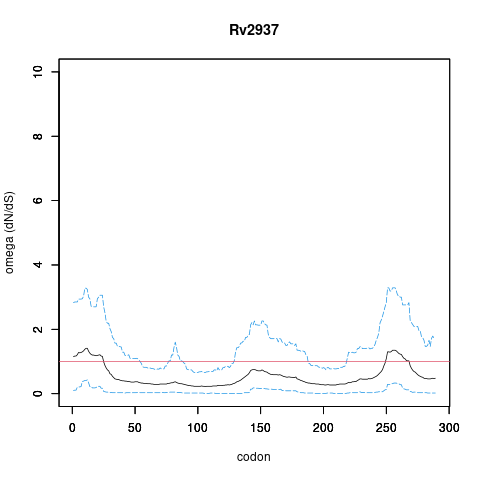
| Property | Value | Creator | Evidence | PMID | Comment |
| Interaction | PhysicalInteraction Rv2939 | shahanup86 | TAS | | Operon (Functional linkage)
authors,JS. Cox,B. Chen,M. McNeil,WR. Jacobs Complex lipid determines tissue-specific replication of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in mice. Nature 1999 |
| Interaction | PhysicalInteraction Rv2939 | shahanup86 | TAS | | Operon (Functional linkage)
LR. Camacho, P. Constant et al. Analysis of the phthiocerol dimycocerosate locus of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Evidence that this lipid is involved in the cell wall permeability barrier. J. Biol. Chem. 2001 |
| Interaction | Operon Rv2938 | razeeth.new | IMP | | two-hybrid (Physical interaction)
authors,LR. Camacho,D. Ensergueix,E. Perez,B. Gicquel,C. Guilhot Identification of a virulence gene cluster of Mycobacterium tuberculosis by signature-tagged transposon mutagenesis. Mol. Microbiol. 1999 |
| Interaction | Operon Rv2938 | razeeth.new | IMP | | two-hybrid (Physical interaction)
authors,R. Goude,T. Parish The genetics of cell wall biosynthesis in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Future Microbiol 2008 |
| Interaction | PhysicalInteraction Rv2935 | shahanup86 | TAS | | Operon (Functional linkage)
authors,JS. Cox,B. Chen,M. McNeil,WR. Jacobs Complex lipid determines tissue-specific replication of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in mice. Nature 1999 |
| Interaction | Operon Rv2936 | shahanup86 | IEP | | Co-expression
BS. Choudhuri, S. Bhakta et al. Overexpression and functional characterization of an ABC (ATP-binding cassette) transporter encoded by the genes drrA and drrB of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Biochem. J. 2002 |
| Citation | Overexpression and functional characterization of an ABC (ATP-binding cassette) transporter encoded by the genes drrA and drrB of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. BS. Choudhuri, S. Bhakta et al. Biochem. J. 2002 | shahanup86 | IEP | 12057006 | Co-expression |
| Interaction | Operon Rv2936 | shahanup86 | IEP | | Co-expression
BS. Choudhuri, S. Bhakta et al. Overexpression and functional characterization of an ABC (ATP-binding cassette) transporter encoded by the genes drrA and drrB of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Biochem. J. 2002 |
| Interaction | PhysicalInteraction Rv2935 | shahanup86 | TAS | | Operon (Functional linkage)
LR. Camacho, P. Constant et al. Analysis of the phthiocerol dimycocerosate locus of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Evidence that this lipid is involved in the cell wall permeability barrier. J. Biol. Chem. 2001 |
| Interaction | PhysicalInteraction Rv2934 | shahanup86 | TAS | | Operon (Functional linkage)
authors,JS. Cox,B. Chen,M. McNeil,WR. Jacobs Complex lipid determines tissue-specific replication of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in mice. Nature 1999 |
| Interaction | PhysicalInteraction Rv2934 | shahanup86 | TAS | | Operon (Functional linkage)
LR. Camacho, P. Constant et al. Analysis of the phthiocerol dimycocerosate locus of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Evidence that this lipid is involved in the cell wall permeability barrier. J. Biol. Chem. 2001 |
| Interaction | PhysicalInteraction Rv2933 | shahanup86 | TAS | | Operon (Functional linkage)
authors,JS. Cox,B. Chen,M. McNeil,WR. Jacobs Complex lipid determines tissue-specific replication of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in mice. Nature 1999 |
| Interaction | PhysicalInteraction Rv2933 | shahanup86 | TAS | | Operon (Functional linkage)
