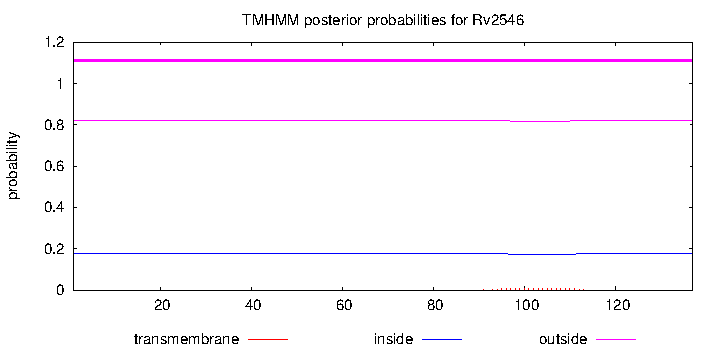
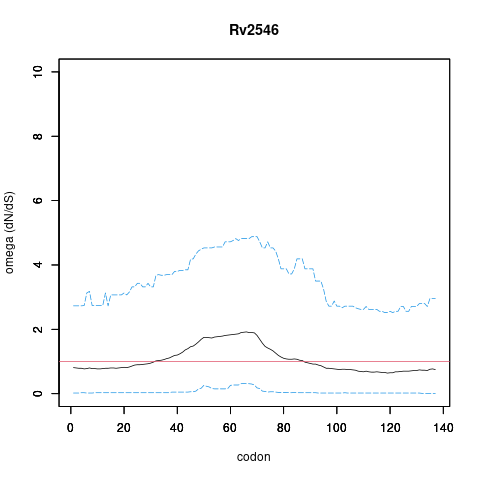
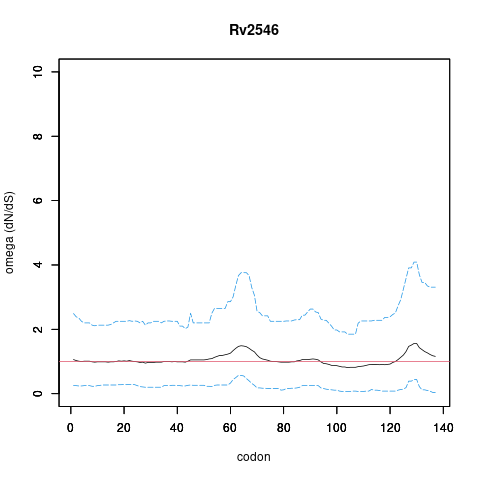
| Property | Value | Creator | Evidence | PMID | Comment |
| Interaction | Regulatory Rv2545 | soumisengupta | ISO | | Gene Neighborhood (Functional linkage)
authors,VL. Arcus,PB. Rainey,SJ. Turner The PIN-domain toxin-antitoxin array in mycobacteria. Trends Microbiol. 2005 |
| Interaction | Regulatory Rv2545 | soumisengupta | ISO | | Gene Neighborhood (Functional linkage)
authors,HR. Ramage,LE. Connolly,JS. Cox Comprehensive functional analysis of Mycobacterium tuberculosis toxin-antitoxin systems: implications for pathogenesis, stress responses, and evolution. PLoS Genet. 2009 |
| Citation | The PIN-domain toxin-antitoxin array in mycobacteria. authors,VL. Arcus,PB. Rainey,SJ. Turner Trends Microbiol. 2005 | soumisengupta | ISO | 15993073 | Gene Neighborhood (Functional linkage) |
| Interaction | Regulatory Rv2545 | soumisengupta | ISO | | Gene Neighborhood (Functional linkage)
authors,VL. Arcus,PB. Rainey,SJ. Turner The PIN-domain toxin-antitoxin array in mycobacteria. Trends Microbiol. 2005 |
| Citation | Comprehensive functional analysis of Mycobacterium tuberculosis toxin-antitoxin systems: implications for pathogenesis, stress responses, and evolution. authors,HR. Ramage,LE. Connolly,JS. Cox PLoS Genet. 2009 | soumisengupta | ISO | 20011113 | Gene Neighborhood (Functional linkage) |
| Interaction | Regulatory Rv2545 | soumisengupta | ISO | | Gene Neighborhood (Functional linkage)
authors,HR. Ramage,LE. Connolly,JS. Cox Comprehensive functional analysis of Mycobacterium tuberculosis toxin-antitoxin systems: implications for pathogenesis, stress responses, and evolution. PLoS Genet. 2009 |
| Citation | Comprehensive functional analysis of Mycobacterium tuberculosis toxin-antitoxin systems: implications for pathogenesis, stress responses, and evolution. authors,HR. Ramage,LE. Connolly,JS. Cox PLoS Genet. 2009 | jlew | | 20011113 | VapC homolog, PIN domain, Not toxic when expressed in Msmeg |
| Symbol | VapC | jlew | | |
authors,BA. Ahidjo,D. Kuhnert,JL. McKenzie,EE. Machowski,BG. Gordhan,V. Arcus,GL. Abrahams,V. Mizrahi VapC toxins from Mycobacterium tuberculosis are ribonucleases that differentially inhibit growth and are neutralized by cognate VapB antitoxins. PLoS ONE 2011 |
| Citation | VapC toxins from Mycobacterium tuberculosis are ribonucleases that differentially inhibit growth and are neutralized by cognate VapB antitoxins. authors,BA. Ahidjo,D. Kuhnert,JL. McKenzie,EE. Machowski,BG. Gordhan,V. Arcus,GL. Abrahams,V. Mizrahi PLoS ONE 2011 | jlew | | 21738782 | None |
| Symbol | VapC18 | jlew | | | We report the heterologous toxicity of these TA loci in Escherichia coli and show that only a few of the M. tuberculosis-encoded toxins can inhibit E. coli growth and have a killing effect. This killing effect can be suppressed by coexpression of the cognate antitoxin.
