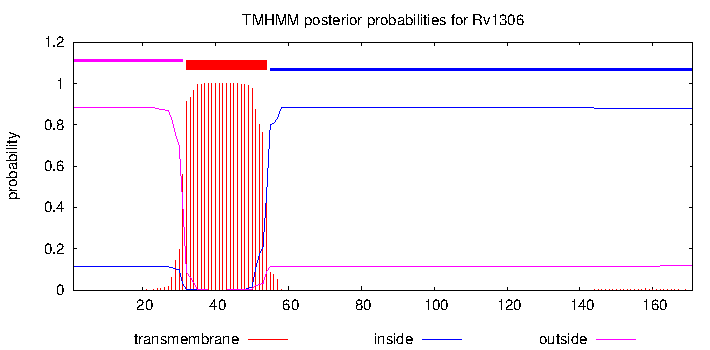
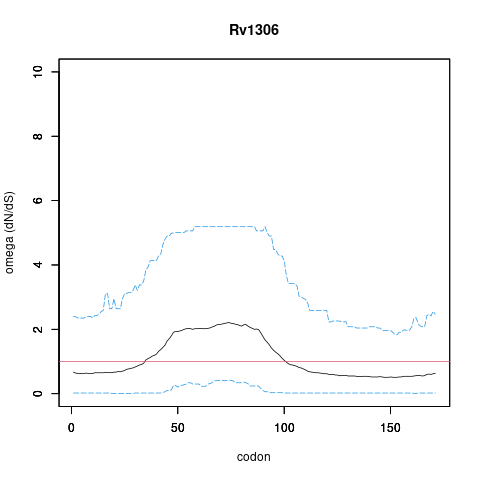
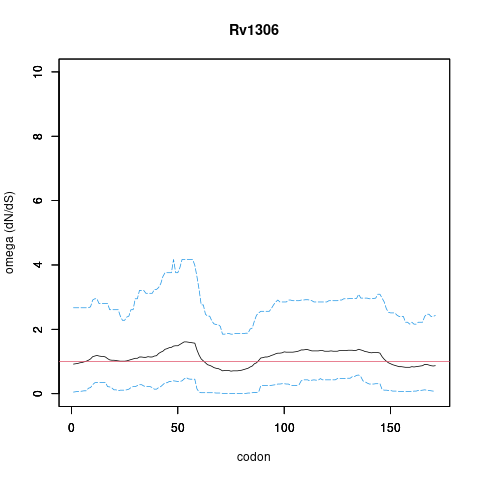
| Property | Value | Creator | Evidence | PMID | Comment |
| Interaction | PhysicalInteraction Rv1304 | priti.priety | IDA | | structural analysis
MR. de Jonge, LH. Koymans et al. A computational model of the inhibition of Mycobacterium tuberculosis ATPase by a new drug candidate R207910. Proteins 2007 |
| Interaction | PhysicalInteraction Rv1305 | priti.priety | IDA | | structural analysis
MR. de Jonge, LH. Koymans et al. A computational model of the inhibition of Mycobacterium tuberculosis ATPase by a new drug candidate R207910. Proteins 2007 |
| Citation | Diarylquinolines are bactericidal for dormant mycobacteria as a result of disturbed ATP homeostasis. A. Koul,L. Vranckx,N. Dendouga,W. Balemans,I. Van den Wyngaert,K. Vergauwen,HW. Ghlmann,R. Willebrords,A. Poncelet,J. Guillemont,D. Bald,K. Andries J. Biol. Chem. 2008 | priti.priety | IDA | 18625705 | structural analysis |
| Interaction | PhysicalInteraction Rv1304 | priti.priety | IDA | | structural analysis
A. Koul,L. Vranckx,N. Dendouga,W. Balemans,I. Van den Wyngaert,K. Vergauwen,HW. Ghlmann,R. Willebrords,A. Poncelet,J. Guillemont,D. Bald,K. Andries Diarylquinolines are bactericidal for dormant mycobacteria as a result of disturbed ATP homeostasis. J. Biol. Chem. 2008 |
| Interaction | PhysicalInteraction Rv1305 | priti.priety | IDA | | structural analysis
A. Koul,L. Vranckx,N. Dendouga,W. Balemans,I. Van den Wyngaert,K. Vergauwen,HW. Ghlmann,R. Willebrords,A. Poncelet,J. Guillemont,D. Bald,K. Andries Diarylquinolines are bactericidal for dormant mycobacteria as a result of disturbed ATP homeostasis. J. Biol. Chem. 2008 |
| Interaction | PhysicalInteraction Rv1304 | priti.priety | IDA | | structural analysis
authors,M. Rappas,H. Niwa,X. Zhang Mechanisms of ATPases--a multi-disciplinary approach. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2004 |
| Interaction | PhysicalInteraction Rv1305 | priti.priety | IDA | | structural analysis
authors,M. Rappas,H. Niwa,X. Zhang Mechanisms of ATPases--a multi-disciplinary approach. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2004 |
| Citation | Structure of the F1-binding domain of the stator of bovine F1Fo-ATPase and how it binds an alpha-subunit. authors,RJ. Carbajo,FA. Kellas,MJ. Runswick,MG. Montgomery,JE. Walker,D. Neuhaus J. Mol. Biol. 2005 | priti.priety | IDA | 16045926 | structural analysis |
| Interaction | PhysicalInteraction Rv1304 | priti.priety | IDA | | structural analysis
authors,RJ. Carbajo,FA. Kellas,MJ. Runswick,MG. Montgomery,JE. Walker,D. Neuhaus Structure of the F1-binding domain of the stator of bovine F1Fo-ATPase and how it binds an alpha-subunit. J. Mol. Biol. 2005 |
| Interaction | PhysicalInteraction Rv1305 | priti.priety | IDA | | structural analysis
authors,RJ. Carbajo,FA. Kellas,MJ. Runswick,MG. Montgomery,JE. Walker,D. Neuhaus Structure of the F1-binding domain of the stator of bovine F1Fo-ATPase and how it binds an alpha-subunit. J. Mol. Biol. 2005 |
| Citation | Dormancy phenotype displayed by extracellular Mycobacterium tuberculosis within artificial granulomas in mice. PC. Karakousis, T. Yoshimatsu et al. J. Exp. Med. 2004 | priti.priety | IDA | 15353557 | structural analysis |
