Rv0732 (secY)
Current annotations:
TBCAP: (community-based annotations - see table at bottom of page )
TBDB: preprotein translocase subunit secY
REFSEQ: preprotein translocase subunit SecY
PATRIC: Preprotein translocase secY subunit (TC 3.A.5.1.1)
TUBERCULIST: Probable preprotein translocase SecY
NCBI: Probable preprotein translocase SecY
updated information (H37Rv4):
gene name: secY
function:
reference:
Type: Not Target
Start: 824800
End: 826125
Operon:
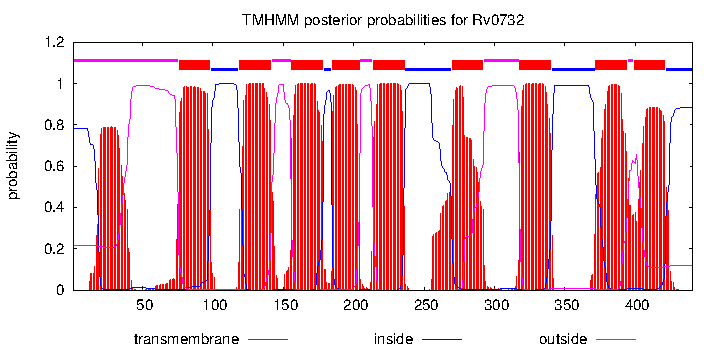
Trans-membrane region:
Role: III.D - Protein and peptide secretion
GO terms:
Reaction(s) (based on iSM810 metabolic model):
Gene Expression Profile Gene Modules Orthologs among selected mycobacteria Protein structure:
Search for Homologs in PDB Top 10 Homologs in PDB (as of Nov 2020): PDB aa ident species PDB title 6ITC 44% Geobacillus thermodenitrificans (strain NG80-2) Structure of a substrate engaged SecA-SecY protein translocation machine 5EUL 44% Geobacillus thermodenitrificans (strain NG80-2) Structure of the SecA-SecY complex with a translocating polypeptide substrate 6R7L 42% Escherichia coli Ribosome-bound SecYEG translocon in a nanodisc 5MG3 42% Escherichia coli EM fitted model of bacterial holo-translocon 5GAE 42% Escherichia coli RNC in complex with a translocating SecYEG 5ABB 42% ESCHERICHIA COLI Visualization of a polytopic membrane protein during SecY-mediated membrane insertion 4V6M 42% Escherichia coli 536 Structure of the ribosome-SecYE complex in the membrane environment 3J45 42% Escherichia coli Structure of a non-translocating SecY protein channel with the 70S ribosome 5NCO 42% Escherichia coli Quaternary complex between SRP, SR, and SecYEG bound to the translating ribosome 3J46 42% Escherichia coli Structure of the SecY protein translocation channel in action
Links to additional information on secY:
Amino Acid Sequence
VLSAFISSLRTVDLRRKILFTLGIVILYRVGAALPSPGVNFPNVQQCIKEASAGEAGQIYSLINLFSGGALLKLTVFAVGVMPYITASIIVQLLTVVIPR
FEELRKEGQAGQSKMTQYTRYLAIALAILQATSIVALAANGGLLQGCSLDIIADQSIFTLVVIVLVMTGGAALVMWMGELITERGIGNGMSLLIFVGIAA
RIPAEGQSILESRGGVVFTAVCAAALIIIVGVVFVEQGQRRIPVQYAKRMVGRRMYGGTSTYLPLKVNQAGVIPVIFASSLIYIPHLITQLIRSGSGVVG
NSWWDKFVGTYLSDPSNLVYIGIYFGLIIFFTYFYVSITFNPDERADEMKKFGGFIPGIRPGRPTADYLRYVLSRITLPGSIYLGVIAVLPNLFLQIGAG
GTVQNLPFGGTAVLIMIGVGLDTVKQIESQLMQRNYEGFLK
(
Nucleotide sequence available on
KEGG )
Additional Information
Analysis of Positive Selection in Clinical Isolates
*new*
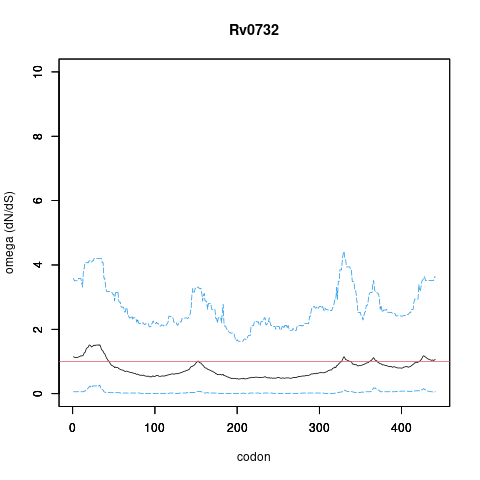
Analysis of dN/dS (omega) in two collections of Mtb clinical isolates using GenomegaMap (Window model) (see description of methods )
Moldova: 2,057 clinical isolates