authors,A. Gupta Killing activity and rescue function of genome-wide toxin-antitoxin loci of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2009 |
| Citation | Killing activity and rescue function of genome-wide toxin-antitoxin loci of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. authors,A. Gupta FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2009 | jlew | | 19016878 | We report the heterologous toxicity of these TA loci in Escherichia coli and show that only a few of the M. tuberculosis-encoded toxins can inhibit E. coli growth and have a killing effect. This killing effect can be suppressed by coexpression of the cognate antitoxin. |
| Other | strand:+ | rslayden | | | MTCY08D5.24c (226 aa), FASTA scores: opt: 272, E(): 1.3e-11, (39.7% identity in 136 aa overlap); O33299 |
| Other | start:2868154 | rslayden | | | Rv2757c |
| Other | stop:2868567 | rslayden | | | Rv2757c |
| Other | strand:+ | rslayden | | | Rv2757c |
| Other | start:2868154 | rslayden | | | MTV002.22c (138 aa), FASTA scores: opt: 265, E(): 2.5e-11, (38.5% identity in 135 aa overlap); P95026 |
| Other | stop:2868567 | rslayden | | | MTV002.22c (138 aa), FASTA scores: opt: 265, E(): 2.5e-11, (38.5% identity in 135 aa overlap); P95026 |
| Other | strand:+ | rslayden | | | MTV002.22c (138 aa), FASTA scores: opt: 265, E(): 2.5e-11, (38.5% identity in 135 aa overlap); P95026 |
| Other | start:2868154 | rslayden | | | Rv2527 |
| Other | stop:2868567 | rslayden | | | Rv2527 |
| Other | strand:+ | rslayden | | | Rv2527 |
| Other | start:2868154 | rslayden | | | MTCY159.29c (133 aa), FASTA scores: opt: 206, E(): 2.6e-07, (38.0% identity in 100 aa overlap); etc. |
| Other | stop:2868567 | rslayden | | | MTCY159.29c (133 aa), FASTA scores: opt: 206, E(): 2.6e-07, (38.0% identity in 100 aa overlap); etc. |
| Other | strand:+ | rslayden | | | MTCY159.29c (133 aa), FASTA scores: opt: 206, E(): 2.6e-07, (38.0% identity in 100 aa overlap); etc. |
| Other | start:2868154 | rslayden | | | Conserved hypothetical protein. Some similarity to several HYPOTHETICAL PROTEINS from Mycobacterium tuberculosis (strain H37Rv and CDC1551) e.g. P96411 |
| Other | stop:2868567 | rslayden | | | Conserved hypothetical protein. Some similarity to several HYPOTHETICAL PROTEINS from Mycobacterium tuberculosis (strain H37Rv and CDC1551) e.g. P96411 |
| Other | strand:+ | rslayden | | | Conserved hypothetical protein. Some similarity to several HYPOTHETICAL PROTEINS from Mycobacterium tuberculosis (strain H37Rv and CDC1551) e.g. P96411 |
| Other | start:2868154 | rslayden | | | Rv0229c |
| Other | stop:2868567 | rslayden | | | Rv0229c |
| Other | strand:+ | rslayden | | | Rv0229c |
| Other | start:2868154 | rslayden | | | MTCY08D5.24c (226 aa), FASTA scores: opt: 272, E(): 1.3e-11, (39.7% identity in 136 aa overlap); O33299 |
| Other | stop:2868567 | rslayden | | | MTCY08D5.24c (226 aa), FASTA scores: opt: 272, E(): 1.3e-11, (39.7% identity in 136 aa overlap); O33299 |