LR. Camacho, P. Constant et al. Analysis of the phthiocerol dimycocerosate locus of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Evidence that this lipid is involved in the cell wall permeability barrier. J. Biol. Chem. 2001 |
| Interaction | PhysicalInteraction Rv2932 | shahanup86 | TAS | | Operon (Functional linkage)
authors,JS. Cox,B. Chen,M. McNeil,WR. Jacobs Complex lipid determines tissue-specific replication of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in mice. Nature 1999 |
| Interaction | PhysicalInteraction Rv2932 | shahanup86 | TAS | | Operon (Functional linkage)
LR. Camacho, P. Constant et al. Analysis of the phthiocerol dimycocerosate locus of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Evidence that this lipid is involved in the cell wall permeability barrier. J. Biol. Chem. 2001 |
| Interaction | PhysicalInteraction Rv2931 | shahanup86 | TAS | | Operon (Functional linkage)
authors,JS. Cox,B. Chen,M. McNeil,WR. Jacobs Complex lipid determines tissue-specific replication of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in mice. Nature 1999 |
| Interaction | PhysicalInteraction Rv2931 | shahanup86 | TAS | | Operon (Functional linkage)
LR. Camacho, P. Constant et al. Analysis of the phthiocerol dimycocerosate locus of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Evidence that this lipid is involved in the cell wall permeability barrier. J. Biol. Chem. 2001 |
| Interaction | PhysicalInteraction Rv2930 | shahanup86 | TAS | | Operon (Functional linkage)
authors,JS. Cox,B. Chen,M. McNeil,WR. Jacobs Complex lipid determines tissue-specific replication of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in mice. Nature 1999 |
| Interaction | PhysicalInteraction Rv2930 | shahanup86 | TAS | | Operon (Functional linkage)
LR. Camacho, P. Constant et al. Analysis of the phthiocerol dimycocerosate locus of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Evidence that this lipid is involved in the cell wall permeability barrier. J. Biol. Chem. 2001 |
| Interaction | RegulatedBy Rv3692 | yamir.moreno | IDA | | One hybrid reporter system. Physical binding of the regulator to the regulated promoter proved by using electrophoretic mobility shift assay. .
M. Guo, H. Feng et al. Dissecting transcription regulatory pathways through a new bacterial one-hybrid reporter system. Genome Res. 2009 |
| Interaction | RegulatedBy Rv3416 | yamir.moreno | IDA | | One hybrid reporter system. Physical binding of the regulator to the regulated promoter proved by using electrophoretic mobility shift assay. .
M. Guo, H. Feng et al. Dissecting transcription regulatory pathways through a new bacterial one-hybrid reporter system. Genome Res. 2009 |
| Interaction | RegulatedBy Rv2745c | yamir.moreno | IDA | | One hybrid reporter system. Physical binding of the regulator to the regulated promoter proved by using electrophoretic mobility shift assay. .
M. Guo, H. Feng et al. Dissecting transcription regulatory pathways through a new bacterial one-hybrid reporter system. Genome Res. 2009 |
| Interaction | RegulatedBy Rv1956 | yamir.moreno | IDA | | One hybrid reporter system. Physical binding of the regulator to the regulated promoter proved by using electrophoretic mobility shift assay. .
M. Guo, H. Feng et al. Dissecting transcription regulatory pathways through a new bacterial one-hybrid reporter system. Genome Res. 2009 |
| Interaction | RegulatedBy Rv1359 | yamir.moreno | IDA | | One hybrid reporter system. Physical binding of the regulator to the regulated promoter proved by using electrophoretic mobility shift assay. .