| Interaction | PhysicalInteraction Rv1304 | priti.priety | IDA | | structural analysis
PC. Karakousis, T. Yoshimatsu et al. Dormancy phenotype displayed by extracellular Mycobacterium tuberculosis within artificial granulomas in mice. J. Exp. Med. 2004 |
| Interaction | PhysicalInteraction Rv1305 | priti.priety | IDA | | structural analysis
PC. Karakousis, T. Yoshimatsu et al. Dormancy phenotype displayed by extracellular Mycobacterium tuberculosis within artificial granulomas in mice. J. Exp. Med. 2004 |
| Citation | A computational model of the inhibition of Mycobacterium tuberculosis ATPase by a new drug candidate R207910. MR. de Jonge, LH. Koymans et al. Proteins 2007 | priti.priety | IDA | 17387738 | structural analysis |
| Interaction | PhysicalInteraction Rv1305 | priti.priety | IDA | | spectrophotometric assy
PC. Karakousis, T. Yoshimatsu et al. Dormancy phenotype displayed by extracellular Mycobacterium tuberculosis within artificial granulomas in mice. J. Exp. Med. 2004 |
| Citation | A computational model of the inhibition of Mycobacterium tuberculosis ATPase by a new drug candidate R207910. MR. de Jonge, LH. Koymans et al. Proteins 2007 | priti.priety | IDA | 17387738 | spectrophotometric assy |
| Interaction | PhysicalInteraction Rv1304 | priti.priety | IDA | | spectrophotometric assy
MR. de Jonge, LH. Koymans et al. A computational model of the inhibition of Mycobacterium tuberculosis ATPase by a new drug candidate R207910. Proteins 2007 |
| Interaction | PhysicalInteraction Rv1305 | priti.priety | IDA | | spectrophotometric assy
MR. de Jonge, LH. Koymans et al. A computational model of the inhibition of Mycobacterium tuberculosis ATPase by a new drug candidate R207910. Proteins 2007 |
| Citation | Diarylquinolines are bactericidal for dormant mycobacteria as a result of disturbed ATP homeostasis. A. Koul,L. Vranckx,N. Dendouga,W. Balemans,I. Van den Wyngaert,K. Vergauwen,HW. Ghlmann,R. Willebrords,A. Poncelet,J. Guillemont,D. Bald,K. Andries J. Biol. Chem. 2008 | priti.priety | IDA | 18625705 | spectrophotometric assy |
| Interaction | PhysicalInteraction Rv1304 | priti.priety | IDA | | spectrophotometric assy
A. Koul,L. Vranckx,N. Dendouga,W. Balemans,I. Van den Wyngaert,K. Vergauwen,HW. Ghlmann,R. Willebrords,A. Poncelet,J. Guillemont,D. Bald,K. Andries Diarylquinolines are bactericidal for dormant mycobacteria as a result of disturbed ATP homeostasis. J. Biol. Chem. 2008 |
| Interaction | PhysicalInteraction Rv1305 | priti.priety | IDA | | spectrophotometric assy
A. Koul,L. Vranckx,N. Dendouga,W. Balemans,I. Van den Wyngaert,K. Vergauwen,HW. Ghlmann,R. Willebrords,A. Poncelet,J. Guillemont,D. Bald,K. Andries Diarylquinolines are bactericidal for dormant mycobacteria as a result of disturbed ATP homeostasis. J. Biol. Chem. 2008 |
| Citation | Mechanisms of ATPases--a multi-disciplinary approach. authors,M. Rappas,H. Niwa,X. Zhang Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2004 | priti.priety | IDA | 15078220 | structural analysis |
| Interaction | PhysicalInteraction Rv1305 | priti.priety | IDA | | structural analysis
A. Koul,L. Vranckx,N. Dendouga,W. Balemans,I. Van den Wyngaert,K. Vergauwen,HW. Ghlmann,R. Willebrords,A. Poncelet,J. Guillemont,D. Bald,K. Andries Diarylquinolines are bactericidal for dormant mycobacteria as a result of disturbed ATP homeostasis. J. Biol. Chem. 2008 |
