Rv2495c (bkdC)
Current annotations:
TBCAP: (community-based annotations - see table at bottom of page )
TBDB: pyruvate dehydrogenase E2 component (dihydrolipoamide acetyltransferase)
REFSEQ: branched-chain alpha-keto acid dehydrogenase subunit E2
PATRIC: Dihydrolipoamide acyltransferase component of branched-chain alpha-keto acid dehydrogenase complex (EC 2.3.1.168)
TUBERCULIST: Probable branched-chain keto acid dehydrogenase E2 component BkdC
NCBI: Probable branched-chain keto acid dehydrogenase E2 component BkdC
updated information (H37Rv4):
gene name: bkdC
function:
reference:
Type: Not Target
Start: 2808758
End: 2809939
Operon:
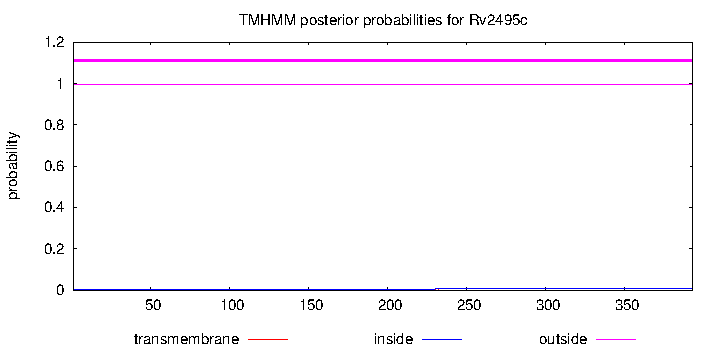
Trans-membrane region:
Role: I.B.2 - Pyruvate dehydrogenase
GO terms:
GO:0043754 - dihydrolipoyllysine-residue (2-methylpropanoyl)transferase activity (Uniprot)
GO:0016746 - transferase activity, transferring acyl groups (Uniprot)
GO:0016740 - transferase activity (Uniprot)
GO:0008152 - metabolic process (Uniprot)
GO:0005886 - plasma membrane (Uniprot)
GO:0005618 - cell wall (Uniprot)
Reaction(s) (based on iSM810 metabolic model):
Gene Expression Profile Gene Modules Orthologs among selected mycobacteria Protein structure: 3l60
Search for Homologs in PDB Top 10 Homologs in PDB (as of Nov 2020): PDB aa ident species PDB title 3L60 100% Mycobacterium tuberculosis Crystal structure of branched-chain alpha-keto acid dehydrogenase subunit e2 from mycobacterium tuberculosis 2L5T 47% Thermoplasma acidophilum Solution NMR structure of E2 lipoyl domain from Thermoplasma acidophilum 6L1Q 43% Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans ATCC 23270 Crystal structure of AfCbbQ2, a MoxR AAA+-ATPase and CbbQO-type Rubisco activase from Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans 1LAC 43% Geobacillus stearothermophilus THREE-DIMENSIONAL STRUCTURE OF THE LIPOYL DOMAIN FROM BACILLUS STEAROTHERMOPHILUS PYRUVATE DEHYDROGENASE MULTIENZYME COMPLEX 1LAB 43% Geobacillus stearothermophilus