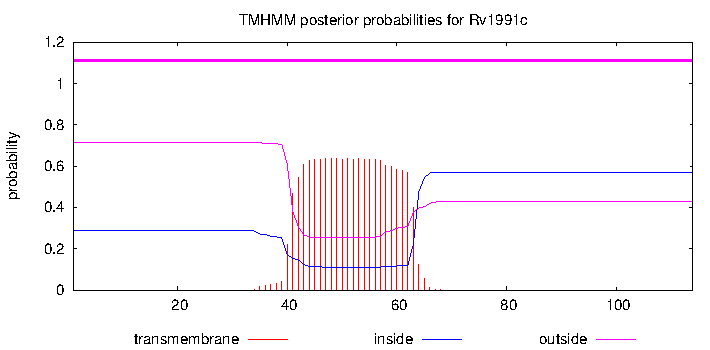
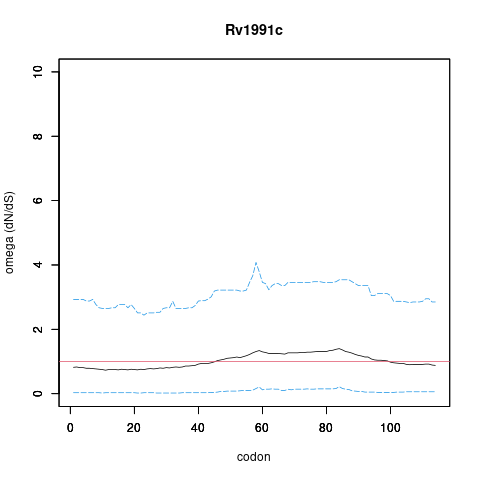
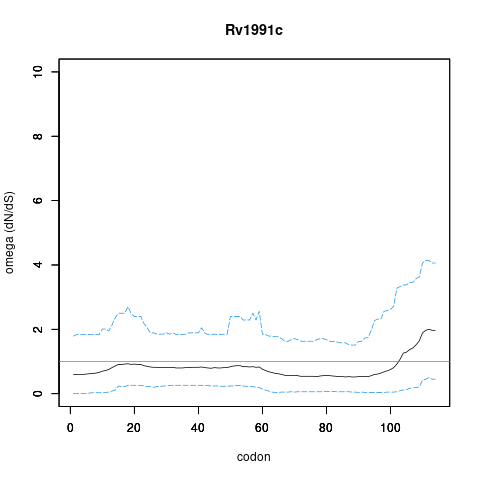
| Property | Value | Creator | Evidence | PMID | Comment |
| Citation | Comprehensive functional analysis of Mycobacterium tuberculosis toxin-antitoxin systems: implications for pathogenesis, stress responses, and evolution. authors,HR. Ramage,LE. Connolly,JS. Cox PLoS Genet. 2009 | jlew | | 20011113 | MazF homolog, Toxic when expressed in Msmeg, rescued by antitoxin (Rv1991A) |
| Symbol | mazF-mt3 | jlew | | | mRNA levels elevated in Mtb in limited O2.. No growth when mazF-mt1 expressed in Ecoli but restored when mazE-mt1 was co-induced. mazF-mt1 could also be partially neutralized by vapB-mt24 or vapB-mt25. Growth inhibition by mazF-mt3; normal growth if mazE-mt1, mazE-mt3, vapB-mt24 or vapB-mt25 were co-expressed. Each pair shows interaction by pull-down.
authors,L. Zhu,JD. Sharp,H. Kobayashi,NA. Woychik,M. Inouye Noncognate Mycobacterium tuberculosis toxin-antitoxins can physically and functionally interact. J. Biol. Chem. 2010 |
| Citation | Noncognate Mycobacterium tuberculosis toxin-antitoxins can physically and functionally interact. authors,L. Zhu,JD. Sharp,H. Kobayashi,NA. Woychik,M. Inouye J. Biol. Chem. 2010 | jlew | | 20876537 | mRNA levels elevated in Mtb in limited O2.. No growth when mazF-mt1 expressed in Ecoli but restored when mazE-mt1 was co-induced. mazF-mt1 could also be partially neutralized by vapB-mt24 or vapB-mt25. Growth inhibition by mazF-mt3; normal growth if mazE-mt1, mazE-mt3, vapB-mt24 or vapB-mt25 were co-expressed. Each pair shows interaction by pull-down. |
| Symbol | MazF6 | jlew | | | Toxic to Ecoli growth. We report the heterologous toxicity of these TA loci in Escherichia coli and show that only a few of the M. tuberculosis-encoded toxins can inhibit E. coli growth and have a killing effect. This killing effect can be suppressed by coexpression of the cognate antitoxin.
