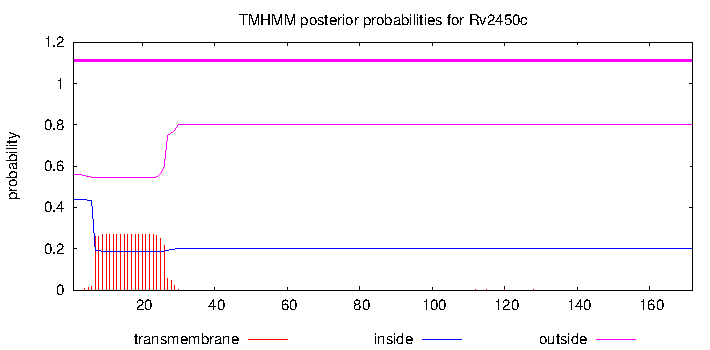
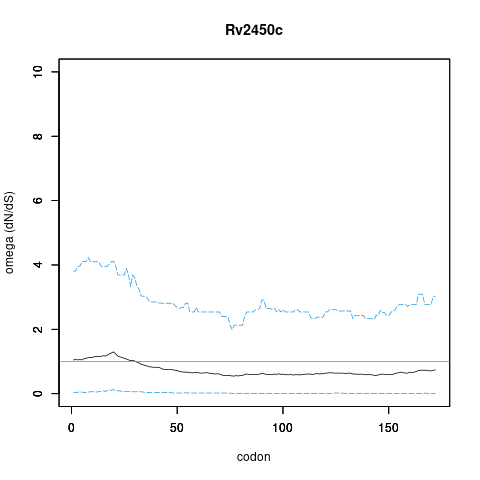
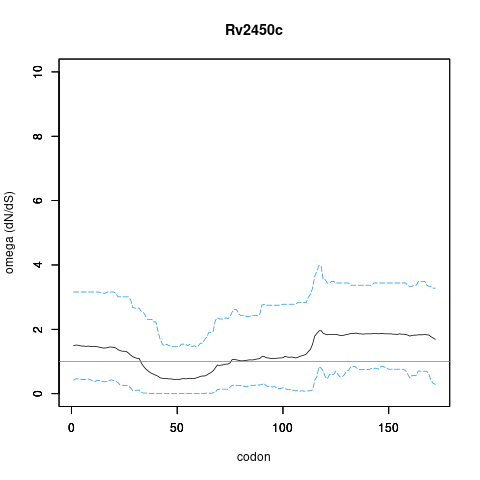
| Property | Value | Creator | Evidence | PMID | Comment |
| Interaction | Operon Rv2948c | ashwinigbhat | NAS | | Co-expression (Functional linkage)
B. Abomoelak, EA. Hoye et al. mosR, a novel transcriptional regulator of hypoxia and virulence in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J. Bacteriol. 2009 |
| Interaction | PhysicalInteraction Rv1477 | singhpankaj2116 | IMP | | Co-expression (Functional linkage)
BD. Kana, BG. Gordhan et al. The resuscitation-promoting factors of Mycobacterium tuberculosis are required for virulence and resuscitation from dormancy but are collectively dispensable for growth in vitro. Mol. Microbiol. 2008 |
| Citation | A partner for the resuscitation-promoting factors of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. EC. Hett, MC. Chao et al. Mol. Microbiol. 2007 | singhpankaj2116 | IMP | 17919286 | Co-expression (Functional linkage) |
| Interaction | PhysicalInteraction Rv1477 | singhpankaj2116 | IMP | | Co-expression (Functional linkage)
EC. Hett, MC. Chao et al. A partner for the resuscitation-promoting factors of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Mol. Microbiol. 2007 |
| Citation | A bacterial cytokine. authors,GV. Mukamolova,AS. Kaprelyants,DI. Young,M. Young,DB. Kell Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 1998 | singhpankaj2116 | IMP | 9671779 | Co-expression (Functional linkage) |
| Interaction | PhysicalInteraction Rv1477 | singhpankaj2116 | IMP | | Co-expression (Functional linkage)
authors,GV. Mukamolova,AS. Kaprelyants,DI. Young,M. Young,DB. Kell A bacterial cytokine. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 1998 |
| Citation | Global expression profiling of strains harbouring null mutations reveals that the five rpf-like genes of Mycobacterium tuberculosis show functional redundancy. KJ. Downing, JC. Betts et al. Tuberculosis (Edinburgh, Scotland) 2004 | richasinha4u | IDA | 15207486 | Yeast two-hybrid (Physical interaction) |
| Interaction | PhysicalInteraction Rv1477 | richasinha4u | IDA | | Yeast two-hybrid (Physical interaction)
KJ. Downing, JC. Betts et al. Global expression profiling of strains harbouring null mutations reveals that the five rpf-like genes of Mycobacterium tuberculosis show functional redundancy. Tuberculosis (Edinburgh, Scotland) 2004 |