THREE-DIMENSIONAL STRUCTURE OF THE LIPOYL DOMAIN FROM BACILLUS STEAROTHERMOPHILUS PYRUVATE DEHYDROGENASE MULTIENZYME COMPLEX 1K8O 41% Homo sapiens Solution Structure of the Lipoic Acid-Bearing Domain of the E2 component of Human, Mitochondrial Branched-Chain alpha-Ketoacid Dehydrogenase 1K8M 41% Homo sapiens Solution Structure of the Lipoic Acid-Bearing Domain of the E2 component of Human, Mitochondrial Branched-Chain alpha-Ketoacid Dehydrogenase 1QJO 41% ESCHERICHIA COLI BL21(DE3) INNERMOST LIPOYL DOMAIN OF THE PYRUVATE DEHYDROGENASE FROM ESCHERICHIA COLI 2K7V 36% Escherichia coli Deletions in a surface loop divert the folding of a protein domain into a metastable dimeric form 1IYV 35% Azotobacter vinelandii LIPOYL DOMAIN OF PYRUVATE DEHYDROGENASE COMPLEX, NMR, 29 STRUCTURES
Links to additional information on bkdC:
Amino Acid Sequence
MSGEDSIRSFPVPDLGEGLQEVTVTCWSVAVGDDVEINQTLCSVETAKAEVEIPSPYAGRIVELGGAEGDVLKVGAELVRIDTGPTAVAQPNGEGAVPTL
VGYGADTAIETSRRTSRPLAAPVVRKLAKELAVDLAALQRGSGAGGVITRADVLAAARGGVGAGPDVRPVHGVHARMAEKMTLSHKEIPTAKASVEVICA
ELLRLRDRFVSAAPEITPFALTLRLLVIALKHNVILNSTWVDSGEGPQVHVHRGVHLGFGAATERGLLVPVVTDAQDKNTRELASRVAELITGAREGTLT
PAELRGSTFTVSNFGALGVDDGVPVINHPEAAILGLGAIKPRPVVVGGEVVARPTMTLTCVFDHRVVDGAQVAQFMCELRDLIESPETALLDL
(
Nucleotide sequence available on
KEGG )
Additional Information
Analysis of Positive Selection in Clinical Isolates
*new*
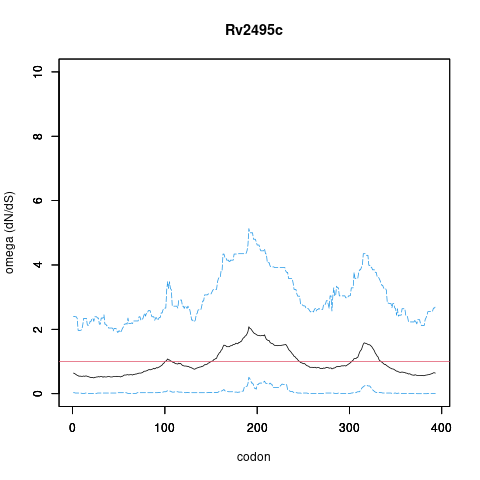
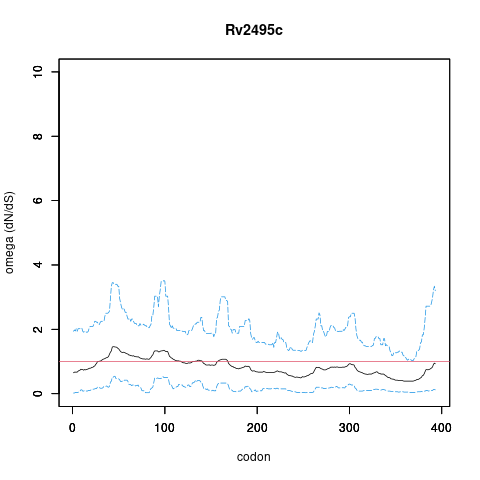
Analysis of dN/dS (omega) in two collections of Mtb clinical isolates using GenomegaMap (Window model) (see description of methods )
Moldova: 2,057 clinical isolates
global set: 5,195 clinical isolates from 15 other countries
In the omega plots, the black line shows the mean estimate of omega (dN/dS) at each codon, and the blue lines are the bounds for the 95% credible interval (95%CI, from MCMC sampling).
A gene is under significant positive selection if the lower-bound of the 95%CI of omega (lower blue line) exceeds 1.0 at any codon.
