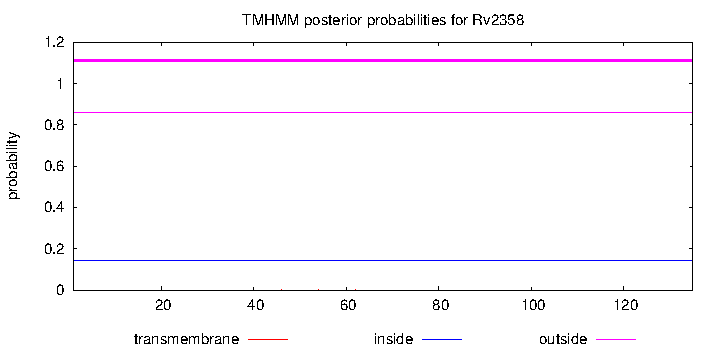
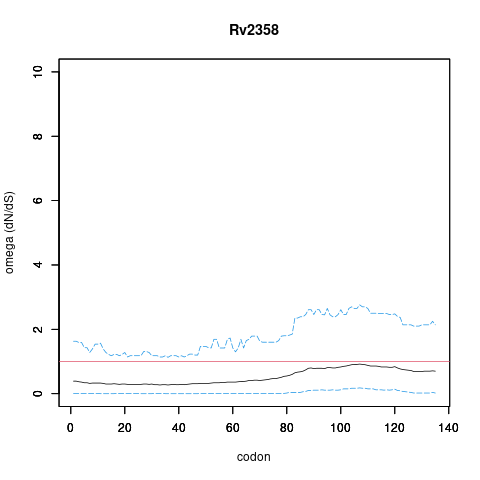
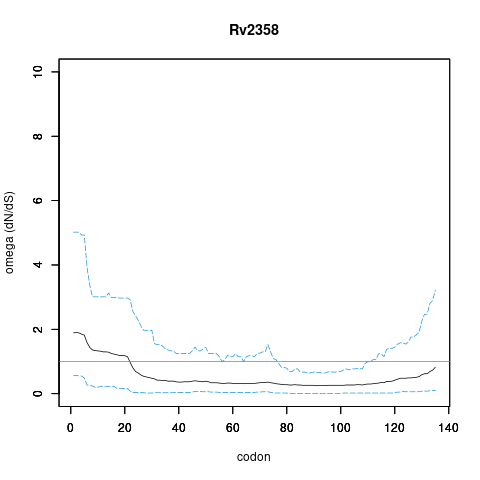
| Property | Value | Creator | Evidence | PMID | Comment |
| Interaction | Transcription Rv2359 | jhum4u2006 | IPI | | Affinity purification (Physical interaction)
F. Canneva, M. Branzoni et al. Rv2358 and FurB: two transcriptional regulators from Mycobacterium tuberculosis which respond to zinc. J. Bacteriol. 2005 |
| Citation | Rv2358 and FurB: two transcriptional regulators from Mycobacterium tuberculosis which respond to zinc. F. Canneva, M. Branzoni et al. J. Bacteriol. 2005 | jhum4u2006 | IPI | 16077132 | Affinity purification (Physical interaction) |
| Interaction | Transcription Rv2359 | jhum4u2006 | IPI | | Affinity purification (Physical interaction)
F. Canneva, M. Branzoni et al. Rv2358 and FurB: two transcriptional regulators from Mycobacterium tuberculosis which respond to zinc. J. Bacteriol. 2005 |
| Interaction | Transcription Rv2358 | jhum4u2006 | IPI | | Affinity purification (Physical interaction)
F. Canneva, M. Branzoni et al. Rv2358 and FurB: two transcriptional regulators from Mycobacterium tuberculosis which respond to zinc. J. Bacteriol. 2005 |
| Interaction | Transcription Rv2358 | jhum4u2006 | IPI | | Affinity purification (Physical interaction)
F. Canneva, M. Branzoni et al. Rv2358 and FurB: two transcriptional regulators from Mycobacterium tuberculosis which respond to zinc. J. Bacteriol. 2005 |
| Interaction | Regulates Rv2359 | yamir.moreno | IDA | | Electrophoretic mobility shift assays EMSA. Physical binding of the regulator to the regulated promoter proved by using electrophoretic mobility shift assay. . LacZ-promoter fusion. expression levels of LacZ- regulated promoter fusion measured and compared between wild-type and trans-element mutation (knockout, over expression etc.).
F. Canneva, M. Branzoni et al. Rv2358 and FurB: two transcriptional regulators from Mycobacterium tuberculosis which respond to zinc. J. Bacteriol. 2005 |
| Citation | Rv2358 and FurB: two transcriptional regulators from Mycobacterium tuberculosis which respond to zinc. F. Canneva, M. Branzoni et al. J. Bacteriol. 2005 | yamir.moreno | IEP | 16077132 | Electrophoretic mobility shift assays EMSA. Physical binding of the regulator to the regulated promoter proved by using electrophoretic mobility shift assay. . LacZ-promoter fusion. expression levels of LacZ- regulated promoter fusion measured and compared between wild-type and trans-element mutation (knockout, over expression etc.). |
| Interaction | Regulates Rv2359 | yamir.moreno | IEP | | Electrophoretic mobility shift assays EMSA. Physical binding of the regulator to the regulated promoter proved by using electrophoretic mobility shift assay. . LacZ-promoter fusion. expression levels of LacZ- regulated promoter fusion measured and compared between wild-type and trans-element mutation (knockout, over expression etc.).