authors,A. Gupta Killing activity and rescue function of genome-wide toxin-antitoxin loci of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2009 |
| Citation | Killing activity and rescue function of genome-wide toxin-antitoxin loci of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. authors,A. Gupta FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2009 | jlew | | 19016878 | Toxic to Ecoli growth. We report the heterologous toxicity of these TA loci in Escherichia coli and show that only a few of the M. tuberculosis-encoded toxins can inhibit E. coli growth and have a killing effect. This killing effect can be suppressed by coexpression of the cognate antitoxin. |
| Symbol | mazF-mt3 | jlew | | | Caused cell growth arrest when induced in Ecoli.
authors,L. Zhu,Y. Zhang,JS. Teh,J. Zhang,N. Connell,H. Rubin,M. Inouye Characterization of mRNA interferases from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2006 |
| Citation | Characterization of mRNA interferases from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. authors,L. Zhu,Y. Zhang,JS. Teh,J. Zhang,N. Connell,H. Rubin,M. Inouye J. Biol. Chem. 2006 | jlew | | 16611633 | Caused cell growth arrest when induced in Ecoli. |
| Citation | Expression of Mycobacterium tuberculosis Rv1991c using an arabinose-inducible promoter demonstrates its role as a toxin. P. Carroll, AC. Brown et al. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2007 | jlew | | 17623030 | Expression of Rv1991c inhibits growth of EC but not when expressed with adjacent antitoxin and expression of 1991c in Msmeg resulted in reduction of cell viability. |
| Citation | Biochemical characterization of a chromosomal toxin-antitoxin system in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. L. Zhao & J. Zhang FEBS Lett. 2008 | jlew | | 18258191 | show it's a toxin with ribonuclease activity. Rv1991c and Rv1991A form a complex that can bind its own promoter. |
| Other | start:2234305 | rslayden | | | Conserved hypothetical protein, showing some similarity to P13976 |
| Other | stop:2234649 | rslayden | | | Conserved hypothetical protein, showing some similarity to P13976 |
| Other | strand:+ | rslayden | | | Conserved hypothetical protein, showing some similarity to P13976 |
| Other | start:2234305 | rslayden | | | PEMK_ECOLI pemk protein (133 aa), FASTA scores: opt: 113, E(): 0.043, (29.2% identity in 113 aa overlap); and P96622 |
| Other | stop:2234649 | rslayden | | | PEMK_ECOLI pemk protein (133 aa), FASTA scores: opt: 113, E(): 0.043, (29.2% identity in 113 aa overlap); and P96622 |
| Other | strand:+ | rslayden | | | PEMK_ECOLI pemk protein (133 aa), FASTA scores: opt: 113, E(): 0.043, (29.2% identity in 113 aa overlap); and P96622 |
| Other | start:2234305 | rslayden | | | YDCE PROTEIN from Bacillus subtilis (116 aa), FASTA scores: opt: 227, E(): 6.9e-09, (37.4% identity in 115 aa overlap). Also similar to Mycobacterium tuberculosis Rv2801c, and Rv0659c. |
| Other | stop:2234649 | rslayden | | | YDCE PROTEIN from Bacillus subtilis (116 aa), FASTA scores: opt: 227, E(): 6.9e-09, (37.4% identity in 115 aa overlap). Also similar to Mycobacterium tuberculosis Rv2801c, and Rv0659c. |
| Other | strand:+ | rslayden | | | YDCE PROTEIN from Bacillus subtilis (116 aa), FASTA scores: opt: 227, E(): 6.9e-09, (37.4% identity in 115 aa overlap). Also similar to Mycobacterium tuberculosis Rv2801c, and Rv0659c. |