Moldova (2,057) global set (5,195)
under significant positive selection? NO NO
omega peak height (95%CI lower bound) 2.08 (0.51) 1.45 (0.54)
codons under selection
omega plots
genetic variants* link link
statistics at each codon link link
* example format for variants: "D27 (GAC): D27H (CAC,11)" means "Asp27 (native codon GAC) mutated to His (codon CAC) in 11 isolates"
MtbTnDB - interactive tool for exploring a database of published TnSeq datasets for Mtb
TnSeqCorr
Rv2495c/bkdC,
gene len: 1181 bp, num TA sites: 15
condition dataset call medium method notes
in-vitro DeJesus 2017 mBio non-essential 7H9 HMM fully saturated, 14 TnSeq libraries combined
in-vitro Sassetti 2003 Mol Micro no data 7H9 TRASH essential if hybridization ratio<0.2
in-vivo (mice) Sassetti 2003 PNAS no data BL6 mice TRASH essential if hybridization ratio<0.4, min over 4 timepoints (1-8 weeks)
in-vitro (glycerol) Griffin 2011 PPath uncertain M9 minimal+glycerol Gumbel 2 replicates; Padj<0.05
in-vitro (cholesterol) Griffin 2011 PPath non-essential M9 minimal+cholesterol Gumbel 3 replicates; Padj<0.05
differentially essential in cholesterol Griffin 2011 PPath NO (LFC=1.42) cholesterol vs glycerol resampling-SR YES if Padj<0.05, else not significant; LFC<0 means less insertions/more essential in cholesterol
in-vitro Smith 2022 eLife non-essential 7H9 HMM 6 replicates (raw data in Subramaniam 2017, PMID 31752678)
in-vivo (mice) Smith 2022 eLife non-essential BL6 mice HMM 6 replicates (raw data in Subramaniam 2017, PMID 31752678)
differentially essential in mice Smith 2022 eLife NO (LFC=0.145) in-vivo vs in-vitro ZINB YES if Padj<0.05, else not significant; LFC<0 means less insertions/more essential in mice
in-vitro (minimal) Minato 2019 mSys non-essential minimal medium HMM
in-vitro (YM rich medium) Minato 2019 mSys non-essential YM rich medium HMM 7H9 supplemented with ~20 metabolites (amino acids, cofactors)
differentially essential in YM rich medium Minato 2019 mSys NO (LFC=-0.15) YM rich vs minimal medium resampling
TnSeq Data No data currently available.
No TnSeq data currently available for this Target.
RNASeq Data No data currently available.
No RNA-Seq data currently available for this Target.
Metabolomic Profiles No data currently available.
No Metabolomic data currently available for this Target.
Proteomic Data No data currently available.
No Proteomic data currently available for this Target.
Regulatory Relationships from Systems Biology
BioCyc
Gene interactions based on ChIPSeq and Transcription Factor Over-Expression (TFOE) (Systems Biology )
NOTE:
Green edges represent the connected genes being classified as differentially essential as a result of the middle gene being knocked out. These interactions are inferred based on RNASeq.
Interactions based on ChIPSeq data
RNA processing and modification
Energy production and conversion
Chromatin structure and dynamics
Amino acid transport and metabolism
Cell cycle control, cell division, chromosome partitioning
Carbohydrate transport and metabolism
Nucleotide transport and metabolism
Lipid transport and metabolism
Coenzyme transport and metabolism
Translation, ribosomal structure and biogenesis
Cell wall/membrane/envelope biogenesis
Replication, recombination and repair
Posttranslational modification, protein turnover, chaperones
Secondary metabolites biosynthesis, transport and catabolism
Inorganic ion transport and metabolism
General function prediction only
Intracellular trafficking, secretion, and vesicular transport
Signal transduction mechanisms
Differentially expressed as result of RNASeq in glycerol environment (Only top 20 genes shown sorted by log fold change with p_adj 0.05).
Conditionally essential as result of TNSeq (Only top 20 genes shown sorted by log fold change with p_adj 0.05).
Binds To:
No bindings to other targets were found.
Bound By:
No bindings from other targets were found.
Binds To:
No bindings to other targets were found.
Bound By:
Upregulates:
Does not upregulate other genes.
Upregulated by:
Not upregulated by other genes.
Downregulates:
Does not downregulate other genes.
Downregulated by:
Not downregulated by other genes.