F. Canneva, M. Branzoni et al. Rv2358 and FurB: two transcriptional regulators from Mycobacterium tuberculosis which respond to zinc. J. Bacteriol. 2005 |
| Citation | Rv2358 and FurB: two transcriptional regulators from Mycobacterium tuberculosis which respond to zinc. F. Canneva, M. Branzoni et al. J. Bacteriol. 2005 | yamir.moreno | IDA | 16077132 | Electrophoretic mobility shift assays EMSA. Physical binding of the regulator to the regulated promoter proved by using electrophoretic mobility shift assay. . LacZ-promoter fusion. expression levels of LacZ- regulated promoter fusion measured and compared between wild-type and trans-element mutation (knockout, over expression etc.). |
| Interaction | Regulates Rv2358 | yamir.moreno | IDA | | Electrophoretic mobility shift assays EMSA. Physical binding of the regulator to the regulated promoter proved by using electrophoretic mobility shift assay. . LacZ-promoter fusion. expression levels of LacZ- regulated promoter fusion measured and compared between wild-type and trans-element mutation (knockout, over expression etc.).
F. Canneva, M. Branzoni et al. Rv2358 and FurB: two transcriptional regulators from Mycobacterium tuberculosis which respond to zinc. J. Bacteriol. 2005 |
| Interaction | RegulatedBy Rv2358 | yamir.moreno | IDA | | Electrophoretic mobility shift assays EMSA. Physical binding of the regulator to the regulated promoter proved by using electrophoretic mobility shift assay. . LacZ-promoter fusion. expression levels of LacZ- regulated promoter fusion measured and compared between wild-type and trans-element mutation (knockout, over expression etc.).
F. Canneva, M. Branzoni et al. Rv2358 and FurB: two transcriptional regulators from Mycobacterium tuberculosis which respond to zinc. J. Bacteriol. 2005 |
| Citation | Rv2358 and FurB: two transcriptional regulators from Mycobacterium tuberculosis which respond to zinc. F. Canneva, M. Branzoni et al. J. Bacteriol. 2005 | yamir.moreno | IEP | 16077132 | Electrophoretic mobility shift assays EMSA. Physical binding of the regulator to the regulated promoter proved by using electrophoretic mobility shift assay. . LacZ-promoter fusion. expression levels of LacZ- regulated promoter fusion measured and compared between wild-type and trans-element mutation (knockout, over expression etc.). |
| Interaction | Regulates Rv2358 | yamir.moreno | IEP | | Electrophoretic mobility shift assays EMSA. Physical binding of the regulator to the regulated promoter proved by using electrophoretic mobility shift assay. . LacZ-promoter fusion. expression levels of LacZ- regulated promoter fusion measured and compared between wild-type and trans-element mutation (knockout, over expression etc.).
F. Canneva, M. Branzoni et al. Rv2358 and FurB: two transcriptional regulators from Mycobacterium tuberculosis which respond to zinc. J. Bacteriol. 2005 |
| Interaction | RegulatedBy Rv2358 | yamir.moreno | IEP | | Electrophoretic mobility shift assays EMSA. Physical binding of the regulator to the regulated promoter proved by using electrophoretic mobility shift assay. . LacZ-promoter fusion. expression levels of LacZ- regulated promoter fusion measured and compared between wild-type and trans-element mutation (knockout, over expression etc.).
F. Canneva, M. Branzoni et al. Rv2358 and FurB: two transcriptional regulators from Mycobacterium tuberculosis which respond to zinc. J. Bacteriol. 2005 |
| Citation | Rv2358 and FurB: two transcriptional regulators from Mycobacterium tuberculosis which respond to zinc. F. Canneva, M. Branzoni et al. J. Bacteriol. 2005 | yamir.moreno | IDA | 16077132 | Electrophoretic mobility shift assays EMSA. Physical binding of the regulator to the regulated promoter proved by using electrophoretic mobility shift assay. . LacZ-promoter fusion. expression levels of LacZ- regulated promoter fusion measured and compared between wild-type and trans-element mutation (knockout, over expression etc.). |
| Citation | The temporal response of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis gene regulatory network during growth arrest. G. Balzsi, AP. Heath et al. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2008 | yamir.moreno | TAS | 18985025 | Literature previously reported link (from Balazsi et al. 2008). Traceable author statement to experimental support. |
| Interaction | Regulates Rv2358 | yamir.moreno | TAS | | Literature previously reported link (from Balazsi et al. 2008). Traceable author statement to experimental support.
G. Balzsi, AP. Heath et al. The temporal response of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis gene regulatory network during growth arrest. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2008 |
| Interaction | RegulatedBy Rv2358 | yamir.moreno | TAS | | Literature previously reported link (from Balazsi et al. 2008). Traceable author statement to experimental support.
G. Balzsi, AP. Heath et al. The temporal response of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis gene regulatory network during growth arrest. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2008 |
| Citation | The temporal response of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis gene regulatory network during growth arrest. G. Balzsi, AP. Heath et al. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2008 | yamir.moreno | TAS | 18985025 | Literature previously reported link (from Balazsi et al. 2008). Traceable author statement to experimental support. |
| Interaction | Regulates Rv2359 | yamir.moreno | TAS | | Literature previously reported link (from Balazsi et al. 2008). Traceable author statement to experimental support.
G. Balzsi, AP. Heath et al. The temporal response of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis gene regulatory network during growth arrest. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2008 |