M. Guo, H. Feng et al. Dissecting transcription regulatory pathways through a new bacterial one-hybrid reporter system. Genome Res. 2009 |
| Interaction | RegulatedBy Rv0445c | yamir.moreno | IDA | | One hybrid reporter system. Physical binding of the regulator to the regulated promoter proved by using electrophoretic mobility shift assay. .
M. Guo, H. Feng et al. Dissecting transcription regulatory pathways through a new bacterial one-hybrid reporter system. Genome Res. 2009 |
| Interaction | RegulatedBy Rv0117 | yamir.moreno | IDA | | One hybrid reporter system. Physical binding of the regulator to the regulated promoter proved by using electrophoretic mobility shift assay. .
M. Guo, H. Feng et al. Dissecting transcription regulatory pathways through a new bacterial one-hybrid reporter system. Genome Res. 2009 |
| Interaction | RegulatedBy Rv0981 | yamir.moreno | IEP | | Microarrays. mRNA levels of regulated element measured and compared between wild-type and trans-element mutation (knockout, over expression etc.) performed by using microarray (or macroarray) experiments..
H. He, R. Hovey et al. MprAB is a stress-responsive two-component system that directly regulates expression of sigma factors SigB and SigE in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J. Bacteriol. 2006 |
| Name | Component of the DrrABC ABC-transporter involved in the translocation of phthiocerol dimycocerosates across the plasma membrane and in drug-resistance; integral membrane protein | mjackson | IMP | | Phthiocerol dimycocerosates (PDIM), phenolic glycolipids (PGL) and para-hydroxybenzoic acid derivatives |
| Other | TBPWY:Phthiocerol dimycocerosates, PGL & pHBAD | mjackson | | | Component of the DrrABC ABC-transporter involved in the translocation of phthiocerol dimycocerosates across the plasma membrane and in drug-resistance; integral membrane protein (phenotypic [mycobacterial and E. coli recombinant strains])
BS. Choudhuri, S. Bhakta et al. Overexpression and functional characterization of an ABC (ATP-binding cassette) transporter encoded by the genes drrA and drrB of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Biochem. J. 2002 |
| Citation | Inactivation of polyketide synthase and related genes results in the loss of complex lipids in Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv. SJ. Waddell, GA. Chung et al. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2005 | mjackson | | 15715645 | Component of the DrrABC ABC-transporter involved in the translocation of phthiocerol dimycocerosates across the plasma membrane and in drug-resistance; integral membrane protein (phenotypic [mycobacterial and E. coli recombinant strains]) |
| Other | TBPWY:Phthiocerol dimycocerosates, PGL & pHBAD | mjackson | | | Component of the DrrABC ABC-transporter involved in the translocation of phthiocerol dimycocerosates across the plasma membrane and in drug-resistance; integral membrane protein (phenotypic [mycobacterial and E. coli recombinant strains])
SJ. Waddell, GA. Chung et al. Inactivation of polyketide synthase and related genes results in the loss of complex lipids in Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2005 |
| Citation | Overexpression and functional characterization of an ABC (ATP-binding cassette) transporter encoded by the genes drrA and drrB of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. BS. Choudhuri, S. Bhakta et al. Biochem. J. 2002 | mjackson | | 12057006 | Component of the DrrABC ABC-transporter involved in the translocation of phthiocerol dimycocerosates across the plasma membrane and in drug-resistance; integral membrane protein (phenotypic [mycobacterial and E. coli recombinant strains]) |
| Citation | Interaction between polyketide synthase and transporter suggests coupled synthesis and export of virulence lipid in M. tuberculosis. M. Jain & JS. Cox PLoS Pathog. 2005 | jjmcfadden | | 16201014 | Inferred from direct assay |
| Other | EC: | jjmcfadden | | | Inferred from direct assay
M. Jain & JS. Cox Interaction between polyketide synthase and transporter suggests coupled synthesis and export of virulence lipid in M. tuberculosis. PLoS Pathog. 2005 |