Property Value Creator Evidence PMID Comment
Interaction Operon Rv2497c akankshajain.21 IEP CoexpressionJ. Tian, R. Bryk et al. Mycobacterium tuberculosis appears to lack alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase and encodes pyruvate dehydrogenase in widely separated genes. Mol. Microbiol. 2005
Citation Mycobacterium tuberculosis appears to lack alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase and encodes pyruvate dehydrogenase in widely separated genes. J. Tian, R. Bryk et al. Mol. Microbiol. 2005 akankshajain.21 IEP 16045627 Coexpression
Interaction Operon Rv2496c akankshajain.21 IEP CoexpressionJ. Tian, R. Bryk et al. Mycobacterium tuberculosis appears to lack alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase and encodes pyruvate dehydrogenase in widely separated genes. Mol. Microbiol. 2005
Interaction Operon Rv2497c akankshajain.21 IEP CoexpressionJ. Tian, R. Bryk et al. Mycobacterium tuberculosis appears to lack alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase and encodes pyruvate dehydrogenase in widely separated genes. Mol. Microbiol. 2005
Interaction Operon Rv2496c akankshajain.21 IEP CoexpressionJ. Tian, R. Bryk et al. Mycobacterium tuberculosis appears to lack alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase and encodes pyruvate dehydrogenase in widely separated genes. Mol. Microbiol. 2005
Interaction RegulatedBy Rv0348 yamir.moreno IEP Microarrays. mRNA levels of regulated element measured and compared between wild-type and trans-element mutation (knockout, over expression etc.) performed by using microarray (or macroarray) experiments..B. Abomoelak, EA. Hoye et al. mosR, a novel transcriptional regulator of hypoxia and virulence in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J. Bacteriol. 2009
Citation Central carbon metabolism in Mycobacterium tuberculosis: an unexpected frontier. authors,KY. Rhee,LP. de Carvalho,R. Bryk,S. Ehrt,J. Marrero,SW. Park,D. Schnappinger,A. Venugopal,C. Nathan Trends Microbiol. 2011 extern:JZUCKER 21561773 Traceable author statement to experimental support
Term EC:2.3.1.168 Dihydrolipoyllysine-residue (2-methylpropanoyl)transferase. - NR extern:JZUCKER NR Traceable author statement to experimental supportauthors,KY. Rhee,LP. de Carvalho,R. Bryk,S. Ehrt,J. Marrero,SW. Park,D. Schnappinger,A. Venugopal,C. Nathan Central carbon metabolism in Mycobacterium tuberculosis: an unexpected frontier. Trends Microbiol. 2011
Term EC:2.3.1.12 Dihydrolipoyllysine-residue acetyltransferase. - NR extern:JZUCKER NR Traceable author statement to experimental supportauthors,KY. Rhee,LP. de Carvalho,R. Bryk,S. Ehrt,J. Marrero,SW. Park,D. Schnappinger,A. Venugopal,C. Nathan Central carbon metabolism in Mycobacterium tuberculosis: an unexpected frontier. Trends Microbiol. 2011
Citation Virulence of Mycobacterium tuberculosis depends on lipoamide dehydrogenase, a member of three multienzyme complexes. authors,A. Venugopal,R. Bryk,S. Shi,K. Rhee,P. Rath,D. Schnappinger,S. Ehrt,C. Nathan Cell Host Microbe 2011 extern:JZUCKER 21238944 Inferred from mutant phenotype
Term EC:2.3.1.168 Dihydrolipoyllysine-residue (2-methylpropanoyl)transferase. - NR extern:JZUCKER NR Inferred from mutant phenotypeauthors,A. Venugopal,R. Bryk,S. Shi,K. Rhee,P. Rath,D. Schnappinger,S. Ehrt,C. Nathan Virulence of Mycobacterium tuberculosis depends on lipoamide dehydrogenase, a member of three multienzyme complexes. Cell Host Microbe 2011
Term EC:2.3.1.12 Dihydrolipoyllysine-residue acetyltransferase. - NR extern:JZUCKER NR Inferred from mutant phenotypeauthors,A. Venugopal,R. Bryk,S. Shi,K. Rhee,P. Rath,D. Schnappinger,S. Ehrt,C. Nathan Virulence of Mycobacterium tuberculosis depends on lipoamide dehydrogenase, a member of three multienzyme complexes. Cell Host Microbe 2011