| Property | Value | Creator | Evidence | PMID | Comment |
| Citation | Lipid composition and virulence of Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv. authors,GK. Khuller,R. Taneja,S. Kaur,JN. Verma Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci 1982 | njamshidi | ISS | 6819845 | Added for PE metabolism - these phospholipids (i.e. phosphatidylethanolamine) are known to be in Mtb (see for example: PMID: 6819845), however the details of the pathways have not been identified yet (for example do the phospholipase reactions take place in the intra-cellular space, within the cell wall, or extracellular?). |
| Term | EC:2.7.8.8 CDP-diacylglycerol--serine O-phosphatidyltransferase. - ISS | njamshidi | ISS | 6819845 | Added for PE metabolism - these phospholipids (i.e. phosphatidylethanolamine) are known to be in Mtb (see for example: PMID: 6819845), however the details of the pathways have not been identified yet (for example do the phospholipase reactions take place in the intra-cellular space, within the cell wall, or extracellular?).
authors,GK. Khuller,R. Taneja,S. Kaur,JN. Verma Lipid composition and virulence of Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci 1982 |
| Term | TBRXN:PSSA160 Phosphatidylserine syntase (n-C16:0) - ISS | njamshidi | ISS | 6819845 | Added for PE metabolism - these phospholipids (i.e. phosphatidylethanolamine) are known to be in Mtb (see for example: PMID: 6819845), however the details of the pathways have not been identified yet (for example do the phospholipase reactions take place in the intra-cellular space, within the cell wall, or extracellular?).
authors,GK. Khuller,R. Taneja,S. Kaur,JN. Verma Lipid composition and virulence of Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci 1982 |
| Citation | Lipid composition and virulence of Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv. authors,GK. Khuller,R. Taneja,S. Kaur,JN. Verma Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci 1982 | njamshidi | ISS | 6819845 | Added for PE metabolism - these phospholipids (i.e. phosphatidylethanolamine) are known to be in Mtb (see for example: PMID: 6819845), however the details of the pathways have not been identified yet (for example do the phospholipase reactions take place in the intra-cellular space, within the cell wall, or extracellular?). |
| Term | EC:2.7.8.8 CDP-diacylglycerol--serine O-phosphatidyltransferase. - ISS | njamshidi | ISS | 6819845 | Added for PE metabolism - these phospholipids (i.e. phosphatidylethanolamine) are known to be in Mtb (see for example: PMID: 6819845), however the details of the pathways have not been identified yet (for example do the phospholipase reactions take place in the intra-cellular space, within the cell wall, or extracellular?).
authors,GK. Khuller,R. Taneja,S. Kaur,JN. Verma Lipid composition and virulence of Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci 1982 |
| Term | TBRXN:PSSA180 Phosphatidylserine syntase (n-C18:0) - ISS | njamshidi | ISS | 6819845 | Added for PE metabolism - these phospholipids (i.e. phosphatidylethanolamine) are known to be in Mtb (see for example: PMID: 6819845), however the details of the pathways have not been identified yet (for example do the phospholipase reactions take place in the intra-cellular space, within the cell wall, or extracellular?).
authors,GK. Khuller,R. Taneja,S. Kaur,JN. Verma Lipid composition and virulence of Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci 1982 |
| Citation | Lipid composition and virulence of Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv. authors,GK. Khuller,R. Taneja,S. Kaur,JN. Verma Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci 1982 | njamshidi | IPI | 6819845 | Added for PE metabolism - these phospholipids (i.e. phosphatidylethanolamine) are known to be in Mtb (see for example: PMID: 6819845), however the details of the pathways have not been identified yet (for example do the phospholipase reactions take place in the intra-cellular space, within the cell wall, or extracellular?). |
| Term | EC:2.7.8.8 CDP-diacylglycerol--serine O-phosphatidyltransferase. - IPI | njamshidi | IPI | 6819845 | Added for PE metabolism - these phospholipids (i.e. phosphatidylethanolamine) are known to be in Mtb (see for example: PMID: 6819845), however the details of the pathways have not been identified yet (for example do the phospholipase reactions take place in the intra-cellular space, within the cell wall, or extracellular?).
authors,GK. Khuller,R. Taneja,S. Kaur,JN. Verma Lipid composition and virulence of Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci 1982 |
| Term | TBRXN:PSSA180 Phosphatidylserine syntase (n-C18:0) - IPI | njamshidi | IPI | 6819845 | Added for PE metabolism - these phospholipids (i.e. phosphatidylethanolamine) are known to be in Mtb (see for example: PMID: 6819845), however the details of the pathways have not been identified yet (for example do the phospholipase reactions take place in the intra-cellular space, within the cell wall, or extracellular?).
authors,GK. Khuller,R. Taneja,S. Kaur,JN. Verma Lipid composition and virulence of Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci 1982 |
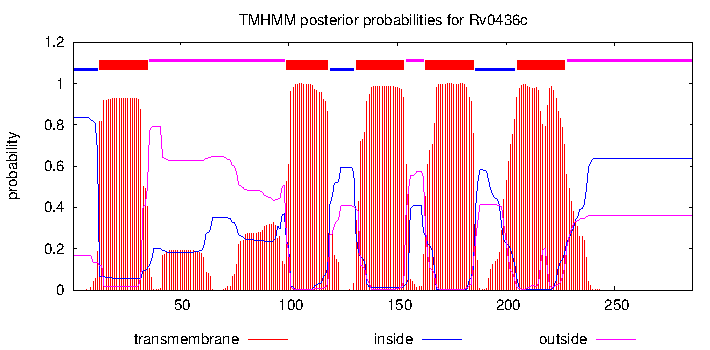
| Name | Putative phosphatidylserine synthase | mjackson | ISS | | Phospholipid biosynthesis |
| Citation | Phosphatidylinositol is an essential phospholipid of mycobacteria. M. Jackson,DC. Crick,PJ. Brennan J. Biol. Chem. 2000 | mjackson | | 10889206 | Putative phosphatidylserine synthase |
| Term | TBPWY:Phospholipid-Biosynthesis Phospholipid Biosynthesis - NR | mjackson | NR | | Putative phosphatidylserine synthase
M. Jackson,DC. Crick,PJ. Brennan Phosphatidylinositol is an essential phospholipid of mycobacteria. J. Biol. Chem. 2000 |