global set: 5,195 clinical isolates from 15 other countries
In the omega plots, the black line shows the mean estimate of omega (dN/dS) at each codon, and the blue lines are the bounds for the 95% credible interval (95%CI, from MCMC sampling).
A gene is under significant positive selection if the lower-bound of the 95%CI of omega (lower blue line) exceeds 1.0 at any codon.
Moldova (2,057) global set (5,195)
under significant positive selection? NO NO
omega peak height (95%CI lower bound) 1.52 (0.27) 1.79 (0.67)
codons under selection
omega plots
genetic variants* link link
statistics at each codon link link
* example format for variants: "D27 (GAC): D27H (CAC,11)" means "Asp27 (native codon GAC) mutated to His (codon CAC) in 11 isolates"
MtbTnDB - interactive tool for exploring a database of published TnSeq datasets for Mtb
TnSeqCorr
Rv0732/secY,
gene len: 1325 bp, num TA sites: 28
condition dataset call medium method notes
in-vitro DeJesus 2017 mBio essential 7H9 HMM fully saturated, 14 TnSeq libraries combined
in-vitro Sassetti 2003 Mol Micro essential 7H9 TRASH essential if hybridization ratio<0.2
in-vivo (mice) Sassetti 2003 PNAS no data BL6 mice TRASH essential if hybridization ratio<0.4, min over 4 timepoints (1-8 weeks)
in-vitro (glycerol) Griffin 2011 PPath essential M9 minimal+glycerol Gumbel 2 replicates; Padj<0.05
in-vitro (cholesterol) Griffin 2011 PPath essential M9 minimal+cholesterol Gumbel 3 replicates; Padj<0.05
differentially essential in cholesterol Griffin 2011 PPath NO (LFC=-0.15) cholesterol vs glycerol resampling-SR YES if Padj<0.05, else not significant; LFC<0 means less insertions/more essential in cholesterol
in-vitro Smith 2022 eLife essential 7H9 HMM 6 replicates (raw data in Subramaniam 2017, PMID 31752678)
in-vivo (mice) Smith 2022 eLife essential BL6 mice HMM 6 replicates (raw data in Subramaniam 2017, PMID 31752678)
differentially essential in mice Smith 2022 eLife NO (LFC=0.035) in-vivo vs in-vitro ZINB YES if Padj<0.05, else not significant; LFC<0 means less insertions/more essential in mice
in-vitro (minimal) Minato 2019 mSys essential minimal medium HMM
in-vitro (YM rich medium) Minato 2019 mSys essential YM rich medium HMM 7H9 supplemented with ~20 metabolites (amino acids, cofactors)
differentially essential in YM rich medium Minato 2019 mSys NO (LFC=0.97) YM rich vs minimal medium resampling
TnSeq Data No data currently available.
No TnSeq data currently available for this Target.
RNASeq Data No data currently available.
No RNA-Seq data currently available for this Target.
Metabolomic Profiles No data currently available.