| Citation | Mechanisms of ATPases--a multi-disciplinary approach. authors,M. Rappas,H. Niwa,X. Zhang Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2004 | priti.priety | IDA | 15078220 | spectrophotometric assy |
| Interaction | PhysicalInteraction Rv1304 | priti.priety | IDA | | spectrophotometric assy
authors,M. Rappas,H. Niwa,X. Zhang Mechanisms of ATPases--a multi-disciplinary approach. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2004 |
| Interaction | PhysicalInteraction Rv1305 | priti.priety | IDA | | spectrophotometric assy
authors,M. Rappas,H. Niwa,X. Zhang Mechanisms of ATPases--a multi-disciplinary approach. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2004 |
| Citation | Structure of the F1-binding domain of the stator of bovine F1Fo-ATPase and how it binds an alpha-subunit. authors,RJ. Carbajo,FA. Kellas,MJ. Runswick,MG. Montgomery,JE. Walker,D. Neuhaus J. Mol. Biol. 2005 | priti.priety | IDA | 16045926 | spectrophotometric assy |
| Interaction | PhysicalInteraction Rv1304 | priti.priety | IDA | | spectrophotometric assy
authors,RJ. Carbajo,FA. Kellas,MJ. Runswick,MG. Montgomery,JE. Walker,D. Neuhaus Structure of the F1-binding domain of the stator of bovine F1Fo-ATPase and how it binds an alpha-subunit. J. Mol. Biol. 2005 |
| Interaction | PhysicalInteraction Rv1305 | priti.priety | IDA | | spectrophotometric assy
authors,RJ. Carbajo,FA. Kellas,MJ. Runswick,MG. Montgomery,JE. Walker,D. Neuhaus Structure of the F1-binding domain of the stator of bovine F1Fo-ATPase and how it binds an alpha-subunit. J. Mol. Biol. 2005 |
| Citation | Dormancy phenotype displayed by extracellular Mycobacterium tuberculosis within artificial granulomas in mice. PC. Karakousis, T. Yoshimatsu et al. J. Exp. Med. 2004 | priti.priety | IDA | 15353557 | spectrophotometric assy |
| Interaction | PhysicalInteraction Rv1304 | priti.priety | IDA | | spectrophotometric assy
PC. Karakousis, T. Yoshimatsu et al. Dormancy phenotype displayed by extracellular Mycobacterium tuberculosis within artificial granulomas in mice. J. Exp. Med. 2004 |
| Interaction | PhysicalInteraction Rv1305 | priti.priety | IDA | | structural analysis
authors,RJ. Carbajo,FA. Kellas,MJ. Runswick,MG. Montgomery,JE. Walker,D. Neuhaus Structure of the F1-binding domain of the stator of bovine F1Fo-ATPase and how it binds an alpha-subunit. J. Mol. Biol. 2005 |
| Interaction | PhysicalInteraction Rv1305 | priti.priety | IDA | | structural analysis
PC. Karakousis, T. Yoshimatsu et al. Dormancy phenotype displayed by extracellular Mycobacterium tuberculosis within artificial granulomas in mice. J. Exp. Med. 2004 |
| Interaction | PhysicalInteraction Rv1305 | priti.priety | IDA | | structural analysis
MR. de Jonge, LH. Koymans et al. A computational model of the inhibition of Mycobacterium tuberculosis ATPase by a new drug candidate R207910. Proteins 2007 |
| Interaction | PhysicalInteraction Rv1305 | priti.priety | IDA | | spectrophotometric assy
MR. de Jonge, LH. Koymans et al. A computational model of the inhibition of Mycobacterium tuberculosis ATPase by a new drug candidate R207910. Proteins 2007 |
| Interaction | PhysicalInteraction Rv1305 | priti.priety | IDA | | spectrophotometric assy
