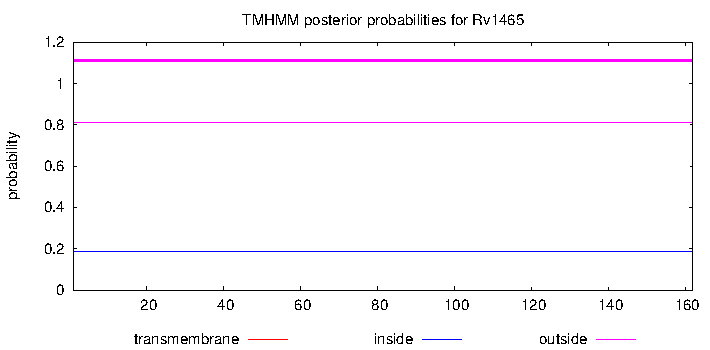
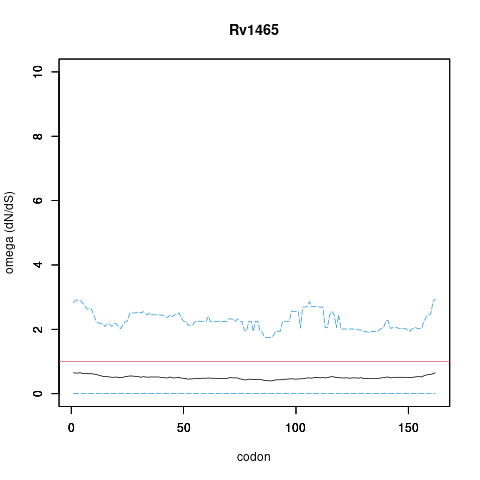
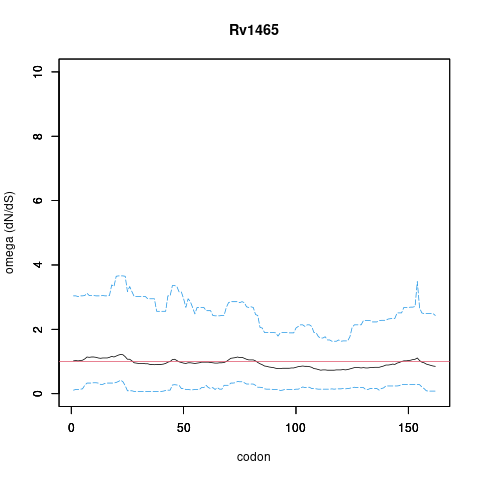
| Property | Value | Creator | Evidence | PMID | Comment |
| Citation | GlbN (cyanoglobin) is a peripheral membrane protein that is restricted to certain Nostoc spp. authors,DR. Hill,TJ. Belbin,MV. Thorsteinsson,D. Bassam,S. Brass,A. Ernst,P. Bger,H. Paerl,ME. Mulligan,M. Potts J. Bacteriol. 1996 | priti.priety | IEP | 8932316 | Co-expression (Functional linkage) |
| Interaction | PhysicalInteraction Rv1542c | priti.priety | IEP | | Co-expression (Functional linkage)
authors,DR. Hill,TJ. Belbin,MV. Thorsteinsson,D. Bassam,S. Brass,A. Ernst,P. Bger,H. Paerl,ME. Mulligan,M. Potts GlbN (cyanoglobin) is a peripheral membrane protein that is restricted to certain Nostoc spp. J. Bacteriol. 1996 |
| Citation | GlbN (cyanoglobin) is a peripheral membrane protein that is restricted to certain Nostoc spp. authors,DR. Hill,TJ. Belbin,MV. Thorsteinsson,D. Bassam,S. Brass,A. Ernst,P. Bger,H. Paerl,ME. Mulligan,M. Potts J. Bacteriol. 1996 | ashwinigbhat | IEP | 8932316 | Co-expression (Functional linkage) |
| Interaction | PhysicalInteraction Rv1542c | ashwinigbhat | IEP | | Co-expression (Functional linkage)
authors,DR. Hill,TJ. Belbin,MV. Thorsteinsson,D. Bassam,S. Brass,A. Ernst,P. Bger,H. Paerl,ME. Mulligan,M. Potts GlbN (cyanoglobin) is a peripheral membrane protein that is restricted to certain Nostoc spp. J. Bacteriol. 1996 |
| Interaction | RegulatedBy Rv3557c | yamir.moreno | IDA | | One hybrid reporter system. Physical binding of the regulator to the regulated promoter proved by using electrophoretic mobility shift assay. .
M. Guo, H. Feng et al. Dissecting transcription regulatory pathways through a new bacterial one-hybrid reporter system. Genome Res. 2009 |
| Interaction | RegulatedBy Rv3416 | yamir.moreno | IDA | | One hybrid reporter system. Physical binding of the regulator to the regulated promoter proved by using electrophoretic mobility shift assay. .
M. Guo, H. Feng et al. Dissecting transcription regulatory pathways through a new bacterial one-hybrid reporter system. Genome Res. 2009 |
| Interaction | RegulatedBy Rv1931c | yamir.moreno | IDA | | One hybrid reporter system. Physical binding of the regulator to the regulated promoter proved by using electrophoretic mobility shift assay. .
M. Guo, H. Feng et al. Dissecting transcription regulatory pathways through a new bacterial one-hybrid reporter system. Genome Res. 2009 |
| Interaction | RegulatedBy Rv1359 | yamir.moreno | IDA | | One hybrid reporter system. Physical binding of the regulator to the regulated promoter proved by using electrophoretic mobility shift assay. .
M. Guo, H. Feng et al. Dissecting transcription regulatory pathways through a new bacterial one-hybrid reporter system. Genome Res. 2009 |
| Interaction | RegulatedBy Rv0818 | yamir.moreno | IDA | | One hybrid reporter system. Physical binding of the regulator to the regulated promoter proved by using electrophoretic mobility shift assay. .
M. Guo, H. Feng et al. Dissecting transcription regulatory pathways through a new bacterial one-hybrid reporter system. Genome Res. 2009 |
| Interaction | RegulatedBy Rv0445c | yamir.moreno | IDA | | One hybrid reporter system. Physical binding of the regulator to the regulated promoter proved by using electrophoretic mobility shift assay. .
M. Guo, H. Feng et al. Dissecting transcription regulatory pathways through a new bacterial one-hybrid reporter system. Genome Res. 2009 |
| Interaction | RegulatedBy Rv0260c | yamir.moreno | IDA | | One hybrid reporter system. Physical binding of the regulator to the regulated promoter proved by using electrophoretic mobility shift assay. .
M. Guo, H. Feng et al. Dissecting transcription regulatory pathways through a new bacterial one-hybrid reporter system. Genome Res. 2009 |