No Metabolomic data currently available for this Target.
Proteomic Data No data currently available.
No Proteomic data currently available for this Target.
Regulatory Relationships from Systems Biology
BioCyc
Gene interactions based on ChIPSeq and Transcription Factor Over-Expression (TFOE) (Systems Biology )
NOTE:
Green edges represent the connected genes being classified as differentially essential as a result of the middle gene being knocked out. These interactions are inferred based on RNASeq.
Interactions based on ChIPSeq data
RNA processing and modification
Energy production and conversion
Chromatin structure and dynamics
Amino acid transport and metabolism
Cell cycle control, cell division, chromosome partitioning
Carbohydrate transport and metabolism
Nucleotide transport and metabolism
Lipid transport and metabolism
Coenzyme transport and metabolism
Translation, ribosomal structure and biogenesis
Cell wall/membrane/envelope biogenesis
Replication, recombination and repair
Posttranslational modification, protein turnover, chaperones
Secondary metabolites biosynthesis, transport and catabolism
Inorganic ion transport and metabolism
General function prediction only
Intracellular trafficking, secretion, and vesicular transport
Signal transduction mechanisms
Differentially expressed as result of RNASeq in glycerol environment (Only top 20 genes shown sorted by log fold change with p_adj 0.05).
Conditionally essential as result of TNSeq (Only top 20 genes shown sorted by log fold change with p_adj 0.05).
Binds To:
No bindings to other targets were found.
Bound By:
No bindings from other targets were found.
Binds To:
No bindings to other targets were found.
Bound By:
Upregulates:
Does not upregulate other genes.
Upregulated by:
Not upregulated by other genes.
Downregulates:
Does not downregulate other genes.
Downregulated by:
Not downregulated by other genes.
Property Value Creator Evidence PMID Comment
Interaction Translation Rv3610c shahanup86 IDA Affinity purification (Physical interaction)authors,R. Srinivasan,H. Rajeswari,P. Ajitkumar Analysis of degradation of bacterial cell division protein FtsZ by the ATP-dependent zinc-metalloprotease FtsH in vitro. Microbiol. Res. 2008
Interaction Translation Rv3610c shahanup86 IDA Affinity purification (Physical interaction)authors,G. Anilkumar,R. Srinivasan,SP. Anand,P. Ajitkumar Bacterial cell division protein FtsZ is a specific substrate for the AAA family protease FtsH. Microbiology (Reading, Engl.) 2001
Interaction Translation Rv3610c shahanup86 IDA Affinity purification (Physical interaction)G. Anilkumar, R. Srinivasan et al. Genomic organization and in vivo characterization of proteolytic activity of FtsH of Mycobacterium smegmatis SN2. Microbiology (Reading, Engl.) 2004
Interaction Translation Rv3610c shahanup86 IDA Affinity purification (Physical interaction)authors,H. Zheng,L. Lu,B. Wang,S. Pu,X. Zhang,G. Zhu,W. Shi,L. Zhang,H. Wang,S. Wang,G. Zhao,Y. Zhang Genetic basis of virulence attenuation revealed by comparative genomic analysis of Mycobacterium tuberculosis strain H37Ra versus H37Rv. PLoS ONE 2008
Interaction Translation Rv3610c shahanup86 IDA Affinity purification (Physical interaction)authors,C. Herman,D. Thvenet,R. D'Ari,P. Bouloc Degradation of sigma 32, the heat shock regulator in Escherichia coli, is governed by HflB. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 1995
Interaction Translation Rv3610c shahanup86 IDA Affinity purification (Physical interaction)G. Anilkumar, MM. Chauhan et al. Cloning and expression of the gene coding for FtsH protease from Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv. Gene 1998