| Citation | The resuscitation-promoting factors of Mycobacterium tuberculosis are required for virulence and resuscitation from dormancy but are collectively dispensable for growth in vitro. BD. Kana, BG. Gordhan et al. Mol. Microbiol. 2008 | richasinha4u | IDA | 18186793 | Yeast two-hybrid (Physical interaction) |
| Interaction | PhysicalInteraction Rv1477 | richasinha4u | IDA | | Yeast two-hybrid (Physical interaction)
BD. Kana, BG. Gordhan et al. The resuscitation-promoting factors of Mycobacterium tuberculosis are required for virulence and resuscitation from dormancy but are collectively dispensable for growth in vitro. Mol. Microbiol. 2008 |
| Citation | Individual Mycobacterium tuberculosis resuscitation-promoting factor homologues are dispensable for growth in vitro and in vivo. authors,JM. Tufariello,WR. Jacobs,J. Chan Infect. Immun. 2004 | richasinha4u | IDA | 14688133 | Yeast two-hybrid (Physical interaction) |
| Interaction | PhysicalInteraction Rv1477 | richasinha4u | IDA | | Yeast two-hybrid (Physical interaction)
authors,JM. Tufariello,WR. Jacobs,J. Chan Individual Mycobacterium tuberculosis resuscitation-promoting factor homologues are dispensable for growth in vitro and in vivo. Infect. Immun. 2004 |
| Citation | A partner for the resuscitation-promoting factors of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. EC. Hett, MC. Chao et al. Mol. Microbiol. 2007 | richasinha4u | IDA | 17919286 | Yeast two-hybrid (Physical interaction) |
| Interaction | PhysicalInteraction Rv1477 | richasinha4u | IDA | | Yeast two-hybrid (Physical interaction)
EC. Hett, MC. Chao et al. A partner for the resuscitation-promoting factors of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Mol. Microbiol. 2007 |
| Citation | The resuscitation-promoting factors of Mycobacterium tuberculosis are required for virulence and resuscitation from dormancy but are collectively dispensable for growth in vitro. BD. Kana, BG. Gordhan et al. Mol. Microbiol. 2008 | singhpankaj2116 | IMP | 18186793 | Co-expression (Functional linkage) |
| Interaction | Regulatory Rv2389c | sourish10 | IMP | | Co-expression (Functional linkage)
KJ. Downing, JC. Betts et al. Global expression profiling of strains harbouring null mutations reveals that the five rpf-like genes of Mycobacterium tuberculosis show functional redundancy. Tuberculosis (Edinburgh, Scotland) 2004 |
| Interaction | ActivatedBy Rv1477 | vijayachitra | IPI | | Yeast two-hybrid (Physical interaction)
EC. Hett, MC. Chao et al. A partner for the resuscitation-promoting factors of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Mol. Microbiol. 2007 |
| Name | Resuscitation-promoting factor | mjackson | IMP | | Peptidoglycan turnover |