A. Koul,L. Vranckx,N. Dendouga,W. Balemans,I. Van den Wyngaert,K. Vergauwen,HW. Ghlmann,R. Willebrords,A. Poncelet,J. Guillemont,D. Bald,K. Andries Diarylquinolines are bactericidal for dormant mycobacteria as a result of disturbed ATP homeostasis. J. Biol. Chem. 2008 |
| Interaction | PhysicalInteraction Rv1304 | priti.priety | IDA | | structural analysis
MR. de Jonge, LH. Koymans et al. A computational model of the inhibition of Mycobacterium tuberculosis ATPase by a new drug candidate R207910. Proteins 2007 |
| Interaction | PhysicalInteraction Rv1305 | priti.priety | IDA | | spectrophotometric assy
authors,RJ. Carbajo,FA. Kellas,MJ. Runswick,MG. Montgomery,JE. Walker,D. Neuhaus Structure of the F1-binding domain of the stator of bovine F1Fo-ATPase and how it binds an alpha-subunit. J. Mol. Biol. 2005 |
| Interaction | PhysicalInteraction Rv1305 | priti.priety | IDA | | spectrophotometric assy
PC. Karakousis, T. Yoshimatsu et al. Dormancy phenotype displayed by extracellular Mycobacterium tuberculosis within artificial granulomas in mice. J. Exp. Med. 2004 |
| Interaction | PhysicalInteraction Rv1304 | priti.priety | IDA | | spectrophotometric assy
MR. de Jonge, LH. Koymans et al. A computational model of the inhibition of Mycobacterium tuberculosis ATPase by a new drug candidate R207910. Proteins 2007 |
| Interaction | PhysicalInteraction Rv1304 | priti.priety | IDA | | structural analysis
authors,RJ. Carbajo,FA. Kellas,MJ. Runswick,MG. Montgomery,JE. Walker,D. Neuhaus Structure of the F1-binding domain of the stator of bovine F1Fo-ATPase and how it binds an alpha-subunit. J. Mol. Biol. 2005 |
| Interaction | PhysicalInteraction Rv1304 | priti.priety | IDA | | structural analysis
PC. Karakousis, T. Yoshimatsu et al. Dormancy phenotype displayed by extracellular Mycobacterium tuberculosis within artificial granulomas in mice. J. Exp. Med. 2004 |
| Interaction | PhysicalInteraction Rv1304 | priti.priety | IDA | | spectrophotometric assy
authors,RJ. Carbajo,FA. Kellas,MJ. Runswick,MG. Montgomery,JE. Walker,D. Neuhaus Structure of the F1-binding domain of the stator of bovine F1Fo-ATPase and how it binds an alpha-subunit. J. Mol. Biol. 2005 |
| Interaction | PhysicalInteraction Rv1304 | priti.priety | IDA | | spectrophotometric assy
PC. Karakousis, T. Yoshimatsu et al. Dormancy phenotype displayed by extracellular Mycobacterium tuberculosis within artificial granulomas in mice. J. Exp. Med. 2004 |
| Interaction | RegulatedBy Rv0981 | yamir.moreno | IEP | | Microarrays. mRNA levels of regulated element measured and compared between wild-type and trans-element mutation (knockout, over expression etc.) performed by using microarray (or macroarray) experiments..
H. He, R. Hovey et al. MprAB is a stress-responsive two-component system that directly regulates expression of sigma factors SigB and SigE in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J. Bacteriol. 2006 |
| Interaction | RegulatedBy Rv1221 | yamir.moreno | IEP | | Microarrays. mRNA levels of regulated element measured and compared between wild-type and trans-element mutation (knockout, over expression etc.) performed by using microarray (or macroarray) experiments..
R. Manganelli, MI. Voskuil et al. The Mycobacterium tuberculosis ECF sigma factor sigmaE: role in global gene expression and survival in macrophages. Mol. Microbiol. 2001 |