Interaction Translation Rv3610c shahanup86 IDA Affinity purification (Physical interaction)R. Srinivasan, G. Anilkumar et al. Functional characterization of AAA family FtsH protease of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2006
Interaction PhysicalInteraction Rv1440 shahanup86 TAS authors,F. Duong Binding, activation and dissociation of the dimeric SecA ATPase at the dimeric SecYEG translocase. EMBO J. 2003
Citation The bacterial protein-translocation complex: SecYEG dimers associate with one or two SecA molecules. authors,C. Tziatzios,D. Schubert,M. Lotz,D. Gundogan,H. Betz,H. Schgger,W. Haase,F. Duong,I. Collinson J. Mol. Biol. 2004 anshula.arora1990 IDA 15210351 Structural analysis
Interaction PhysicalInteraction Rv3240c anshula.arora1990 IDA Structural analysisauthors,C. Tziatzios,D. Schubert,M. Lotz,D. Gundogan,H. Betz,H. Schgger,W. Haase,F. Duong,I. Collinson The bacterial protein-translocation complex: SecYEG dimers associate with one or two SecA molecules. J. Mol. Biol. 2004
Interaction PhysicalInteraction Rv1821 anshula.arora1990 IDA Structural analysisauthors,C. Tziatzios,D. Schubert,M. Lotz,D. Gundogan,H. Betz,H. Schgger,W. Haase,F. Duong,I. Collinson The bacterial protein-translocation complex: SecYEG dimers associate with one or two SecA molecules. J. Mol. Biol. 2004
Citation ATPase activity of Mycobacterium tuberculosis SecA1 and SecA2 proteins and its importance for SecA2 function in macrophages. JM. Hou, NG. D'Lima et al. J. Bacteriol. 2008 anshula.arora1990 IDA 18487341 Structural analysis
Interaction PhysicalInteraction Rv3240c anshula.arora1990 IDA Structural analysisJM. Hou, NG. D'Lima et al. ATPase activity of Mycobacterium tuberculosis SecA1 and SecA2 proteins and its importance for SecA2 function in macrophages. J. Bacteriol. 2008
Interaction PhysicalInteraction Rv1821 anshula.arora1990 IDA Structural analysisJM. Hou, NG. D'Lima et al. ATPase activity of Mycobacterium tuberculosis SecA1 and SecA2 proteins and its importance for SecA2 function in macrophages. J. Bacteriol. 2008
Interaction PhysicalInteraction Rv0638 prabhakarsmail ISO Structural Analysisauthors,KL. Bieker,TJ. Silhavy PrlA (SecY) and PrlG (SecE) interact directly and function sequentially during protein translocation in E. coli. Cell 1990
Interaction PhysicalInteraction Rv0638 akankshajain.21 ISO Structural Analysisauthors,EH. Manting,C. van Der Does,H. Remigy,A. Engel,AJ. Driessen SecYEG assembles into a tetramer to form the active protein translocation channel. EMBO J. 2000
Interaction PhysicalInteraction Rv0638 akankshajain.21 ISO Structural Analysisauthors,KL. Bieker,TJ. Silhavy PrlA (SecY) and PrlG (SecE) interact directly and function sequentially during protein translocation in E. coli. Cell 1990
Interaction PhysicalInteraction Rv0638 prabhakarsmail ISO Structural Analysisauthors,EH. Manting,C. van Der Does,H. Remigy,A. Engel,AJ. Driessen SecYEG assembles into a tetramer to form the active protein translocation channel. EMBO J. 2000
Interaction PhysicalInteraction Rv0379 manish.srcp ISO authors,C. Tziatzios,D. Schubert,M. Lotz,D. Gundogan,H. Betz,H. Schgger,W. Haase,F. Duong,I. Collinson The bacterial protein-translocation complex: SecYEG dimers associate with one or two SecA molecules. J. Mol. Biol. 2004
Interaction RegulatedBy Rv1221 yamir.moreno IEP Microarrays. mRNA levels of regulated element measured and compared between wild-type and trans-element mutation (knockout, over expression etc.) performed by using microarray (or macroarray) experiments..R. Manganelli, MI. Voskuil et al. The Mycobacterium tuberculosis ECF sigma factor sigmaE: role in global gene expression and survival in macrophages. Mol. Microbiol. 2001